Body Systems

Immune System
protecting the body from viruses and
infections and identifying threats
components

Lymph Nodes
storing cells that fight
infections and diseases

Spleen
disposing of old/damaged cells,
containing white blood cells that
fight diseases and controls amount
of blood

Bone Marrow
Producing white blood cells
and containing stem cells
Lymphocytes
eliminating antigen
B-cells
Creates antibodies that attack bacteria and toxins
T-cells
Helps destory cancerous cells
Thymus
maturing t-cells
Leukocytes
white cells that fight disease cells
and eliminate pathogens
Lupus
joint pain
Antimalarial drugs
affects the immune system
and can help reduce the risk
of lupus flares
swelling
Reproductive System
allowing the human bodies to grow
and have children

Female Reproductive System
producing female egg cells which
are necessary for reproduction,
producing and transporting gametes and producing sex hormones
Components
Uterus
Developing the fetus

Fallopian Tube
Transporting eggs from
ovaries to the uterus

Vagina
allows menstrual flow to exit the body, acts as a birth canal (allows baby to pass through during pregnancy) and allows penis to enter body during sexual intercourse)
Ovary
producing eggs and hormones
cervical cancer
bleeding between periods
Pap test
cervix cells are scraped and
examined to see if there is any
abnormal growth
increased
vaginal discharge

Skeletal System
providing support, movement, protection,
blood cell protection, calcium storage and endocrine regulation
Components

Bones
supporting the bodies structures,
protecting organs from injuries,
allowing for movement and provide
storage space for minerals such as
calcium

Cartilage
Connects bones together, provides
support, and allows for flexibility in movement.

Ligaments
stabilizing the joint, and preventing
it from moving outside of its motion
range.
Joints
connecting bones within the body, bearing weight and allowing movment

Tendons
connecting skeletal muscles to bones
Osteoporosis
fragile bones
Bones are prone to facture
X-rays
allows doctors to see if bones are truly broken or if there is just a sprain

Nervous System
controlling the body by collecting
sensory input internally and externally, then processing those inputs and providing the body with an output which is usually an action
systems
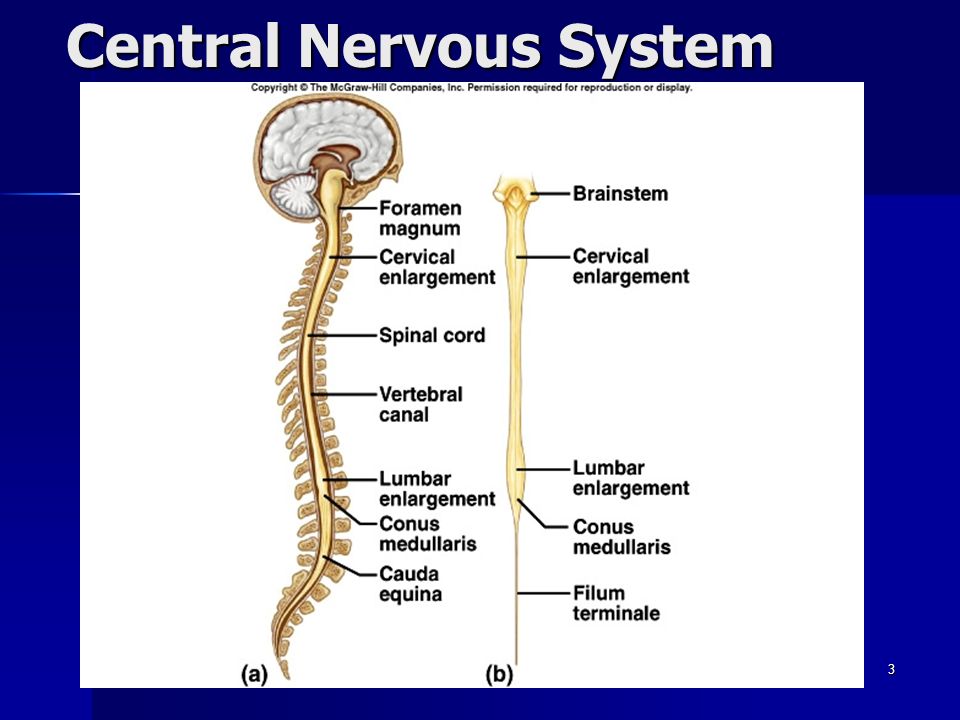
Central Nervous System
Components

Brain
processing and interpreting
sensory information sent out
by the spinal cord
Components
Cerebrum
controlling senses, thoughts
and movements
Cerebellum
controlling posture, balance,
coordination and speech
Brain Stem
controlling breathing, swallowing,
heart rate, blood pressure consciousness and many more

