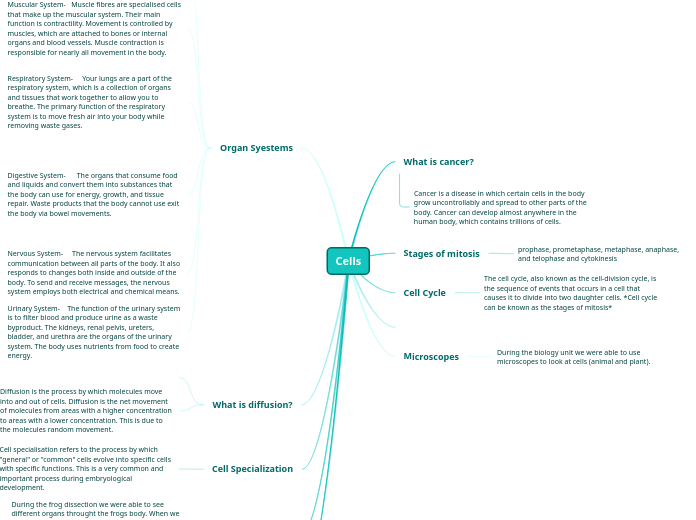
Cancer is a disease in which certain cells in the body grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. Cancer can develop almost anywhere in the human body, which contains trillions of cells.
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase and cytokinesis
The cell cycle, also known as the cell-division cycle, is the sequence of events that occurs in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. *Cell cycle can be known as the stages of mitosis*
During the biology unit we were able to use microscopes to look at cells (animal and plant).
Skeletal System- Your body's skeletal system serves as a support structure. It shapes the body, allows movement, produces blood cells, protects organs, and stores minerals. The musculoskeletal system is another name for the skeletal system.
The four main fibrous and mineralized connective tissues:
- Bones
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Joints
Muscular System- Muscle fibres are specialised cells that make up the muscular system. Their main function is contractility. Movement is controlled by muscles, which are attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels. Muscle contraction is responsible for nearly all movement in the body.
The four major parts of the Muscular System:
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Skeletal Muscal
- Smooth Muscals
Respiratory System- Your lungs are a part of the respiratory system, which is a collection of organs and tissues that work together to allow you to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to move fresh air into your body while removing waste gases.
The seven main organs in the Respiratory System:
-Heart
- Thorat
- Lungs
- Bronchi
- Trachea
- Nose
- Larynx
Digestive System- The organs that consume food and liquids and convert them into substances that the body can use for energy, growth, and tissue repair. Waste products that the body cannot use exit the body via bowel movements.
Organs is the Digestive System:
- Mouth
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Liver
- Anus
- Large Intestine
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
- Esophagus
Nervous System- The nervous system facilitates communication between all parts of the body. It also responds to changes both inside and outside of the body. To send and receive messages, the nervous system employs both electrical and chemical means.
Organs in the Nervous System:
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Censory Organs
Urinary System- The function of the urinary system is to filter blood and produce urine as a waste byproduct. The kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, and urethra are the organs of the urinary system. The body uses nutrients from food to create energy.
Organs in the Urinary System:
- Kidneys
- Renal Pelvis
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Urethra
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move into and out of cells. Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from areas with a higher concentration to areas with a lower concentration. This is due to the molecules random movement.
Cell specialisation refers to the process by which "general" or "common" cells evolve into specific cells with specific functions. This is a very common and important process during embryological development.
During the frog dissection we were able to see different organs throught the frogs body. When we pulled out the organs to lable them I learned what each of the organs look like in an animals body. Human hearts and frog hearts look so different. This lab assisted me in deepining my understanding on this biology unit.