LIFE
Nature of Science
Understanding of the natural world
Observations and Experiments
A Tested Explanation
Theories
Description of a constant Natural Phenomenon
Classification
Protecting Biodiverity
Biodiversity
Ecosystem
Complex ecosystem
Less dependent on certain species
Species benefit from one another
Oxygen, Water, Pollination, pest control, nutrient cycling, climate control, disease control, and food
Destroying Biodiversity
Anthropogenic Climate Change
Bleaching of Corals Reefs

Coral is a keystone organisms which it's ecosystem depends on
The change in climate causes differences in the life cycle of plants and pollination cycle of pollinators.
The difference in timings of the cycles reduce the interaction between plants and polliantators
Animal's food shortages
Decreases growth of fish and increases consumption of dissolved oxygen
Higher altitude environments being exposed to higher temperature causes lower altitude environments to grow and take over
Exploitation of Animals
Hunted for Fur and Horns
Overfishing
Deforestation
Destruction of Habitat
Converted 75% of land not covered in ice
Consume less and more responsibly and waste less food. Educate people who are ignorant of the situation and show them the steps they need to take.
Alive or Not
React to Stimuli
Taxonomists
Taxonomy

Carl Linnaeus
Naturalist from 18th who devised the taxonomy system for organisms on their physical and structural features.
Science of naming and classifying organism
1,5 to 1.7 million species
Tool used to classify and identify closely related organisms
Should always only give two choices for each step
Choices should always be positive "has" or "is"
Choices should be about attributes
Can be a graphical with pictures or written
.gif)
Cells
Prokaryotes
Simple Cell Structure
No membrane-bound nucleus
Smaller than Eukaryotes
Morphology