Spinal Cord
serving as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body
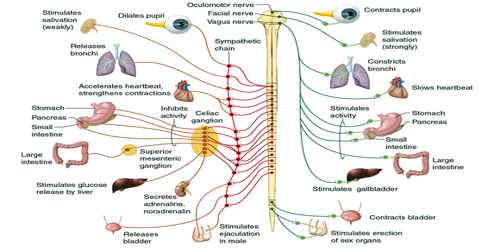
Peripheral Nervous System
Components

Nerves
Carrying information to and from the
central nervous system which help us
live our everyday lives
epilepsy
Temporary confusion
Uncontrollable jerking
movement of arms and legs
Drug therapy
doctors prescribe you with medication
which can help control your seizures
Sends impulse to secrete hormones

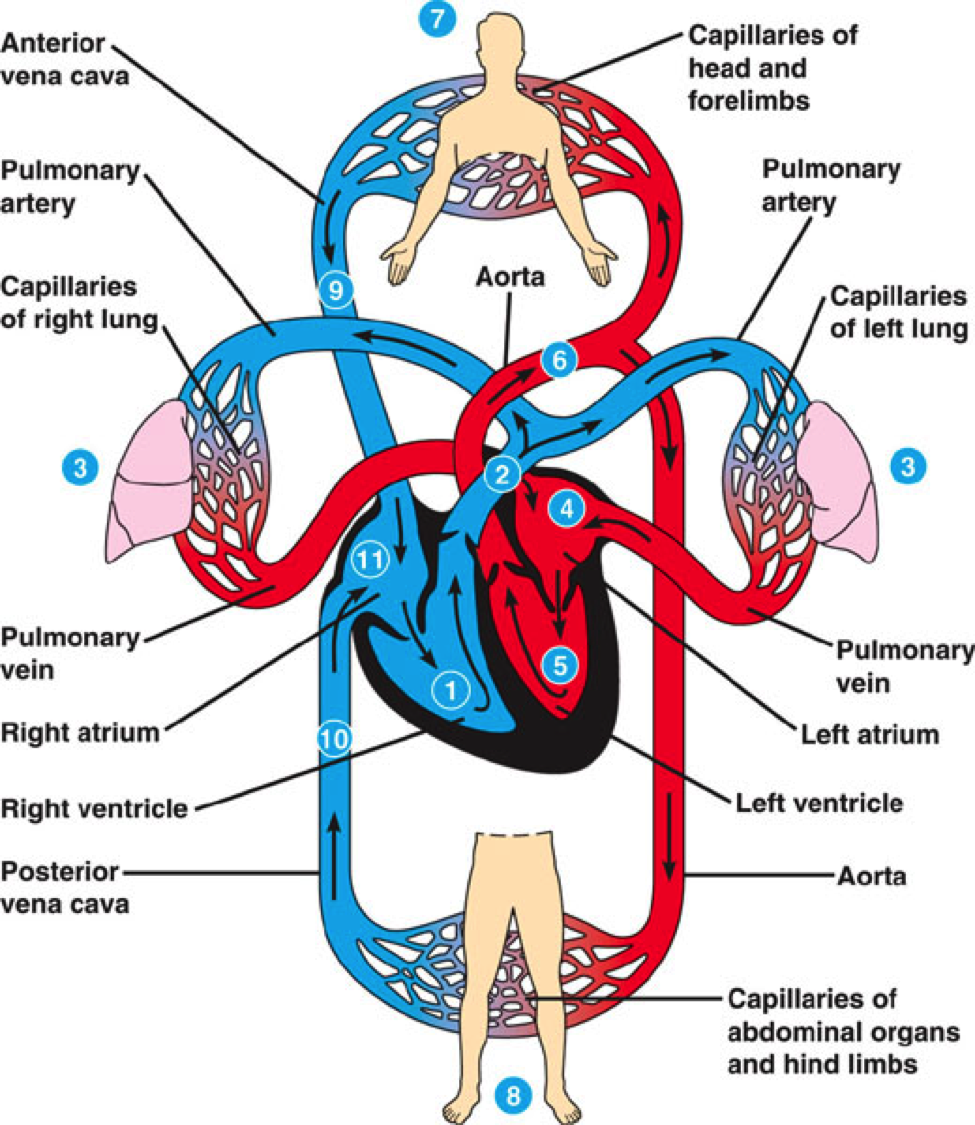
Circulatory System
responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients,
oxygen
Coronary system
Supplying oxygenated blood to
the heart muscle, and draining away
the blood once it has been dyoxygenated
Components
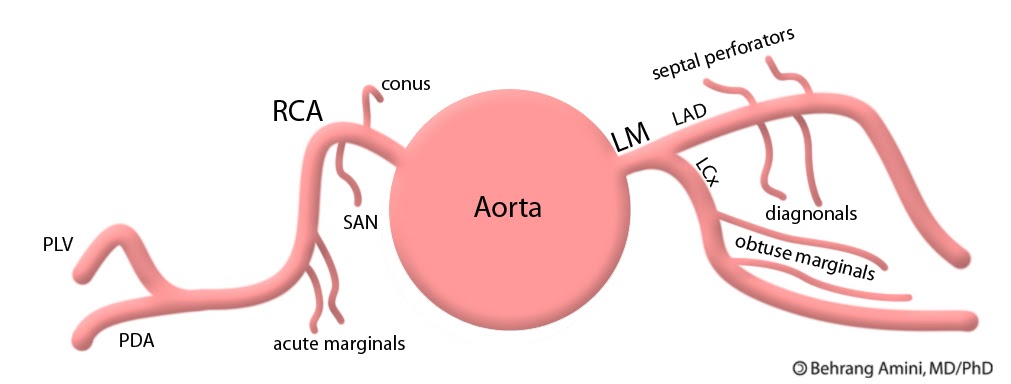
Coronary arteries
Transporting blood in and
out of the cardiac muscle

