Body Systems
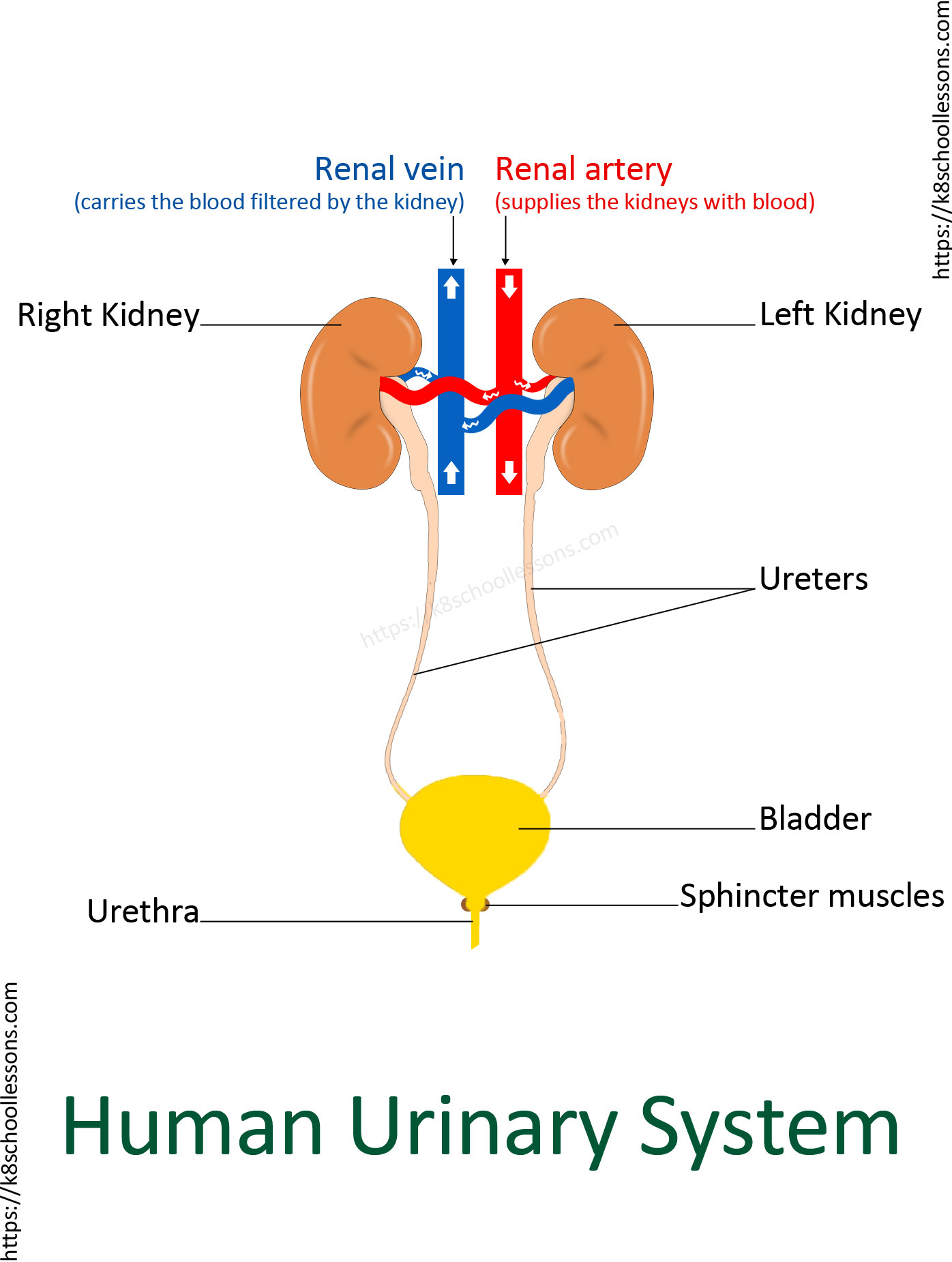
Urinary System
Creates, holds and removes urine
UTI
Bacteria from the bowel (most common cause)
Produce medication and research
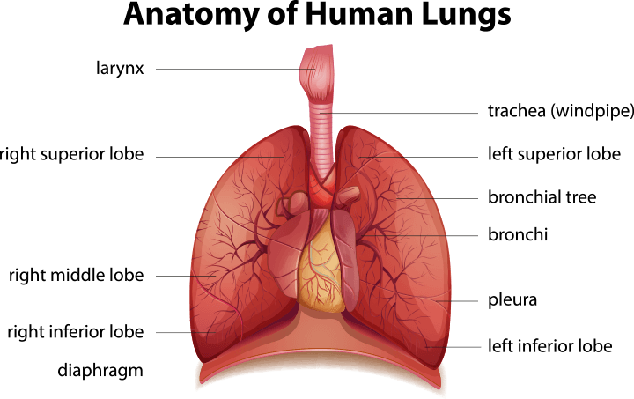
Respiratory system
Components
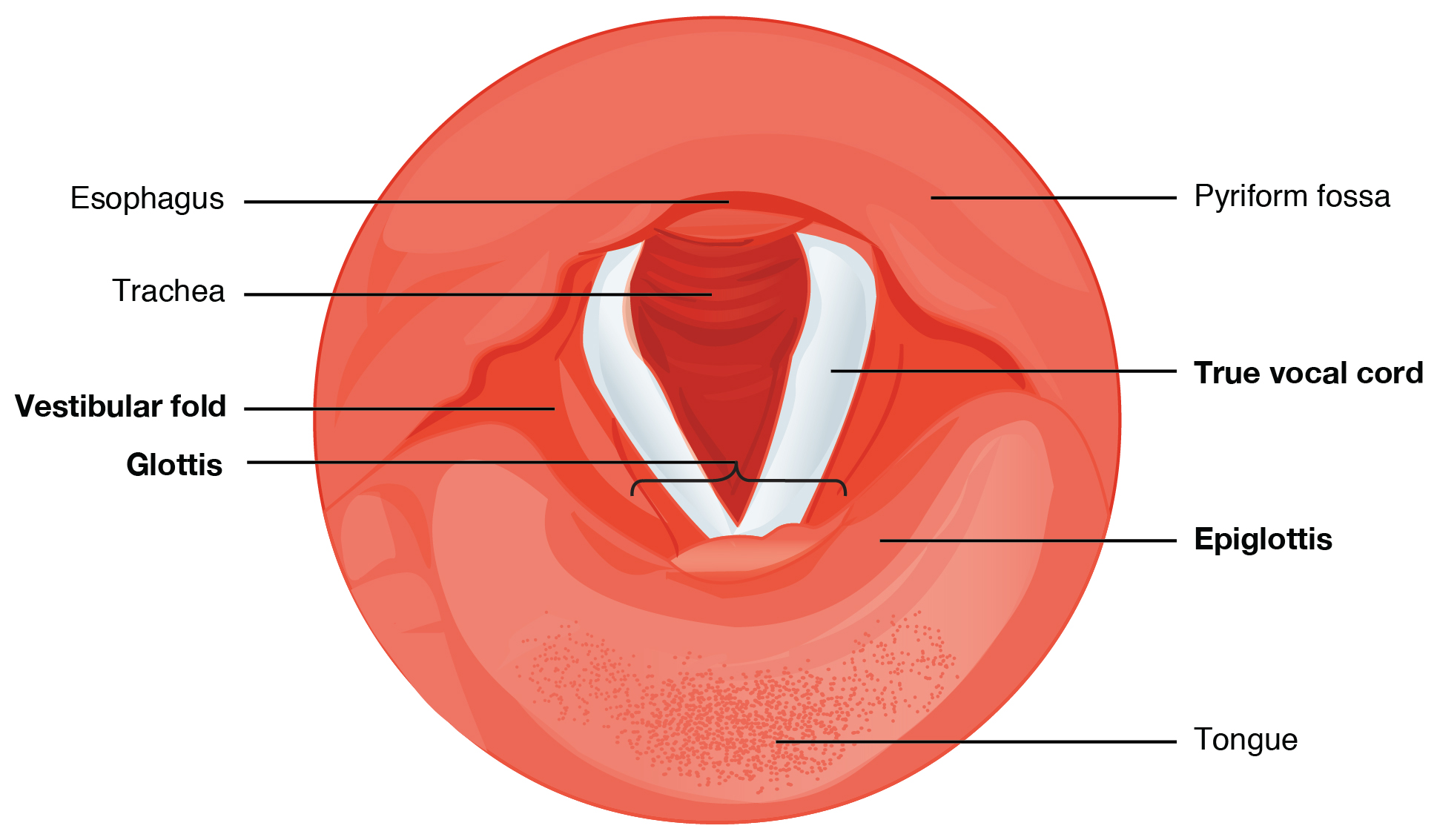
Larynx
Connects pharynx and trachea and allows air to pass through