pl.cocci sl.coccus

pl.baccili sl.baccillus

pl.spirilla sl.spirillum
Mono - One
Diplo - Two
Strepto - Chain
Staphlyo - Cluster
Nutrition
Phototrophs
Use energy from light to make organic molecules
Heterotrophs
Cannot produce it's own food
Chemoautotrophs
Cells create their own energy from inorganic chemicals
Chemoheterotroph
Obtain organic compounds by breaking down chemical
Common Structures:
Cell Wall
Cell Membrane
Flagella
Ribosomes
DNA
Types of Respirtions
Grows in the presence of oxygen
Grows in the absence of oxygen
Must be in the presence of oxygen
Must be in the absence of oxygen
Can grow in the presence of and in the absence of oxygen
Eukaryotes
Complex Structure
Nucleus
Membrane-bound organelles
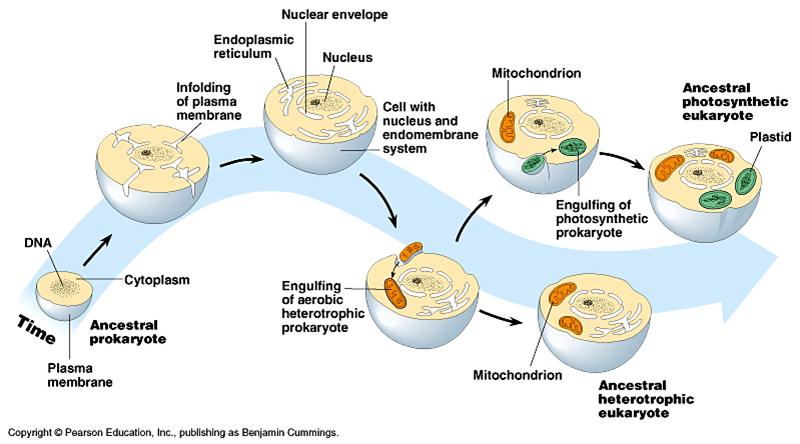
Endosymbiotic Theory
Eukaryotic cells evolved into existence from prokaryotic cells
Originally there were prokaryotes(bacteria) with varying sizes and abilities
Some were able to use photo synthesis
Chloroplasts
Some use oxygen to produce ATP energy
Mitochondria
Larger cells were heterotrophs and consumed other prokaryotes. Certain cases the consumed cells would not be digested and would live together.
Smaller consumed bacteria/prokaryotes would become todays organelles
Mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA
They are the same size as bacteria
Have similar DNA to prokaryote DNA
They duplicate similar to prokaryotes
Viruses
Small non living material
Host Range
The number of host species a virus can infect
Zoonotic Virus
A virus that can infect animals
Vector
An intermediate organism which carries the virus and infects others
Classified
Genetic Material
Method of Reproduction
Lysogenic Cycle
DNA from the virus enters the host cell's chromosomes where it may lay dormant and duplicates as the cells goes through mitosis until it later activates. When it activates it begins to follow the lytic cycle
HIV
Lytic Cycle
DNA from the virus enters the host cell and uses it to make copies of itself until the host cell breaks and continues the cycle
AIDS
Genome Intergration
Integration of DNA from the virus into the DNA of the host cell using an enzyme called Integrase
Unable to reproduce independently
Vaccines
Made from weakened form of viruses
Made of Cells
Can Reproduce
Metabolize
Can Adapt
Can Move
Species
Morphology
Structure/Form
Phylogeny
Species History/Evolution
Ability to Production of Fertile Offspring
8 Ranks
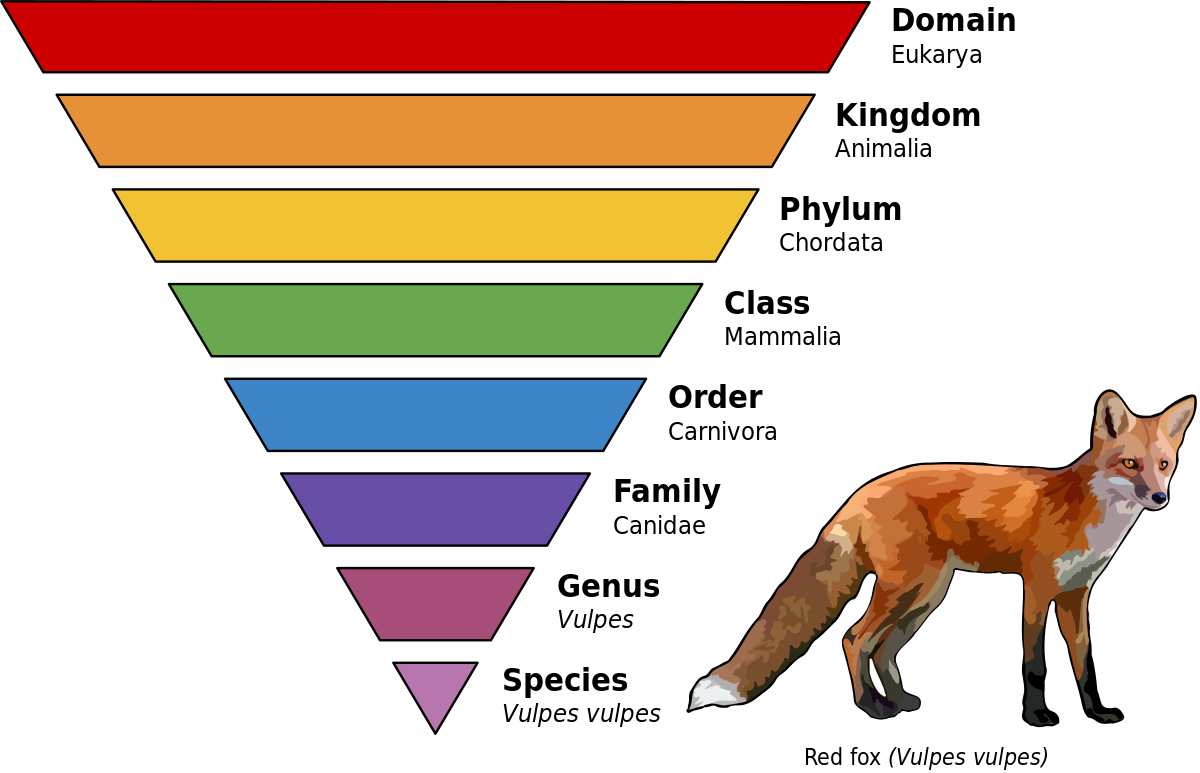
As you go down the more two animals have the same the more closely related they are
Binomial Nomenclature
Genus + species