Cardiac Veins
Returning deoxygenated blood

Pulmonary system
providing oxygen between the heart and lungs
Components

lungs
processing gas exchange
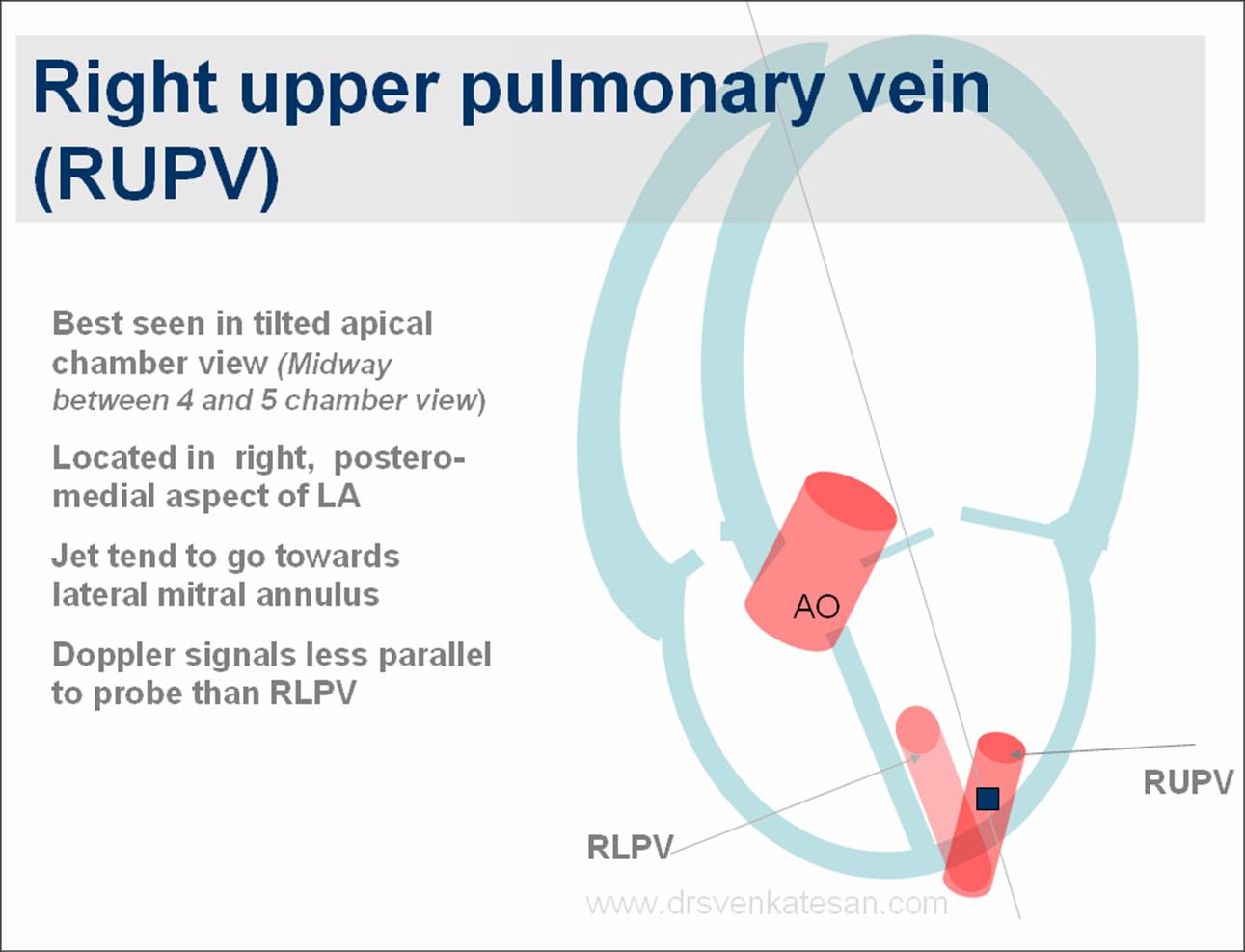
Pulmonary Veins
Carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart

