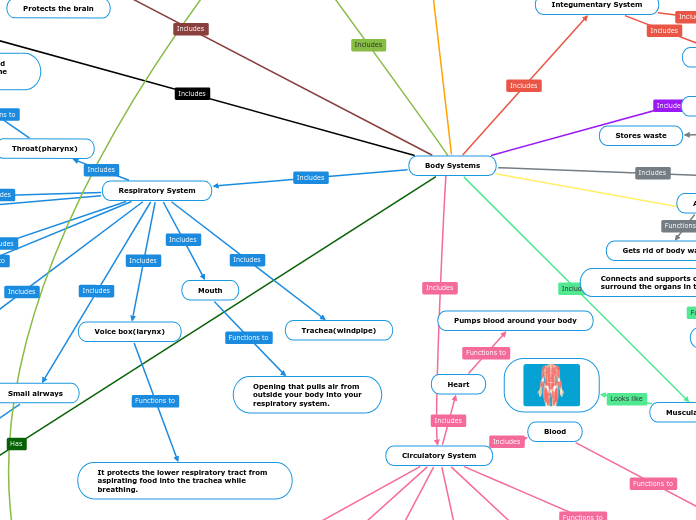
Body Systems
Unrinary system
Urethra
Lets urine leave your bladder and your body
Kidney
Remove wastes and extra fluid from your body
Bladder
Stores Urine
Lymphatic System
Lymph nodes
Monitor the lymph flowing into
them and produce cells and
antibodies
Thymus
Lymphatic vessels
carry lymph through the
body to lymph nodes and
back to veins.
Bone marrow
White blood cells are made in the bone marrow
Spleen
Monitors the blood and detect and respond to pathogens and malignant cells.
Collects and circulates excess fluid in the body.
Endocrine System
Female Ovaries
Play an important role in female traits, such as breast development, body shape, and body hair
Pituitary
It monitors and regulates many bodily functions through the hormones that it produces
Thyroid
Plays a major role in the metabolism, growth and development of the human body
Adrenal Glands
Produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
Muscular System
Tendons
Serve to move the bone or structure
Ligaments
Connect bones and help stabilize joints.
Soft tissues
Connects and supports other tissues and surround the organs in the body.
Muscles
Supports movement
Bones
Provides a framework for your
muscles and other soft tissues.
Helps the body move
and do daily activities.
Integumentary System
Epidermis
Protects your body from the outside world, keeping your skin hydrated, producing new skin cells and determining your skin color.
Dermis
Support and protect the skin and deeper layers, assist in thermoregulation, and aid in sensation.
Hypodermis
Insulating your body, protecting your body from harm, storing energy and connecting your skin to your muscles and bones.
Nails
Helps us pick things up (like food), pick things off (like bugs), and hold tightly onto things.
They carry oxygen
to your lungs.
Hair
It protects the body against trauma and also against ultraviolet damage.
Associated glands
Secrete fluids that enter the urethra
Form a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment
Nervous System
Brain
The seat of intelligence, interpreter of the senses, initiator of body movement, and controller of behavior
Spinal Cord
Sends motor commands from the brain to the body, send sensory information from the body to the brain, and coordinate reflexes
Reproductive System
Ovaries
Produce hormones that help with your menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Store and release an egg each cycle for fertilization
Testes
Making sperm and are also involved in producing a hormone called testosterone
Vagina
Provides a passageway for blood and mucosal tissue from the uterus during a woman's monthly period.
Receives the penis during sexual intercourse and holds the sperm until they pass into the uterus
Provides a passageway for childbirth
Prostate
Produces a fluid that, together with sperm cells from the testicles and fluids from other glands, makes up semen
Penis
The male organ used for urination and sexual intercourse
Fallopian Tubes
Connect the ovaries to the uterus
Cervix
Connects the body of the uterus to the vagina
Uterus
To nourish the developing fetus prior to birth
Respiratory System
Throat(pharynx)
The throat is a passage way for air, food and liquids. It connects the mouth to the trachea
Mouth
Opening that pulls air from
outside your body into your
respiratory system.