Canis lupus
Wolf

Mule
8-11 million species
Eukarya
Animalia
Heterotrophs
Sexually and produce and embryo through gametes. But can reproduce asexually
No cell wall
Classified
Organs, organ systems, tissues
Body Layers
Muscles, blood, and kidney
Lungs, liver pancreas, and stomach lining
Bilateral
Radial
Motile(move)
Sessile(Don't move but do when young
Coelem- A fluid filled body cavity containing organ system
Segmentation
Asexual/Sexual
Animalia Groups
Vertebrates
Chordata
Plantis
Autotrophs

Use photosynthesis and cellular respiration to make food
Store food as starch
But rely on other organism to carry
Vascular/Non-Vascular
Bryophytes
Phylum Bryophyta
Liverwort
Hornwort
Moss

Hylocmium splendens
"Mountain Fern Moss"
Used to locate pollution sources

Marchantiophyta
Help reduce soil erosion
Used to study plant evolution

Anthocerotophyta
Nutrient Cycling
Plants that cannot transfer materials through their bodies because they do not have tubes
Use diffusion and osmosis to transport materials
Rhizoids - Small root like structures
Multicellular
Chloroplasts allowing them to conduct photosynthesis
Cell walls made of cellulose
Large Vacuoles
Sexual and Asexual
Seeds are plant embryos with food which remain dormant to survive harsh conditions for long periods of time
Fragmentation
Spore formation
In favorable conditions a spore can develop into a new organism following a cycle known as alternation of generations
Fungi
Heterotrophs
Absorb nutrients from living things
Release digesting enzyme to absorb nutrients
Consume other oragnisms
Share a relationship with plants
Plants get more nutrients
Fungi gets more sugar(glucose)
Multi-cellular and Uni-Cellular(Yeast)
Made of Chitin
Sexual and asexual
Produce Spores
Budding(YEAST) smaller cell develops and pinches off
Fragmentation
Imperfecti
Asexual
Deuteromycota
Causes athletes foot

Chytrids
(Chytridiomycota)
Spores have flagella
Commonly Uni-cellular
Aquatic
Warts

Zygospores
(Zygomycota)
Multicellular
Terrestrial
Mold

Sac Fungi
(Ascomycota)
Largest group
Yeasts

Club Fungi
(Basidiomycota)
Short Lived Fruiting Bodies
Mushrooms
Food- Bread
Medicine-Penicillin
Protista
Uni-cellular
(except for Algae)
Eukaryotic cell organism which cannot be classified as animalia, plantis, or fungi
Through Nutrition
Protozoan
Heterotrophs
Consume other organisms
Some are paracites
Cercozoa
Have pseudopods
("False Feet")
Amoebas
Ciliophora

Ciliates
Have cilia
"hair"
Sporozoa
In mosquitos
Can give you Malaria
Are parasites
Plasmodium
Zoomastigina
Have flagella
"Little Tail"
Flagellates
Moulds
Oomycota
Can be parastic

Water Moulds
Filamentous
"Thread Like"
Myxomycota

Plasmodial Slime Mould
Slug-like
Heterotrophs
Absorb nutrition from other organisms and decaying material
Acrasiomycota

Cellular Slime Mould
Ingest bacteria and yeast
Individual amoeboid cells
Pseuodoplasmodium form when there is no food
Plant Like
Both autotrophic and heterotrophic
Can conduct photosynthesis
When there is no light will consume other organisms
Contain chlorophyll
Can be uni-cellular(plankton) or multi-cellular(algae)
Chrysophyta

Diatoms
Food source for marine organisms
Cell walls are rigid and has a silica outer layer
Pyrrophyta

Dinoflagellates
Bio luminescene

Cause red algae bloom
Toxic to marine animals and make shellfish toxic to humans
Euglenozoa

