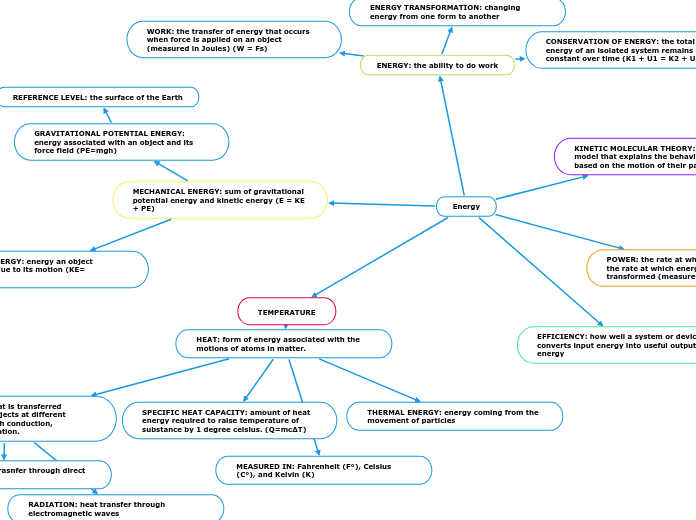
Energy
ENERGY: the ability to do work
ENERGY TRANSFORMATION: changing energy from one form to another
CONSERVATION OF ENERGY: the total energy of an isolated system remains constant over time (K1 + U1 = K2 + U2)
WORK: the transfer of energy that occurs when force is applied on an object (measured in Joules) (W = Fs)
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY: scientific model that explains the behavior of gases based on the motion of their particles
POWER: the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is transferred or transformed (measured in Watts) ( P = E/t)
EFFICIENCY: how well a system or device converts input energy into useful output energy
MECHANICAL ENERGY: sum of gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy (E = KE + PE)
GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY: energy associated with an object and its force field (PE=mgh)
REFERENCE LEVEL: the surface of the Earth
KINETIC ENERGY: energy an object possesses due to its motion (KE= 1/2mv^2)
TEMPERATURE
HEAT: form of energy associated with the motions of atoms in matter.
THERMAL ENERGY: energy coming from the movement of particles
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY: amount of heat energy required to raise temperature of substance by 1 degree celsius. (Q=mcΔT)
MEASURED IN: Fahrenheit (F°), Celsius (C°), and Kelvin (K)
HEAT TRANSFER: Heat is transferred between different objects at different temperatures through conduction, convection, and radiation.
CONDUCTION: heat trasnfer through direct contact
RADIATION: heat transfer through electromagnetic waves
CONVECTION: heat transfer through fluids