Cell- source of current electricity
Light Bulb- two or more cells joined together
Motor- converts electrical energy into light and thermal energy
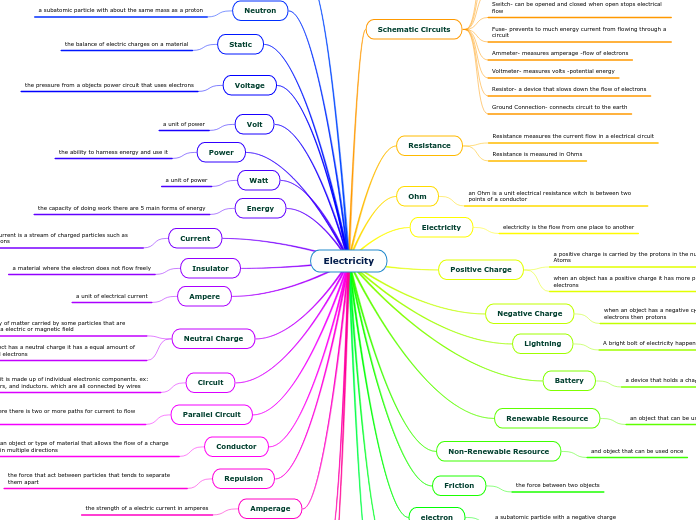
Switch- can be opened and closed when open stops electrical flow
Fuse- prevents to much energy current from flowing through a circuit
Ammeter- measures amperage -flow of electrons
Voltmeter- measures volts -potential energy
Resistor- a device that slows down the flow of electrons
Ground Connection- connects circuit to the earth
Resistance measures the current flow in a electrical circuit
Resistance is measured in Ohms
an Ohm is a unit electrical resistance witch is between two points of a conductor
electricity is the flow from one place to another
a positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of Atoms
when an object has a positive charge it has more protons the electrons
when an object has a negative charge it contains more electrons then protons
A bright bolt of electricity happens when there is a storm
a device that holds a charge of electricity
an object that can be used multiple times
and object that can be used once
the force between two objects
a subatomic particle with a negative charge
a series circuit is a circuit where resistors are arranged in a chain. the current is the same throughout each resistor
Subtopic
a subatomic particle in all atomic nuclei
a subatomic particle with about the same mass as a proton
the balance of electric charges on a material
the pressure from a objects power circuit that uses electrons
a unit of power
the ability to harness energy and use it
a unit of power
the capacity of doing work there are 5 main forms of energy
a electrical current is a stream of charged particles such as electrons or ions
a material where the electron does not flow freely
a unit of electrical current
the property of matter carried by some particles that are effected by a electric or magnetic field
when a object has a neutral charge it has a equal amount of protons and electrons
a circuit is made up of individual electronic components. ex: resistors, and inductors. which are all connected by wires
a circuit where there is two or more paths for current to flow through
an object or type of material that allows the flow of a charge in multiple directions
the force that act between particles that tends to separate them apart
the strength of a electric current in amperes
the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy
the electric or the magnetic force that can draw opposite charged particles together