Pharnyx
Conducting zone
Trachea
Nostrils
Larnyx

Trachea
(Windpipe) Lets air pass through to lungs and connects the larnyx to the rest of the system

Nasal cavity
Passageway for air to enter the body. It filters and moisturizes the air before it enters the lungs

Lungs
Oxygen is separated from other gases and is carried into bloodstream while gases like CO2 are taken out

Diaphragm
Controls breathing and separates chest cavity from abdomen cavity

Epiglottis
CLoses the trachea when consuming food preventing it from blocking the airway
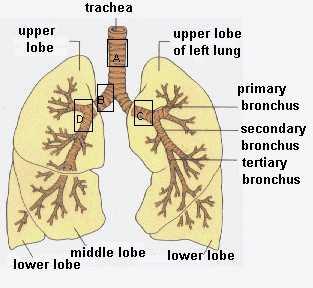
Bronchi
Main passage to lungs allows for oxygen to enter and CO2 to exit

Oral Cavity
Secondary opening (allows air to enter or exit the body)

Pleura
Allows for free movement of lungs
Intake air, keep oxygen in the body and remove all other gases (CO2)

Digestive System
Breaks down food and send nutrients into different parts of our body
Components
Gastrointestinal tract
Subtopic
Hollow Organs

Esophagus
Connects throat to stomach and is a tub like muscles that allows food to reach stomach. It aslo contracts to make digestion easier.

Stomach
Break food down further by using acid and stomach enzymes. Muscles contract and expand within the stomach to enhance digestion

Mouth
Chew and break down food using saliva and enzymes to start digestion process

