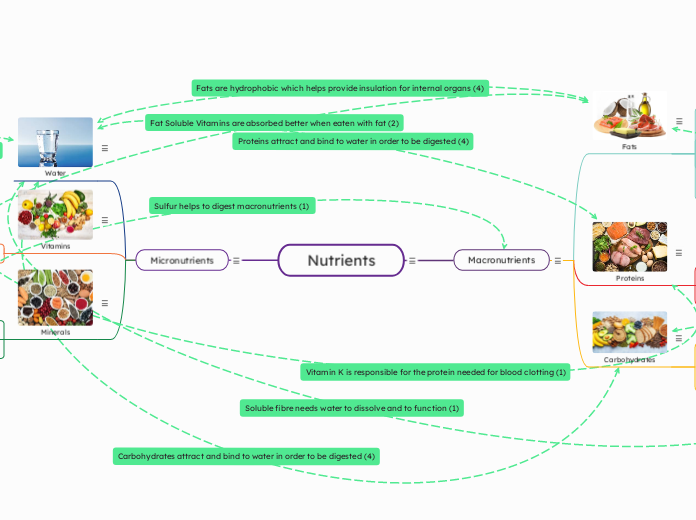
Nutrients
A substance that provides nourishment, promotes growth and maintains life.Non essential nutrient- a nutrient the body can produce itselfEssential nutirent- a nutrient the body cannot produce itself, therefor it must be consumed in the diet(1)
Macronutrients
Eaten in larger amounts because they provide energy for the body. They maintain the body's structure and system.(1)
Fats
Long chain molecules consisting of mainly carbon and hydrogen that are used to build cell membranes, nerve tissue and hormones. They are energy rich containing 9 calories per gram. Sources: fish, butter, avocado, olive oil(1) and (2)
Trans Fats
Trans fats are not naturally occuring substances, they are man made by changing liquid fat into solid fat through a proccess called hydrogenation (adding hydrogen to the double bonds). Sources: Trans fats are used in order to make the shelf life longer, so they are found in lots of baked goods aswell as margerine, and shortning. (1)
Unsaturated fats
Molecules with at least one double or triple bond is unsaturated with hydrogen. They are considered "good fats" as they raise HDL cholesterol and lower LDL cholesterol.Sources: Fats that are liquid at room temperature are usually unsaturated like vegetable oils and fish, avocado.(1)
Monounsaturated fats
Contains only one double bond (1)
Polyunsaturated fats
Contains more than one double bond.(1)
Saturated fats
Fats with single bonds are saturated with hydrogen. They are considered as "bad fats" due to the fact that they raise LDL cholesterol. Sources: Fats that are usually solid at room temperature like cheese, butter, milk, coconut oil, meat(1)
Cholesterol
Waxy subastance found in the blood that helps build cells and produce substances that help you digest foods, like hormones. Cholesterol is a non essential nutrient, as the body can produce it itself. Sources: cholesterol is mainly found in animal sources like eggs, meat, butter, cheese.(1)
HDL
HDL cholesterol (high density lipoproteins) is the form of cholesterol that is used in order to "clean the blood". It gathers cholesterol in the blood and transports it to the liver.(1)
LDL
LDL cholesterol (low density cholesterol) is considered the bad cholesterol. It doesn't do anything for the body. When there is a build up of LDL's it creates plaque, and can cause a blockage. HDL cholesterol can help remove LDL cholesterol.(1)
Proteins
Proteins are used in order to grow and repair cells. They are made from long chains amino acids. Twenty different amino acids form millions of combinations of different kinds of proteins. The body can only synthesize eleven of the twenty amino acids. The other nine are essential nutrients and must be consumed. Sources: Fish, cheese, eggs, nuts(1) and (2)
complete
Complete proteins are proteins that have all hire essential amino acids. Therefore the body has all the amino acids it needsSources: Tofu, poultry, eggs, fish(1)
Incomplete
Incomplete protein does not have all essential amino acids therefore the body must have another source of protein.Sources: Nuts, whole grains, peas, beans(1)
Complementary
Complementary proteins consist of two incomplete proteins that together have all nine essential amino acids.Sources: hummus & pita, rice & beans.(1)
Carbohydrates
A naturally occuring organic compund that consists of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Chains of sugar are broken down into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream. Carbohydrates main function is to provide the body with energy. Sources: vegetables, grains, fruits, pasta(1) and (2)
Simple
Simple carbohydrates are digested very quickly to give a quick burst of energy. Molecules are either monnosacharides or disacharides due to their short chains of sugar. Eating them in larger amounts can lead to weight gain.Sources: white bread, candy, soda, chocolate(1)
Complex
Complex carbohydrates take longer to digest which leads to a longer lasting form of energy. They are polysacharides due to their longer sugar molecules that are harder to break down. Sources: Whole grains, legumes, potatoes, fruits(1)
Fibre