Euglenoids
Autotrophs in Sunlight
Heterotrophs in the Dark
Asexually and Sexually
Achaea
Archaebacteria
Uni-cellular
Not made of peptidogylycan
Methanogenesis
(Unique to Archaea)
Metabolic process under anaerobic conditions that produce methane as a by-product

Crenarchaeota
Bacteria
Eubacteria
Uni-cellular
Made of peptidoglycan
Photosynthesis
Mesophiles
Like to live in moderate conditions
Human Body
Sexually and Asexually
Conjugation(sexual reproduction) in bacteria only occurs in less favorable conditions.
Bacteria cells link by a pilus and exchange/copy DNA
Fermented Foods
Ecosystem
Gut Flora

Ecosystem

Yogurt
Lactobacillus
Leprosy
Food Poisoning
Tuberculosis

Leprosy
Food Poisoning
(Salmonella)

Tuberculosis
(Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
Endospore Formation
(Unique to Bacteria)
Cells develop a highly resistant structure around the chromosomes when under environmental stress and show no signs of life

Grams Stains
A dye made of crystal violet and iodine
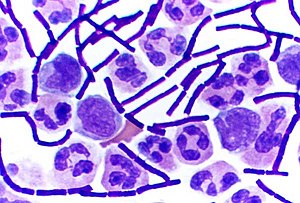
Gram Positive
Cells appear purple
Thick protein layer on cell wall

Gram Negative
Cells appear light pink
Thin protein layer
Pathogenic
Pathogenic: Disease Causing Bacteria
Ex.E.coli
Antibiotics
Kill and prevent the growth of bacteria
Bacteria can build resistance to antibiotics
Excess use of antibiotics on people and animals
Not finishing treatment
Poor hygiene and sanitation
Bacteria to grow rapidly
Structures
Bond using ether bonds
Similar to eukaryotic ribosomes
Extremophiles
Like to live in extreme conditions
Thermophiles
Hot Environments
Acidophiles
Acidic Environment
Halophiles
Salty Environments
Asexually
Binary fission
Budding
Fragmentation

E.Coli
Structure
Nucleic acid
RNA
Positive sense RNA
(+)RNA
Negative sense RNA
(-)RNA
DNA
Structure
Circular
Linear
Segmented
Double Stranded/Single Stranded
Capsid
Shape of virus and is a protein cover for nucleic acid
Equilateral triangle fused to form a sphere
Surrounded by lipid bilayer membrane from host cell

Hollow tube

Both icosahedral and helical

Envelope
Develops when virus buds from host cell and covers the capsid with the cell's membrane
No cell structure
No organelles, membrane, or cytoplasm
Reverse Transcription
Process of turning RNA into DNA
Genetic Diverisity
More variety in species to allow more resistance towards diseases and other variables
Skin and nerve sensory organs
Floating topic
Worms have long bodies shaped like tubes and a distinct head which include eye spots and they are hermaphrodites

Lumbricus terrrestris
"Earth Worms"
Threatens our food and water supply and our climate
Overpopulation and Overconsumption
40% of food produce is wasted
Have xylem and phloem(tubes)
Transports water and minerals
Transports glucose(food)
Vascular
Structure
Support and hold leaves and flovers in the best positions for gathering food and for reproduction
Wide and thin to maximize surface area for photosynthesis and control intake of gases
Seed and Seedless
Angiosperms - flowering plants
Seeds have a protective coating
Use animals to transport seeds in their belly
Pollen is transported by pollinators and the wind into the pollen tube of itself or another plant into the ovary where it fertilizes an egg
Monocots
One Seed Leaves
Leaves in multiples of 3 petals
Parallel Veins on Leaves
Scattered Vascular Bundles

Orchids
Dicots
Two seed leaves
Leaves in multiples of 4-5 petals
Network veins
Vascular Bundles in rings

Rose
Male Part- Stamen
Female Part -Pistil
Gymnosperms - Cone bearing plants
Seeds do not have protective coating
Male and female cones are transported by the wind to produce a seed
Used to anchor the plant and extract minerals from the soil
Tap Root

Fibrous Root