Large Intestine
Reabsorbs water from mixture and temporarily stores waste
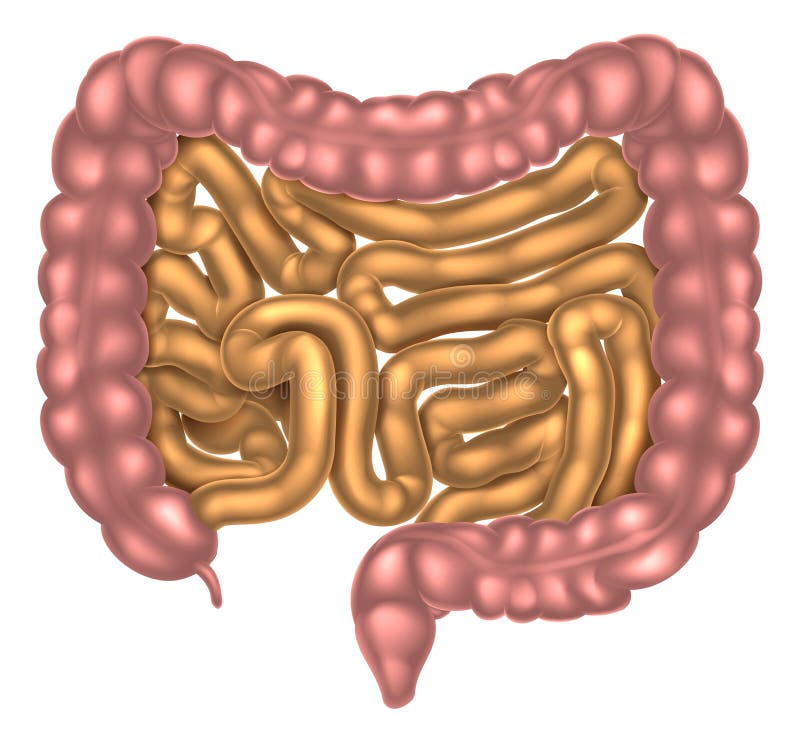
Small Intestine
Absorbing minerals and important nutrients from food
Components
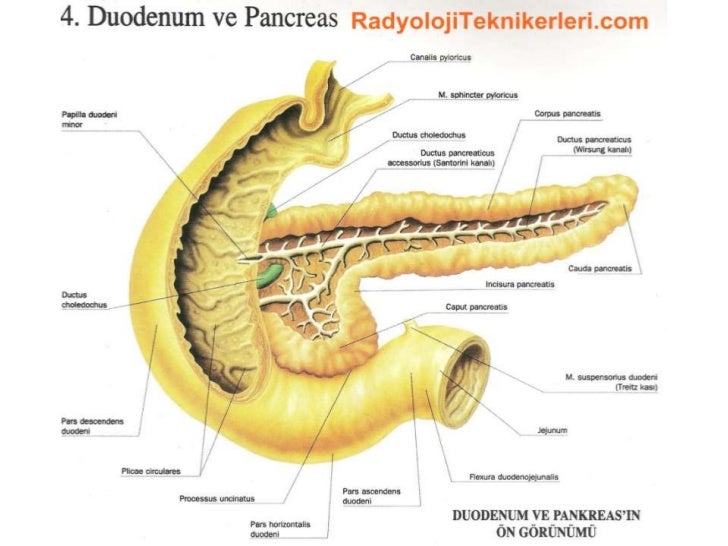
Duodenum
Regulates the removal of stomach contents into small intestine
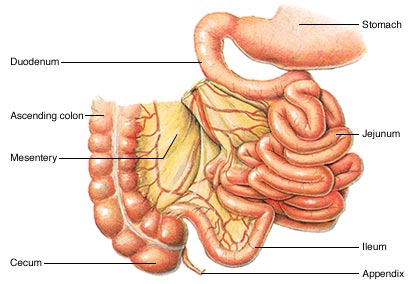
Ileum
Absorbs remaining nutrients that have not been absorbed by jejunum

Jejunum
Absorbs most of the nutrients before passing the food onto Ileum
Anus
To allow and stop the passing of the stool from the body
Solid Organs
Components
Liver
Bile production, excretion and metabolizes carbs, fats and proteins

Pancreas
Regulates blood sugar, and converts food into nutrients

Gallbladder
Production of bile to help break down fatty foods
Gallbladder stones
Ultrasound (abdomen)
lack of water intake

Muscular System
Provides movement, maintains posture, generates heat, and stabilizes joints
Components

Skeletal muscles
Is to contract to move parts of the body closer to the bone that the muscle is attached to, also covers your skeleton

Visceral Muscles
Contract and expand "automatically" help us perform simple tasks
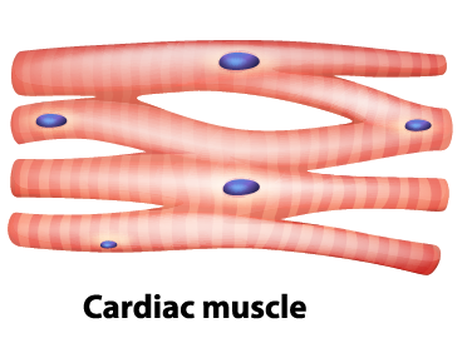
Cardiac Muscles
contracts and helps pump blood throughout the body
inflammatory myopathies
MRI/Ultrasound/ Electromyography
Weak muscles

Nervous System
Responsible for the control of the body and communication among all its parts
Systems
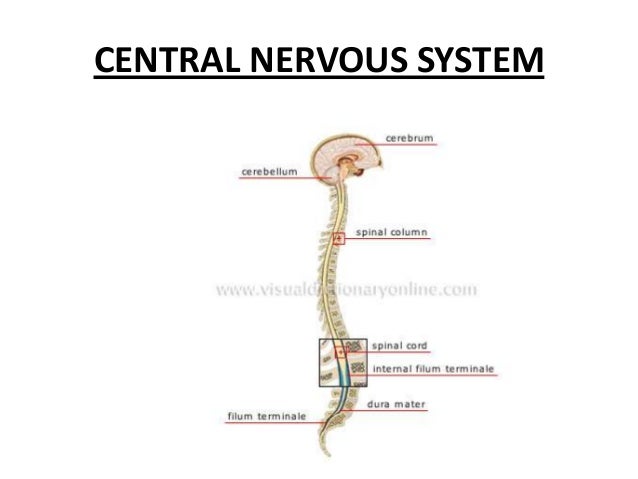
Central Nervous System
Components
/Brain_lobes-571a4c0f5f9b58857db90d7e.jpg)
Brain
Components
Cerebrum
controls actions occurring on both sides of the body (five senses, thoughts, motion)
Cerebellum
receives information from the spinal cord to coordinate voluntary movements
Brain Stem
controls flow of messages and basic body functions including breathing and swallowing

