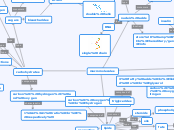
macromolecules
carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
1:2:1 ratio
(respectively)
functions
energy
quickly accessible
storage
structure
cell walls in plants

starches
sugars
monosaccharides

glucose
fructose
bisaccharides

sucrose
(table sugar)
polysaccharides
glycogen
cellulose
proteins
carbon, hydrogen,
oxygen, and nitrogen
amino acids
peptide bonds
functions
hormones
insulin
movement
muscles
immune system
enzymes

fold & twist
into 3D shape
lipids
carbon, oxygen, and
hydrogen
fats
saturated
(no C=C bonds)
unsaturated
(C=C bonds)

vegetable oils
plant & fish fats
oils
steroids
waxes
phospholipids
triglycerides
3 fatty acids
linked to
glycerol
properties
hydrophobic
(doesn't mix
with water)

non-polar
functions
energy storage
cushions organs
insulates body
blubber
(seals, whales)
nucleic acids
store & share
hereditary/genetic
info
RNA

single chain
DNA
double chain

double helix
nucleotides
a base
pentose sugar
5 carbon
phosphate group