Nose
It allows air to enter your body, then filters debris and warms and moistens the air.
Voice box(larynx)
It protects the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing.
Large airways
Another passage for air to pass
through while inhaling or exhaling.
Small airways
The last tunnel that connects the
trachea to the lungs.
Lungs
When you inhale air enters your lungs, and oxygen from that air moves to your blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste gas gets exhaled.
It moves fresh air into your body while
removing waste gases. Without the respiratory system humans wouldn't be
able to breathe.
Trachea(windpipe)
Circulatory System
Veins
Arteries
Help blood move around the body
Heart
Pumps blood around your body
Blood
Carries carbon dioxide to the
lungs and picks up oxygen
Blood vessels
Capillaries
The system moves blood throughout the body. It helps tissues get enough oxygen and nutrients, and it helps them get rid of waste products.
Digestive system
Mouth
Makes food softer so
it's easier to digest.
Small intestine
It helps to further digest food coming from the stomach.
Large intestine
The large intestine absorbs
water and changes the waste
from liquid into stool.
Stomach
The stomach muscles mix the
food and liquid with digestive
juices.
Throat(pharynx)
Delivers food and liquid
to the digestive system.
Esophagus
Rectum
Stores waste
Anus
Gets rid of body waste
Skeletal system
Shoulder blades
Protects the upper back
Collarbone
Provides a brace for the shoulder
Pelvic girdle
Supports the weight of the upper body when sitting and to support the lower limbs when standing.
Skull
Protects the brain
Rib cages
Provides support for the upper organs.
Vertebral column
Surround and protect the spinal cord
Supports important parts of your body
Malfunctions
Reproductive System
Infertility and the loss of the beneficial effects of estrogen and progesterone, including benefits to bone and heart health
Tracking ovulation, egg freezing, genetic screening, uterine transplants, artificial insemination and assisted reproductive technology.
Respiratory System
The usual exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide (CO2) in the lungs does not occur. As a result, the heart, brain, and other organs cannot get enough oxygen. A person may feel sleepy or faint.
Pacemakers send electrical pulses to help your heart beat at a normal rate and rhythm. This can prevent faints in the future
Circulatory System
It leads to necrosis and eventually death of an individual caused due to the lack of oxygen, nutrients and build of toxins within the body.
Technology can monitor the amount of nutrition you need and also can help make breathing easier for people who need it.
Muscular System
You won't be able to properly operate the affected parts of your body
Stimulating muscles repeatedly with electricity may eventually result in muscles that are strengthened
Skeletal System
The person will be left unable to move or even breath on their own as the bones support not only body movement
X-ray vision can help detect a broken bone.
Also if your arms or legs are temporarily broken you can get a prosthetic arm or leg
Lymphatic System
Fluid builds in your tissues and causes swelling, called lymphedema
A lymphedema machine can help treat
lymphedema. It works by putting pressure on the area of swelling and encourages the movement of lymph fluid around the lymph vessels.
Endocrine System
Leads to fatigue, weakness, unintended weight fluctuations, and changes in blood glucose levels or cholesterol levels.
Flash glucose monitors and continuous glucose monitors let you check your sugar levels without you having to prick your fingers. You wear a small sensor on your body day and night that reads your sugar levels so you can see the information on your mobile, or other device.
Nervous System
You can have trouble moving, speaking, swallowing, breathing, or learning. You can also have problems with your memory, senses, or mood
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is a non-invasive treatment using mild continuous stream of air to keep the airway open.
Urinary System
Your blood would be full of waste products and extra water. This could cause other systems, like the cardiovascular system, to malfunction and cause serious health issues.
Internal sphincter implant. A doctor injects a specific material within your urethral wall. This material then bulks up and tightens the urethra, helping control your urine flow
Digestive System
Cause various symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation. Left untreated, they can lead to serious complications, such as malnutrition, dehydration, and even death.
A digital stimulation can be used to
cure constipation.
Integumentary System
A person would be much more susceptible to: Damage to their internal organs and structures
X-ray imaging can help when an
internal organ is damaged or is at risk of being damaged