Spinal Cord
used as a tranmiter that can send information to the brain

Peripheral Nervous System
Components

Nervous Tissues
Neurons
Afferent Neurons (sensory neurons)
transmit sensory signals to the CNS (Central Nervous System) from receptors in the body
Efferent Neurons (Motor neurons)
Transmit signals from CNS to effectors in the body such as muscles and glands
Interneurons
to form complex networks within the CNS to integrate the information from afferent neurons and to direct the function of the body through efferent neurons.
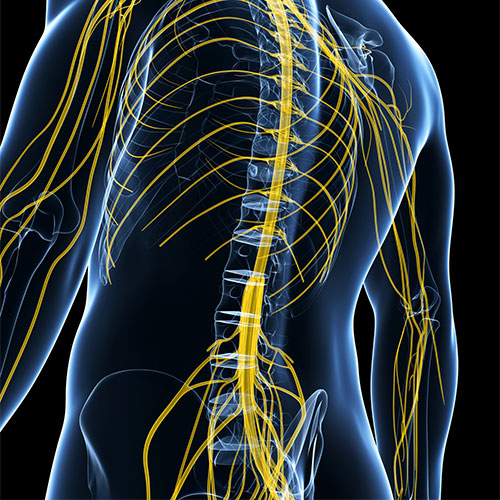
Nerves
act as highways and carry signals between brain and spinal cord
Epilepsy
trauma in the brain
Drug Therapy
to control seizures
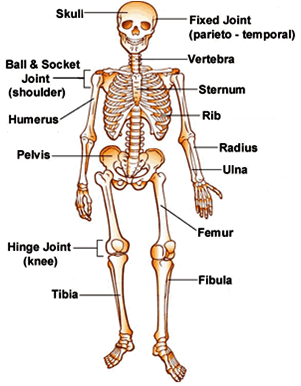
Skeletal System
provide support , movement, protection endocrine regulation and calcium storage
Components

Bones
Support for body structure, allows movement, and provides protection to organs as well as storage space for minerals

Cartilages
provides extra support, connects bones together, and allows flexibility in movement

Ligaments
Stabilizes joint and prevents it from moving out of range of motion.
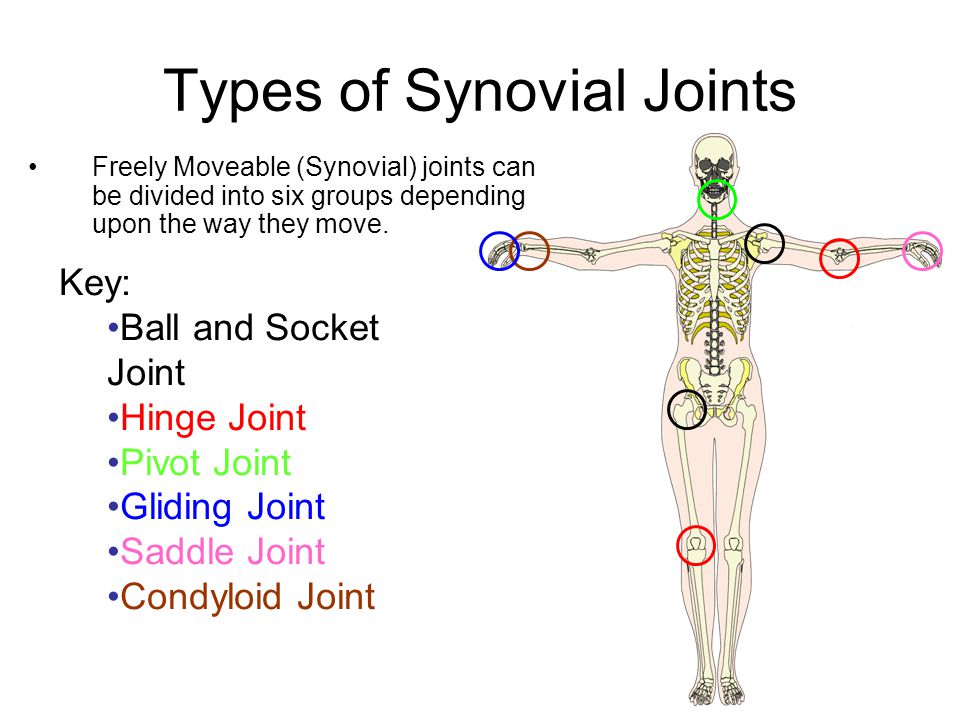
Joints
connects bones within the body, it also allows movement and bears the overall weight
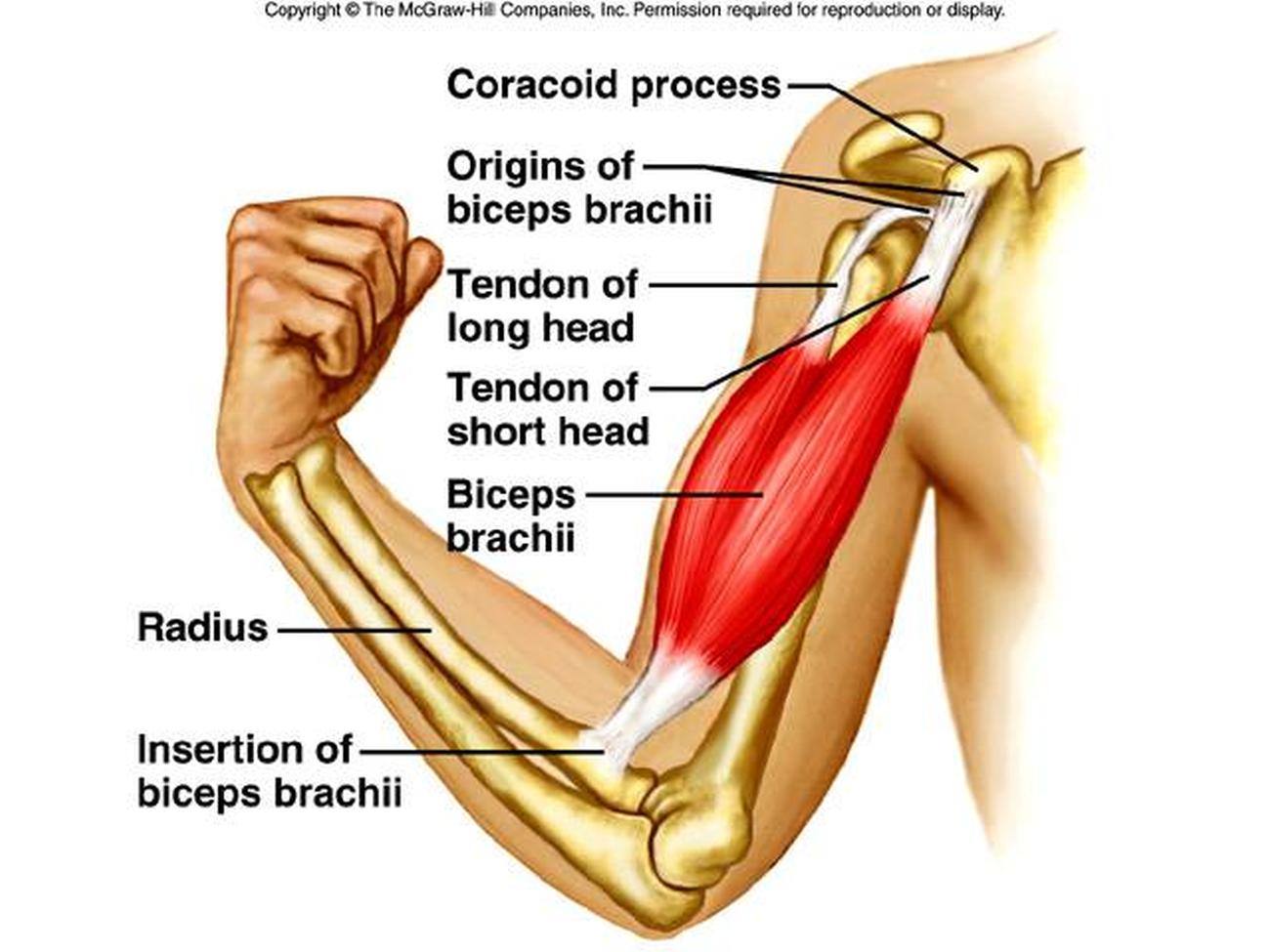
Tendons
connects bones and skeletal muscles
Osteoporosis
X-rays
Drug therapy
When body loses too much bone or too little bone resulting them in becoming weak or even breaking from a fall.