Fibre is a form of carbohydrates that the digestive system cannot digest. It does not provide energy. Instead it is used in order to help digest other foods. Fibre is found in the outer layer of fruits and vegetables.Sources: oats, legumes, whole grains(1)
Soluble
Soluble fibre can dissolve in water to turn into a gel like substace. It controls blood pressure, blood sugar, and LDL cholesterol.Sources: Quinoa, vegetebles, oats, prunes(1)
Insoluble
Insoluble fibre does not dissolve in water. It speeds up digestion and helps prevent constipationSources: Nuts, seeds, whole grains, prunes(1)
Starch
Starch is a form of glucose that is found in plants that help them store energy. The body uses starch as an important energy sourceSources: Potatoes, grains, rice, peas(1)
Micronutrients
Eaten in smaller amounts as the do not provide the body with energy, but have many functions that ensure the body is working properly, (for example: producing enzymes and hormones)(1)
Water
Water is the most important nutrient that the body requires, as it provides a way for all other nutrients to be transported. It also lubricates joints, helps to remove waste, and regulates temperature. Sources: drinking water, melons, broccoli, celery(4)
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic molecules that can be easily broken down by heat and acid. They are important in order to perform a variety of functions for the body to work properly. For example, vitamins can help prevent oxidation within the cells of the body.Sources: mainly in fruits and vegetables, but can also be found in other foods like fish and eggs(1) and (2)
Fat soluble
Fat soluble vitamins are only soluble in fat substances. This means they can be stored longer in the body. However, this also means that injesting too many vitamins could lead to vitamin toxicity. Some examples of fat soluble vitamins are: vitamin A (prevents infection, promotes healthy skin and vision), vitamin E (fights oxidation of cells and helps the immune system), vitamin D (helps with the absorption of minerals which leads to healthy bones)Sources:Vitamin A- carrots, kale, eggsVitamin E- wheat germ, spinachVitamin D- cheese, eggs, fish(1)
Water soluble
Water soluble vitamins are only dissolved in water. They can be easily removed from the body, and cannot cause vitamin toxicity. However, they must be eaten daily for this reason aswell. Some examples of water soluble vitamins are: Vitamin B complex (helps regenerate blood, nervous tissues and skin), vitamin C (synthesizes collagen, helps with immune function, and is an antioxidant).Sources: Vitamin B complex- all four food groupsVitamin C- oranges, broccoli, strawberries(1)
Minerals
Minerals are inorganic substances (don't have carbon) that serve a variety of functions to help the body function properly. For example, minerals regulate the body's fluid balence. Unlike vitamins, minerals do not break down as easily. Sources: Minerals are found in the soil and water but make their way into foods like meat, fish, fruits, and vegetables(1) and (2)
Major
Major minerals are needed in slightly larger amounts then other minerals. Some examples of major minerals include: Calcium (helps with blood clotting, nerve signalling, bone strength), magnesium (helps form bone tissue, proteins, nerve signalling), and sulfur (helps macronutrient digestion, the formation of proetins, and the formation of the hromone insulin)Sources: Calcium- Milk, cheese, nutsMagnesium- Seafood, banana, avocadoSulfur- onion, garlic(1)
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals that contain an electric charge when they are dissolved in water. they mainly keep the body hydrated but have other functions aswell. Some examples of electrolytes are: Sodium chloride (regulates blood pressure, regulates water, transmitting nerve signals), Pottasium (regulates the heartbeat, helps nervous and muscle cells)Sources: Sodium chloride- salt, tomatoesPottasium- spinach, bananas, sweet potatoes, apricots(1) and (2)
Trace Minerals
Trace minerals are needed in smaller amounts than other minerals. Some examples of trace minerals are: Iron (transports oxygen to cells) and zinc (helps immune system).Sources: Iron- meat, spinach, nutsZinc- meat, seafood, dairy(1)