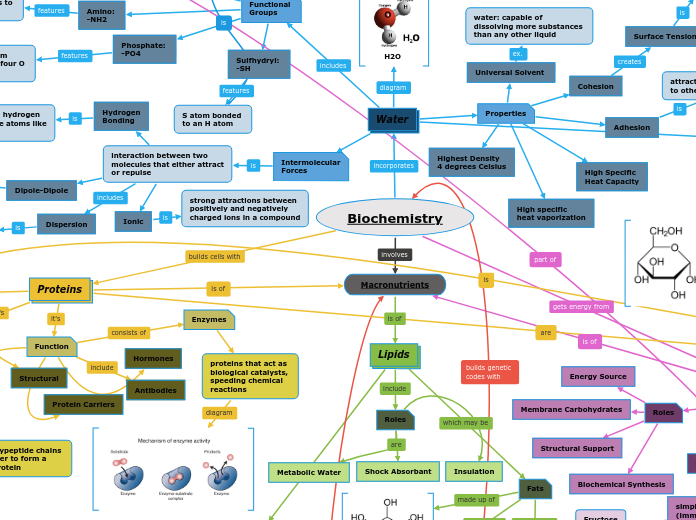
Biochemistry
Water
H2O
Covalent Bonds
chemical bond sharing
electrons form electron
pairs between atoms (non-metals)
Polar
chemical bond where
pair of electrons unequally
shared between two atoms
Non-Polar
two atoms share a pair
of electrons with each
other
Electronegativity
measure atom's
ability attract shared
electrons to itself
Oxygen: High
(strong pull on
electrons)
Hydrogen: Low
(weak pull on
electrons)
Organic
Compound
carbon and hydrogen
chemically linked in long
chains, carbon as backbone,
hydrogen atoms attached to
carbon atoms
Saturated
Hydrocarbons
Alkynes
Alkenes
Benzenes
Unsaturated
Hydrocarbons
Alkanes
Properties
Cohesion
Surface Tension
molecules at surface
having stronger hydrogen
bonds "push back"
Adhesion
attraction of water molecules
to other types of molecules "climb"
Universal Solvent
water: capable of
dissolving more substances
than any other liquid
High Specific
Heat Capacity
High specific
heat vaporization
Highest Density
4 degrees Celsius
Functional
Groups
Hydroxyl:
-OH
O atom joined by single
covalent bond to H atom
Carboxyl:
-COOH
central C atom
joined by covalent
bonds to two
O and OH
Carbonyl:
-CO
central C atom joined
to O atom by double
bond
Amino:
-NH2
one N atom attached
by covalent bonds to
two atoms of H
Phosphate:
-PO4
one P atom
bound to four O
atoms
Sulfhydryl:
-SH
S atom bonded
to an H atom
Intermolecular
Forces
interaction between two
molecules that either attract
or repulse
Dispersion
weakest force, occurring in
non-polar molecules due to
shifts in electron density
Dipole-Dipole
between polar molecules
due to positive and negative
ends of molecules
Ionic
strong attractions between
positively and negatively
charged ions in a compound
Hydrogen
Bonding
attraction between hydrogen
and electronegative atoms like
oxygen or nitrogen
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
simple sugars
(immediate energy)
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Ribose
Deoxyribose
Disaccharides
double sugars
(quick energy)
Lactose
Sucrose
Maltose
Polysaccharides
complex sugars
(long-term energy)
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Molecules
Monomers
small molecule
can bind chemically
to other molecules
(building blocks)
Polymer
large molecule formed
when monomers link
together chemically in chain
Macromolecules
complex molecule composed
repeating units smaller
molecules covalently linked
together
Roles
Energy Source
Membrane Carbohydrates
Structural Support
Biochemical Synthesis
Macronutrients
Lipids
Roles
Metabolic Water
Shock Absorbant
Insulation
Fats
Glycerol
Phospholipids
make up lipid bilayer
of cell membranes
Glycerol + two hydrophobic
fatty acids + hydrophilic
phosphate group
Fatty Acids
Saturated
bonds filled
with hydrogen
of single bonds
Monounsaturated
contain one C-C
double bond hydrogen
is removed
Polyunsaturated
contain more than
one C-C double bond
Triglyceride
hydroxyl group glycerol
bonds with carboxyl group
on fatty acids
are ester linkage and
known as esterification
hydrogenation: hydrogen
atoms added to double bonds
in unsaturated triacylglycerols
Steroids
lipids since they are
hydrophobic and insoluble
in water
Proteins
Amino Acids
building blocks of proteins,
are both amine and carboxyl
Function
Structural
Protein Carriers
Enzymes
proteins that act as
biological catalysts,
speeding chemical
reactions
Hormones
Antibodies
Structure
Peptide Bonds
bonds that hold
amino acids together,
formed by a dehydration
synthesis reaction
Dipeptide
two amino acids
joined by a peptide bond
Polypeptide
chains of amino acids
linked together by peptide
bonds
Primary
linear sequence in
each polypeptide chain
Tertiary
chain undergoes additional
folding due to (R-group)
interactions
Secondary
folds and coils as
polypeptide chain grows
α helix
β pleated sheets
Quaternary
tor more polypeptide chains
come together to form a
functional protein
Nucleic Acids
assembly instructions for
all proteins in living organisms
DNA
stores hereditary information
in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
and many viruses
- Deoxyribose
- Phosphate group
- Nitrogenous bases (A,T,G or C)
RNA
different forms of RNA
involved in protein synthesis
in all cells
- Ribose
- Phosphate
- Nitrogenous bases (A,U, G or C)
Nucleotides
Pentose sugar
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
Purines
two-ringed organic structures
adenine (A) and guanine (G)
Pyrimidine
single organic rings
uracil (U), thymine (T),
and cytosine (C).