Immune System
Protecting body against infectious identifying threats
Components

Lymph nodes
To store leukocytes (white blood cells)
Leukocytes
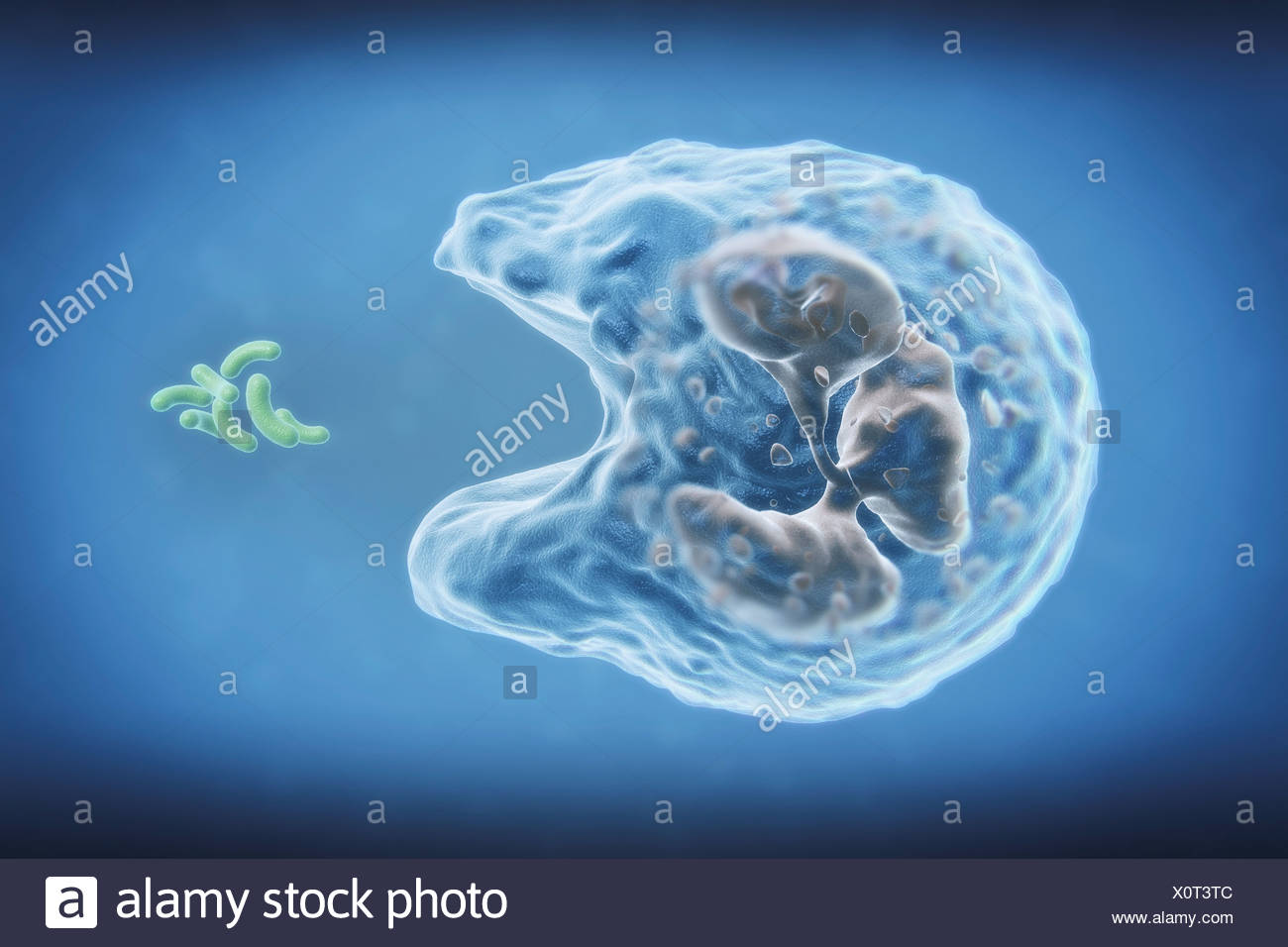
Phagocytes
Chew up invading organisms