Pulmonary arteries
Carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs
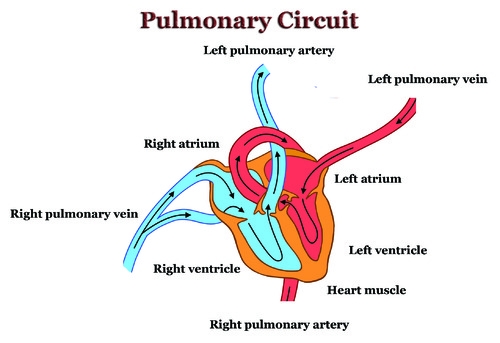
Systemic system
Circulating blood from the heart to the body, and returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Components
arteries
carries blood away from the heart
and toward other tissues and organs
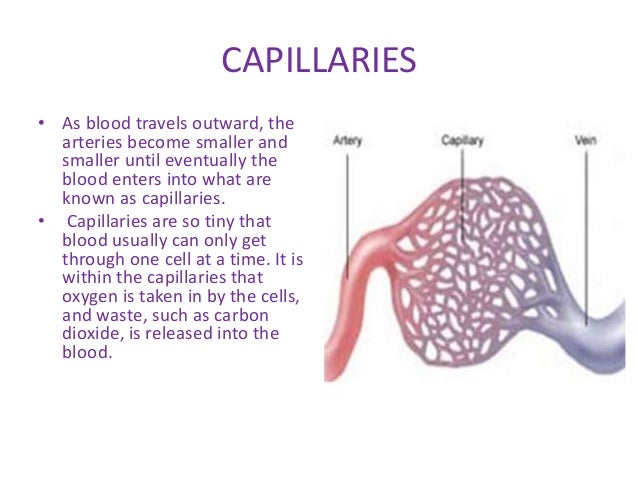
capillaries
Bring nutrients and oxygen to tissues and
remove waste products.
Heart Attacks
Tightness
Fat Attenuation Index
analyses CT images of fat surrounding
the arteries. This allows doctors to predict
those who are prone to heart attacks.
Breath shortness
The circulatory system provides
oxygen to every cell in our body, after our respiratory system rbeathes it in

