Media
Wired
Twisted Pair / Ethernet / Cat5
Coaxial
Fiber Optic
Wireless
Radio Frequency - Wifi
Infrared
Microwave
Topologies
Bus
Every System connected to every other system
Collision
Tree
Network Segmentation
Reduce Collisions
Star
All Systems connected to a central device like a Switch
Central device intelligence can help routing and reduce Collisions
Mesh
Every Device interconnected to every other device
Enables Redundancy
Ring
Built in Collision prevention
Token system
Token gets passed in a ring fashion across all computers on the network
Only the computer that has the token can send the data
Protocols
802.11
Family of Wireless Local Area Networks
Collisions
Vast networks are Bus topology
Collisions are a problem
CSMA / CA
Carrier Sense Multiple Access
With Collision Avoidance
Used in Wireless Networks
CSMA / CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access
Collision Detection
Used in Wired Networks
Devices
Hubs , Repeaters and Concentrators
Least Intelligent
Fastest
Physical addressing and reliable point to point connection
MAC Address
Unique Identifier
Assigned to every NIC manufactured
Used to identify the recipient of the data being sent
Devices
Switches
Interconnect multiple devices
Intelligently forward data to the intended recipient based on MAC
Unless specifically stated, operates at layer 2
Bridges
Connect two network segments together
Protocols
802.1x
Network Access Control
Used for authenticating network devices to a Network
ARP
Translates an IP address into a MAC address
Address Resolution Protocol
PPTP
Point to Point Tunnelling Protocol
Used to create network tunnels
PPP
Point to Point Protocol
Encapsulates IP traffic
Provides Authentication Encryption and Compression
EAP
CHAP
PAP
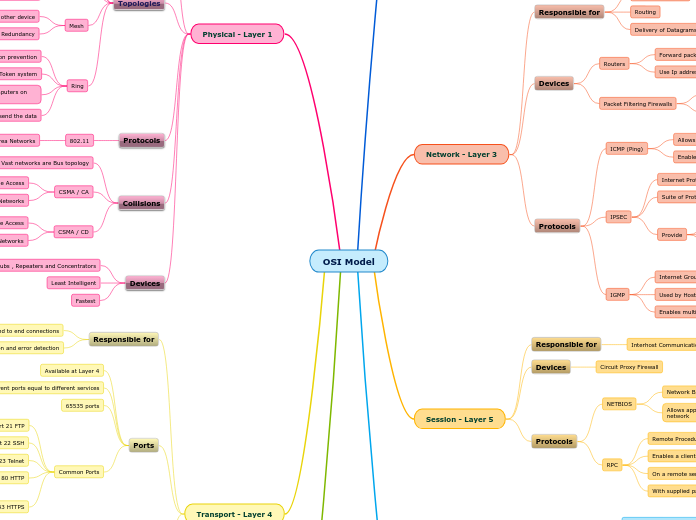
Responsible for
Logical addressing
Routing
Delivery of Datagrams
Devices
Routers
Forward packets between network segments
Use Ip addresses for packet forwarding
Packet Filtering Firewalls
Simplest
Fastest
Protocols
ICMP (Ping)
Allows network devices to send error and control messages
Enables Ping and Tracert Programs
IPSEC
Internet Protocol Security
Suite of Protocols
Provide
Data authentication
Confidentiality
Integrity
IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol
Used by Hosts and adjacent routers
To establish multicast group memberships
Enables multicast groups
To transmit the same packets to multiple systems
Responsible for
Interhost Communications
Devices
Circuit Proxy Firewall
Protocols
NETBIOS
Network Basic Input Output System
Allows applications on systems to communicate over a network
RPC
Remote Procedure Call
Enables a client to execute a command
On a remote server
With supplied parameters
Responsible for
Human Computer Interaction
Application access to network services
Devices
Application Firewalls
Very intelligent Firewalls
Advanced Decision making
Deep packet inspection
High Latency. Can be slow
Protocols
HTTP
Allows clients to request webpages from webservers
HTTPS
DNS
Translates domain names into IP addresses
SNMP
Simple Network Management protocol
Allows collection data from
and remote management of network devices
Routers
Switches
LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
Accessing and maintaining distributed directory information
Connecting
Accessing
Modifying
Searching
Example - Corporate Mail server
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Assign IP addresses to devices as they are
added to the network
Ensure no duplicate IPs
Responsible for
For managing end to end connections
With error correction and error detection
Ports
Available at Layer 4
Different ports equal to different services
65535 ports
Common Ports
Port 21 FTP
Port 22 SSH
Remote Login protocol
Port 23 Telnet
Remote Command Line Protocol
Port 80 HTTP
Connect to a web server
Port 443 HTTPS
Connect to a webserver
Secured using TLS
Protocols
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
Reliable
Ordered
Error checked delivery of packets
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
Fast
Efficient delivery of packets
No error checking
SSL
Secure Socket Layer
Used to Encrypt HTTP traffic
TLS
Transmission Layer Security
Latest version of SSL
Used to encrypt HTTP traffic
Responsible for
Character Conversion
Codecs Compression and decompression
Stream audio and video
Image Conversion and Formatting