Lymphocytes
allow the body to remember and recognize the previous invaders
B-cells
produce antibodies to fight surface antigens of bacteria and viruses
T-cells
Recognize viral antigens outside of infected cells and fight them
Eliminate Pathogens and infectious diseases

Bone Marrow
Produces white blood cells and B-cells. It also stores stem cells

Spleen
Controls the amount of blood in the body. Disposes old/damaged cells and contains white blood cells.
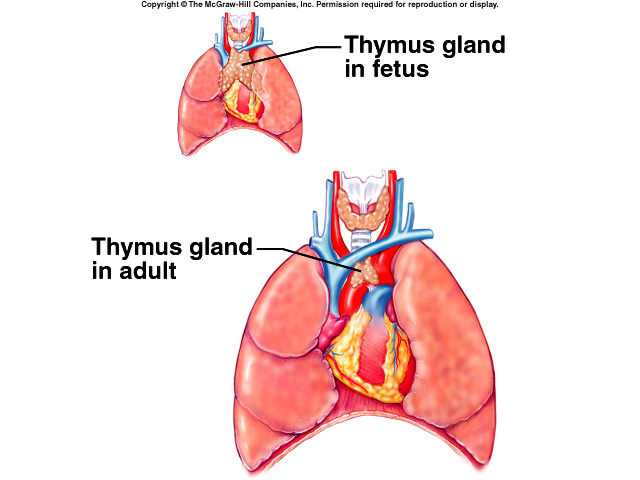
Thymus
Trigger and maintains production of antibodies
Allergies
hypersensitivity of immune system (when the immune system mistakes harmless material as a severe threat)
Inhalers/Puffers
Medications

Endocrine System
Produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth/development, tissue function, sleep and mood
Components

Pituitary
secrete hormones into bloodstreams

Thyroid
that produce store and release hormones into the bloodstream
/pineal-gland-57bf22583df78cc16e1df170.jpg)
Pineal
produces melatonin and helps maintain circadian rhythm and regulate reproductive hormones
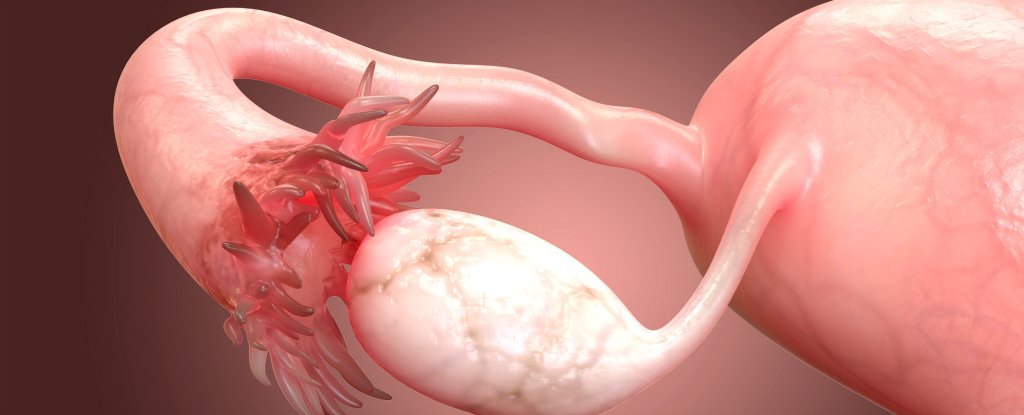
ovaries
discharge hormones (estrogen and progesterone) which is vital for reproduction and fertilization
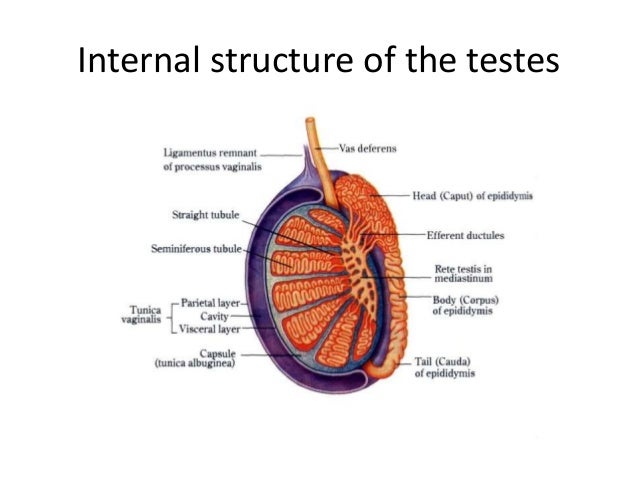
testicles
discharge testosterone (vital for reproduction of sperm in male)

Adrenal
ske
hypothyroidism
Fatigue, hair loss, cold intolerance
Drug Therapy, surgery, biopsy
Reproductive System
Allowing the human body to develop and reproduce