Muscular System
Inflammatory myopathy
muscle weakness
Electromyography
helps identify causes of nerve and muscle
disorders by stimulating nerves and
recording responses
fatigue
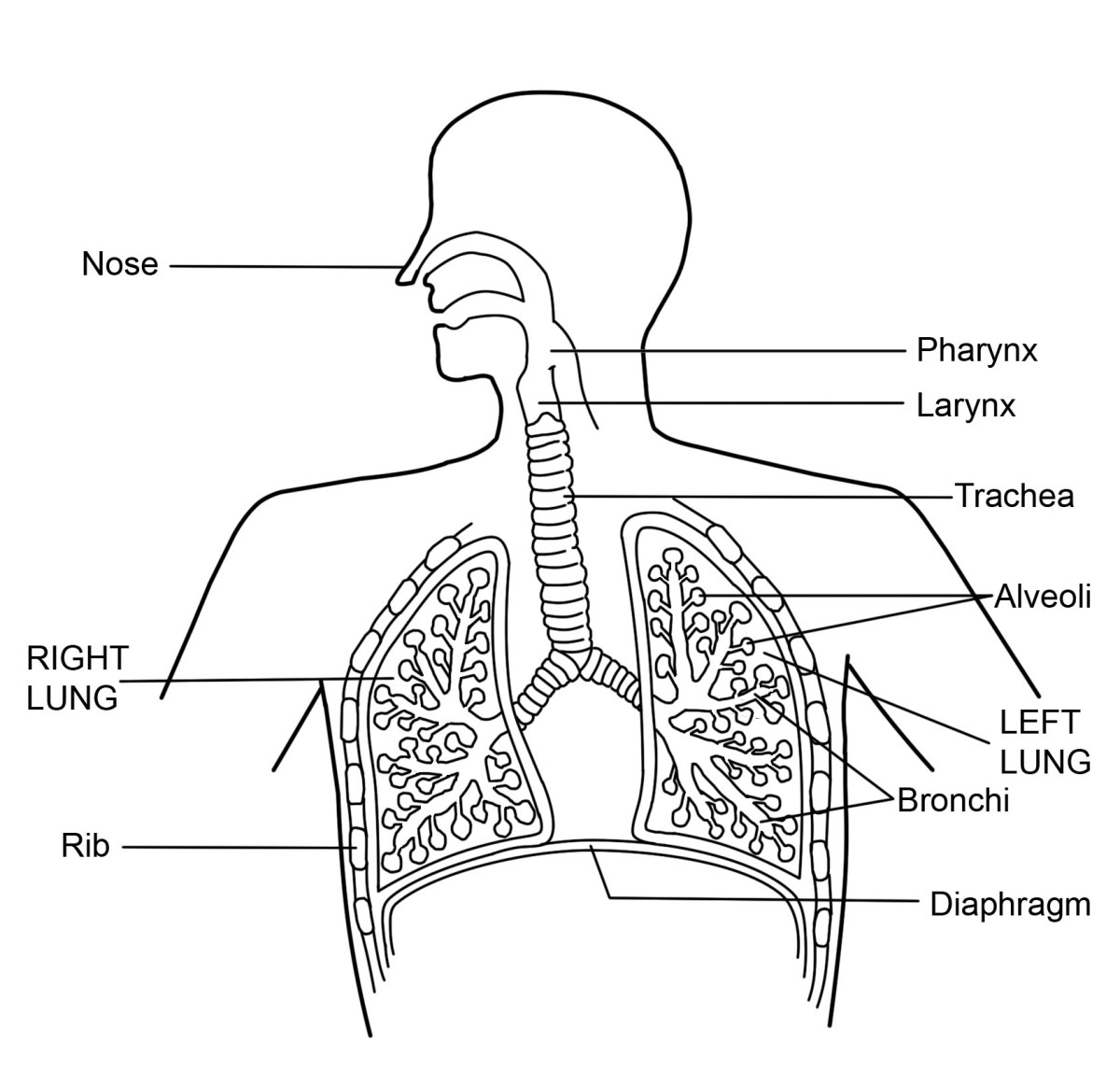
Respiratory System
Taking in oxygen and
letting out carbon dioxide
components

Lungs
Oxygen in the lungs is
carried into the bloodstream
and carbon dioxide is taken out
Diaphragm
Dome shaped muscle, that
controls breathing and separates
chest cavity from abdominal cavity.
Expands and contracts to reduce and
increase pressure in lungs

Epiglottis
Seals off the windpipe, when
your consuming food, preventing
blockage of your airway
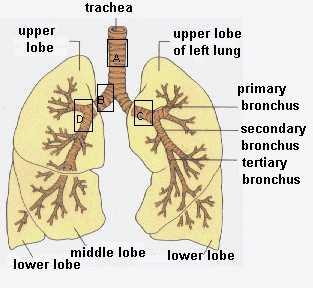
Bronchi
Main passageway into lungs. and allows for oxygen to enter, and carbon dioxide to exit
Larynx
Connects the pharynx to the
trachea and allows air to pass
through into the lungs
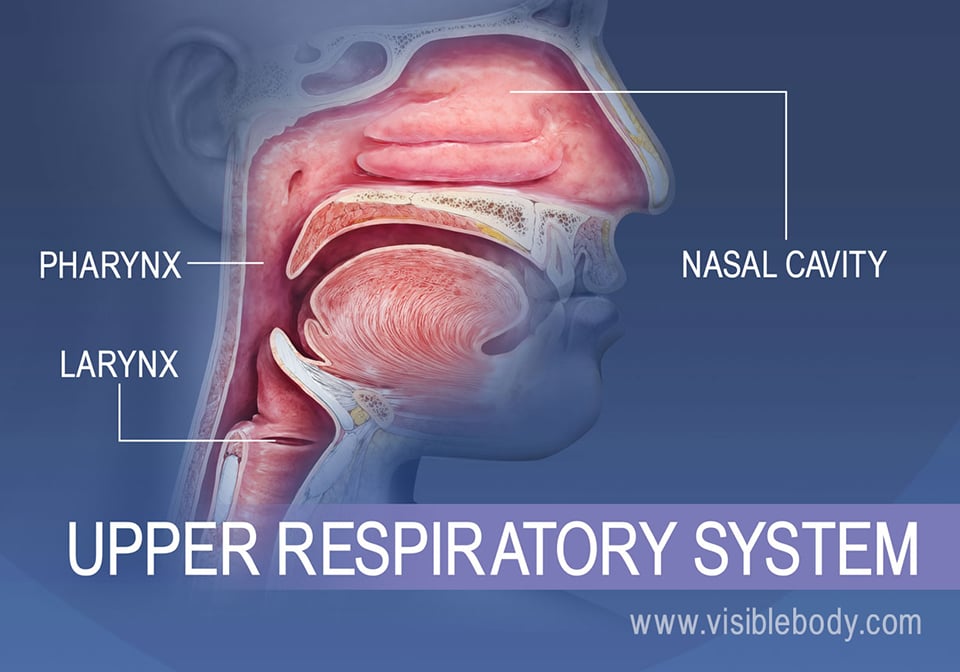
Nasal Cavity
Respiratory tract. A passageway
for air to enter the body. Warms, moisturizes and filters the air
before it enters the lungs

