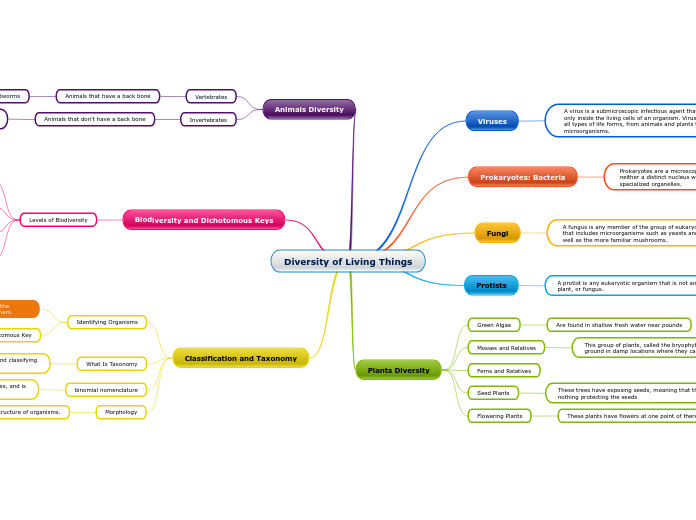
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms.
Prokaryotes are a microscopic single-celled organism that has neither a distinct nucleus with a membrane nor other specialized organelles.
A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms.
A protist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, plant, or fungus.
Green Algae
Are found in shallow fresh water near pounds
Mosses and Relatives
This group of plants, called the bryophytes, grow close to the ground in damp locations where they can get water easily.
Ferns and Relatives
Seed Plants
These trees have exposing seeds, meaning that there is nothing protecting the seeds
Flowering Plants
These plants have flowers at one point of there life.
Vertebrates
Animals that have a back bone
like Sponges, Jellyfish, Flatworms, Roundworms
Invertebrates
Animals that don't have a back bone
like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds,
mammals, and humans
Levels of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is a product of millions of years of evolution as organisms adapt to changes in the environment.
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species.
Species Diversity
Species diversity is the number of different species that are represented in a given community.
Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is the variations of ecosystems within a geographical location.
Identifying Organisms
Scientists use names to identify types of organisms, the organisms are named after the scientist that found them.
Using a Dichotomous Key
A dichotomous key is a tool used by scientists and to identify organisms
What Is Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of naming, identifying, and classifying species.
binomial nomenclature
This system has a two part Latin name for each species, and is the most used system to classify in the.
Morphology
Is the study of form and structure of organisms.