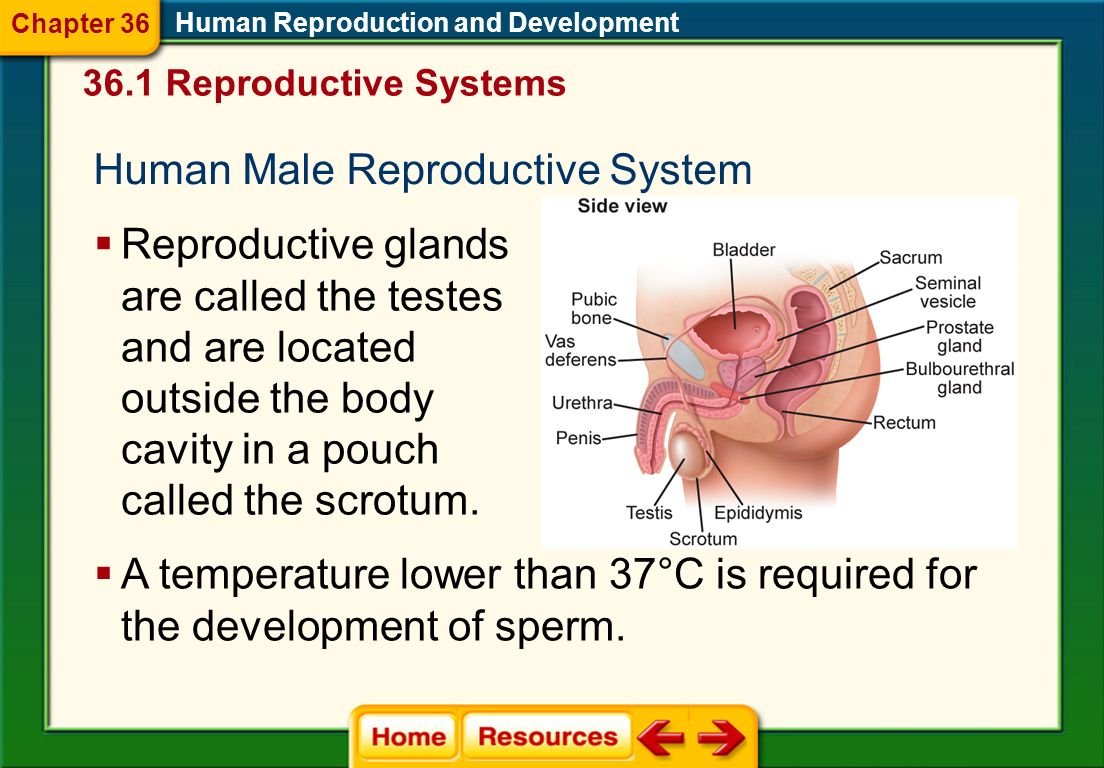
Male Reproductive System
Producing sperm and testosterone for male reproductive system. It is also to transport sperm.
Components

Penis
ejaculate sperm into vagina to fertilize the egg
Urethra

Prostate
additional fluid during ejaculation and nourishes the sperm
Bladder
Erectile dysfunction
Vascular reconstruction surgery
blocked blood flow to penis
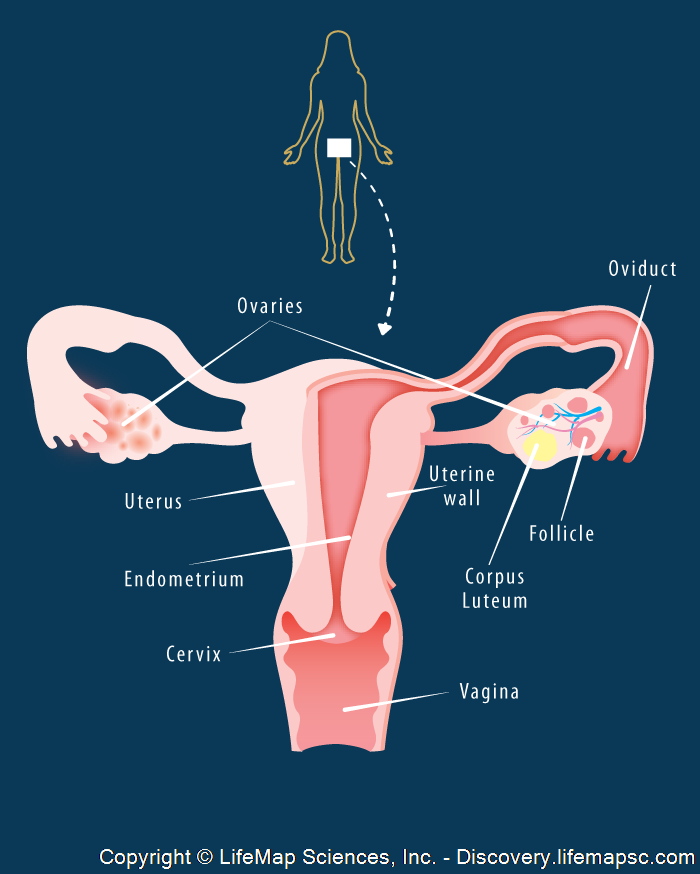
Female Reproductive System
Production of ovum and hormones and transport of gametes.
Components
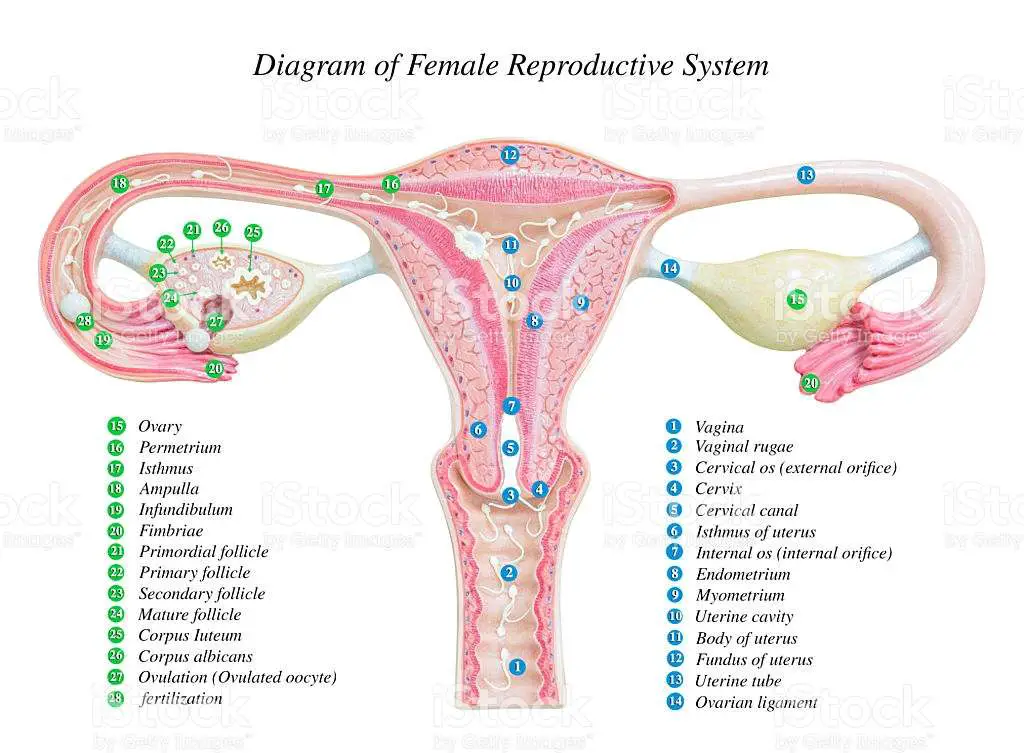
Vagina
Allow menstrual flow to exit body. Allows the baby to pass during labour. Allows the penis to enter the body.