Trachea
An air conducting tube (windpipe),
that connect the larynx to the
rest of respiratory system
Pharynx
Conducting zone
Nostrils
Larynx
Trachea
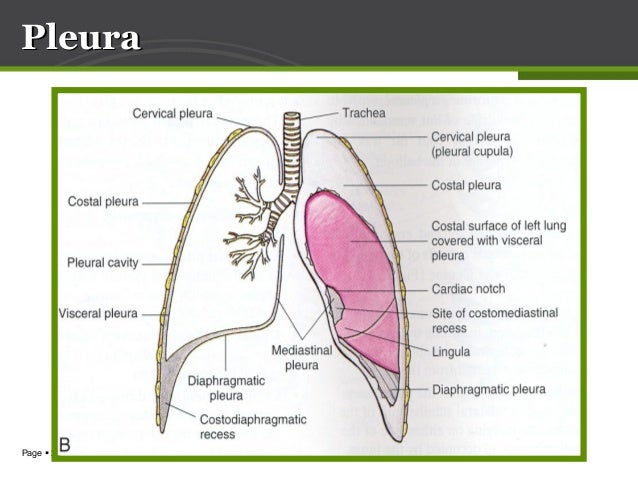
Pleura
Allows for free movement of
the lungs against the chest
wall when we breathe
Oral cavity
Second external opening
for the respiratory tract.
(Another passageway that
allows air to enter the body)

Digestive System
Breaks down food, into small molecules which are sent into our body as nutrients
Components

Gastrointestinal tract
A series of hollow organs connecting
the mouth to the anus
Hollow organs

Mouth
chewing/breaking down food
and using saliva to begin the
digesting process

Esophagus
Connects the pharynx (throat)
to the stomach and is the tube
that allows food to reach the stomach

Stomach
Breaking down food using acid
and enzymes. Stomach muscles
contract and expand churning the
food to enhance digestion
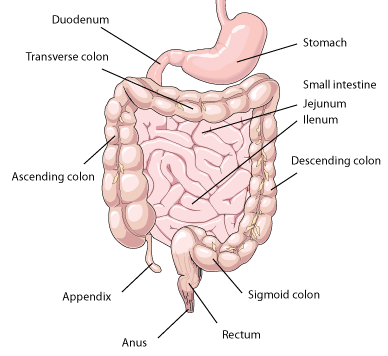
Small Intestine
absorbing nutrients and minerals
from food
Components
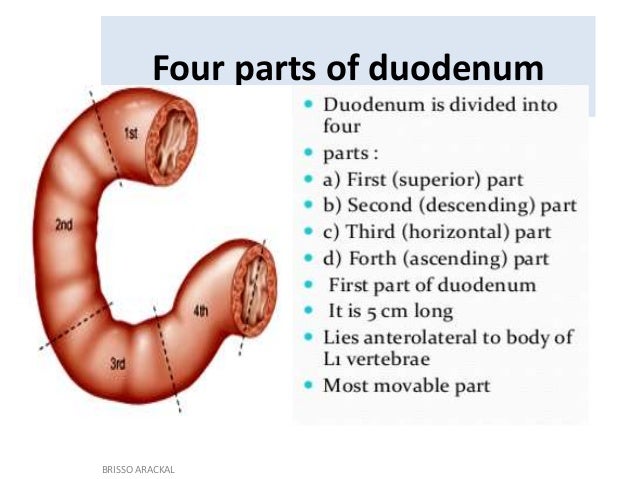
Duodenum
Regulates the emptying of the stomach
contents into the small intestine

Jejunum
absorbing most of the nutrients
present in food, before passing it
on to Ileum

Ileum
absorbing vitamin B12 and
other nutrients not absorbed
by the Jejunum

Large Intestine
reabsorbs water from chime (food mixture)
and acts as a temporary storage for waste
Components

