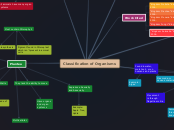
Classification of Organisms
Monera
Prokaryotic
Do not have membrane bound organelles
Nor a well defined nucleus
Live in living and
non-living habitats
Unicellular
Can survive in extreme
climates
Example:
Hotsprings
Have a cell wall
DNA is double stranded
found in cytoplasm
of the cell
Nutrition:
Autotrophic
Make their own food
Chemosynthetic
Photosynthetic
Heterotrophic
Consumers
Parasyte
Saphropytes
Circulation is through diffusion
Move with the help of a flagella
Most reproduction is asexual
Two classes:
Eubacteria
Example:
Methanogens
Archaebacteria
Can be round, comma, rod-like or spiral
Kingdom, Phylum, Class
Order, Family, Genus
Species
all coloured boxes are types of Kingdoms
Fungi
Eukaryotic
Well defined Cell
organelles & nucleus
Usually do not move
Non-vascular
Lack Vascular tissue
Reproduce
through spores
It is possible
for the spore to be
sexual and asexual
Can be unicellular
or made from fibers
known as hyphae
Example:
Mushroom
Have a cell wall
Made of chitin
not cellulose
Heteroptrophic
Consumers
Store their
food as starch
Saphrophytes
Parasites
Symbionts
Have very
small Nuclei
Produce Exoencxyme
during digestion
Example:
Yeast
Either sac, zygote,
imperfect or club
fungi
Work Cited
"Kingdom Protista." Kingdom Protista. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
"Kingdom Plantae." Kingdom Plantae. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
"Kingdom Monera." Kingdom Monera. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
"Kingdom Fungi." Kingdom Fungi. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
"Kingdom Animalia." Kingdom Animalia. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
Protista
Found in water,
moist soil, or on
humans and plants
Example:
Algae
Plasmodium
causes malaria
They are simple
Eukaryotic Organisms
Well defined Cell
Organelles and
Nucleus
Movement
is through
flagella or cilia
All have mitochondria
& some have chloro-
plasts
Aren't plant,
animal or monera
Share characteristics
of all of the above
Can be either
Heterotrophs or
Autotrophs.
Some feed
through
Endocytosis
Reproduction
is either asexual
or sexual
Example:
Plasmodium
Animalia
Eukaryotic
Well defined cell organelles
and nucleus
Heteroptrophic
Consumers
Have the ability to digest
Have no cell wall
Phylum is either
Vertebrates or
invertebrates
Chordata
Non-chordata
Example:
Centipedes
5 different classes of Vertebrates
Amphibia
Example:
Frog
Reptilia
Example:
Snake
Fish
Example:
Salmon
Aves
Example:
Eagle
Mammalia
Example:
Lion
All animals have many organ
systems
Have the ability to move
Most reproduce sexually
Are multicellular
Plantea
Autotrophic
Make their own food
Photosynthesis
Most are Eukaryotic
Well- defined cell organelles and nucleus
Most contain Chlorophyll
Helps in Photosynthesis
Pigment found in Chloroplast
which isn't present in animal
cells
Multicellular
Have Cell Walls
Most are made of
Cellulose
Reproduce Sexually
and Asexually
Example:
Apple Tree,
Hydra
They lack the ability to move
Have organs
and organ
systems