Ovaries
Producing ovum and hormones

Fallopian Tubes
Transporting the ovum to the uterus

Uterus
Devloping the fetus
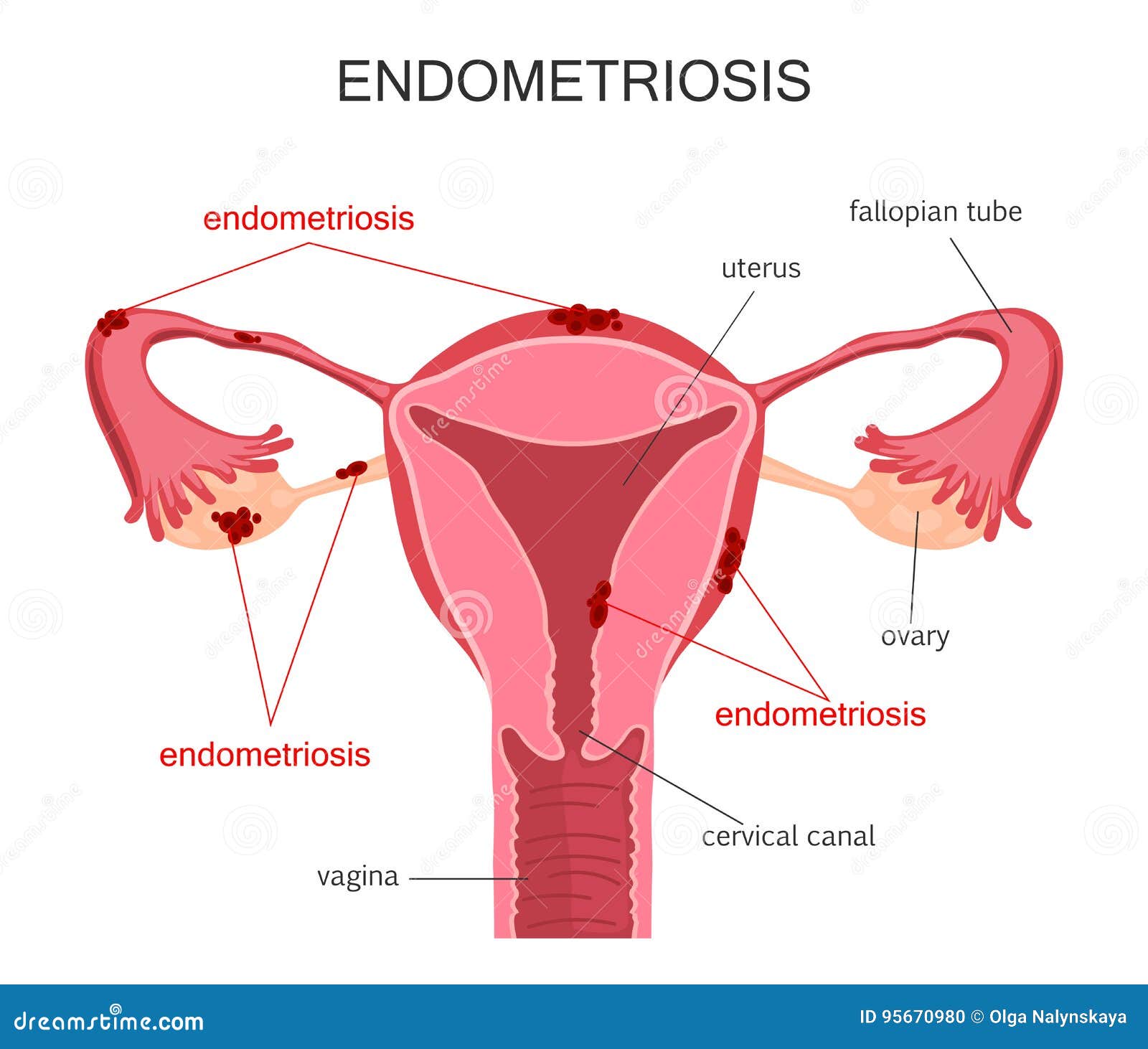
Cervix
Opening to vagina
PCOS (Polycystic ovary syndrome)
hormonal disorder
Surgery
Birth Control Pills

Integumentary System
Protects the body against infections and extreme temperatures. It also maintains balance of fluids
Components

Skin
Epidermis
Produce Keratin and gives structure durability and waterproofing
Dermis
to give strength and elasticity
Hypodermis
Stores energy in triglycerides

Hair
Protects areas from UV radiation. Also provides insulation

Nails
Reinforce and protect ends of fingers and toes from physical injury

Exocrine Glands
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Produce a secretion of water and sodium chloride
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Ducts extend to follicles of hairs so that the sweat produce exits the body along the hair shaft
Nerves
Acne
Disturbance often occurs as a result of over-productive sebaceous glands
UV radiation
Circulatory System
Responsible for circulation of blood, nutrients, and oxygen
Components
Coronary System
Supply oxygenated blood to heart muscles and drains away blood once its been dyoxygenated
Coronary arteries
Cardiac Veins
Heart
Pulmonary System
Lungs
Pulmonary Veins
Pulmonary Arteries
Systemic System

Ureter
Carry urine from kidney to bladder
Components

Urethra
Carrys urine out of the body from the bladder

Bladder
Stores urine (controlled) until a signal is given)

Kidney
Remove urea (waste product produced by breakdown of proteins) from blood