Cecum
absorb fluids and salts that remain
after digesting process

Colon
process waste products and prepare
for the elimination of these products
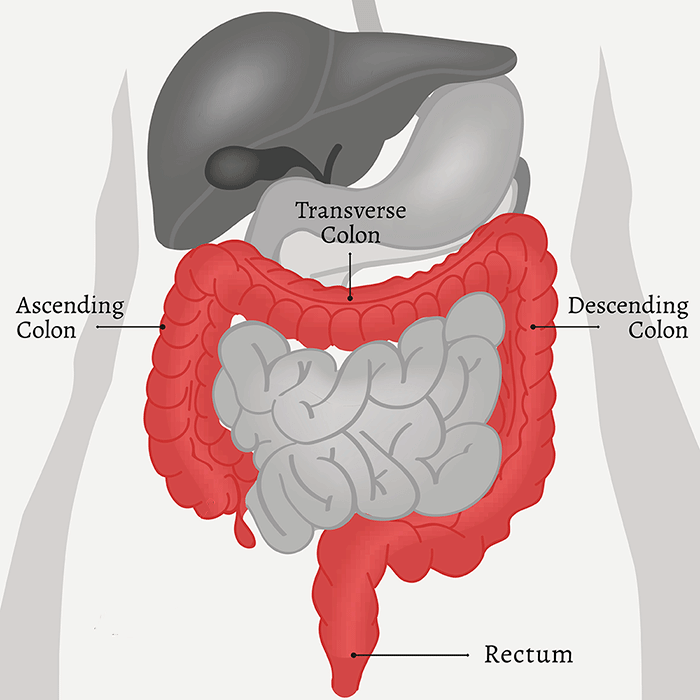
Rectum
temporary storage to contain feces

Anal Canal
a passageway allowing waste
to exit the body

Anus
using muscles to allow and stop stool
from escaping the body
Solid organs
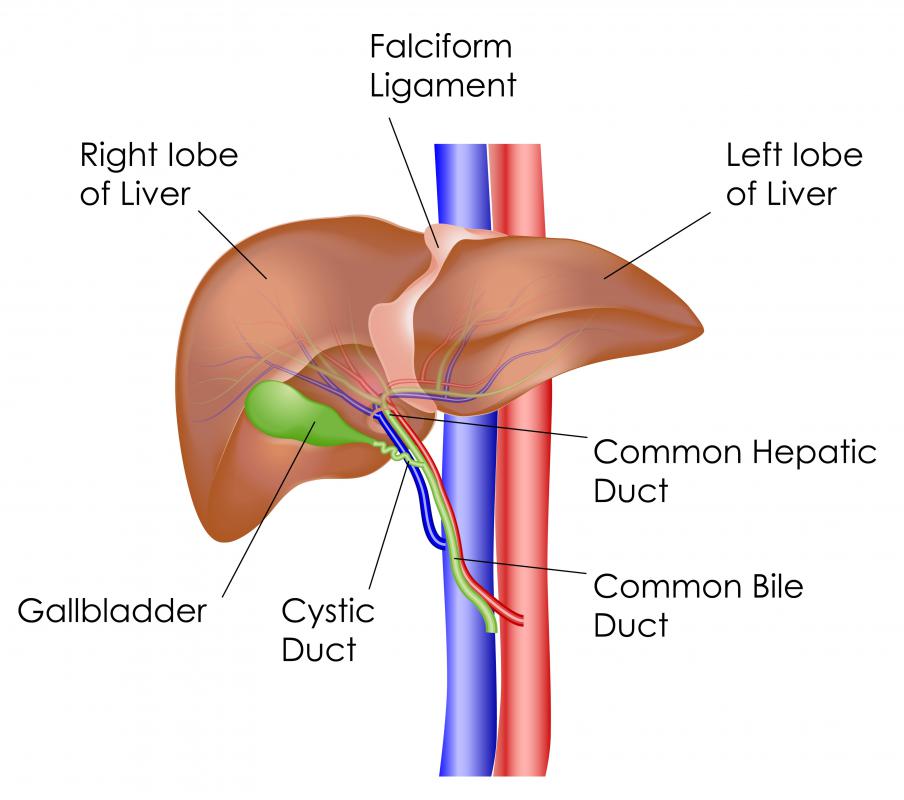
Liver
Bile production, excretion and metabolizing
fats, proteins and carbohydrates

Pancreas
Converting food into nutrients for
our body cells and regulating blood
sugar

Gallbladder
Involved in the production of bile
(yellowish, brown fluid), which breaks down and digests fatty foods.
Gallbladder stones
bloating
Nausea
Aching in certain areas
abdominal
ultrasound
allows doctors to see
clearly what the problem is
uses sound waves to
produce pictures of the
internal body

Endocrine System
producing hormones and chemical
substances that regulate the activity
of cells, organs, the body's growth,
metabolism and sexual development
Components

Pituitary
Discharging hormones into the bloodstream
Thyroid
Producing hormones that regulate
the body's metabolism as well as
heart and digestive function

Parathyroids
Producing hormones that control
the body's calcium levels

Adrenals
Producing hormones that control blood
sugar, burn proteins/fats and regulate
blood pressure

Pineal
(unknown) might
regulate sleeping
patterns

Ovaries
Producing reproductive hormones
which are vital to having female
characteristics
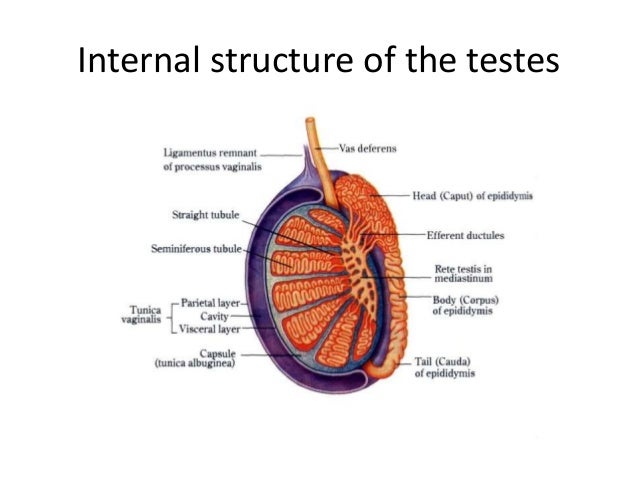
Testes
Discharging testosterone (a hormone)
which is vital for developing male
characteristics amd allowing for
production
of sperm
Parathyroid disease
Lump in the neck
Speaking difficulity
machinery
allows for doctors to surgically remove
parts of the gland
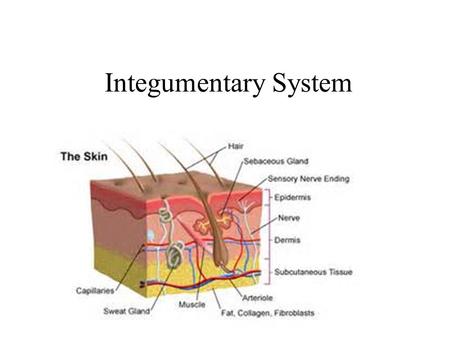
Integumentary System
protect the body from the
"outside world".
components

Hair
protect sensitive areas from
dust and small particles and
provides insulation to the head

Skin
providing protection from pressure,
temperature, micro-organisms,
radiation and chemicals

Nails
protect the tips of finger and toes
from mechanical injury
Nerves
allowing the body to sense when
it's in pain
Glands
maintaining body temperatures,
and preventing our hair and skin
from drying out
Acne
Laser
cause the acne to disappear
or at least reduce in size
heats the upper dermis
below the skin surface
itching
redness

Renal System
produces, stores and eliminates urine
Components

Ureter
tube carrying urine from the
kidney to the bladder

Kidney
Removing urea (waste product formed by
the breakdown of nutrients)from the bloodstream.

Bladder
Stores urine, allowing it to
be controlled

Urethra
Tube carrying urine from the
bladder to the outside of the body
Cystisis
persistent urge
to urinate
strong-smelling
urine
Cytoscopy
a thing tube with a light and
camera attached, are inserted
through the urethra, into the bladder
to see signs of a disease
chronic diseases
Asthma
Breath Shortness
Chest Pain
Wheezing

Hypothalamus
Releasing hormones and regulating
body temperatures
An app
allows doctors to monitor
the health of those dealing with
asthma.
allows patients to input any time they deal with any symptoms. This allows doctors to keep track of the patients health.
Components

Bladder
storing urine

Prostate
contributing additional fluid during
ejaculation and nourishing the sperm

Urethra
carries urine from the bladder, to outside of the body

Penis
ejaculates eperm into the vagina during sexual intercourse

Male Reproductive System
Producing, and transporting sperm and
producing male hormones which are
essential for the male reproductive system
male infertility
unable to cause pregnancy
in a female
Sperm injections
Males who are low on sperm
may have sperm injected in to them
as well as other hormonal genes to allow
for proper growth to occur

Corpus
Expanding and contracting to be able to
hold the devloping baby

Cervix
Opening into the vagina,
allowing sperm to enter
providing movement, stabilising
joints, maintaining our posture,
and generating heat during activity
Components

Skeletal Muscle
covers your skeleton, giving
your body shape, allows for
movement by contracting and
generates heat to maintain body
temperature

Smooth Muscle
contract and expand automatically
without us knowing and help us perform
simple tasks. For example, the muscular walls of the intestine contract to push food
through the body

Cardiac Muscle
contracts the heart
to pump blood