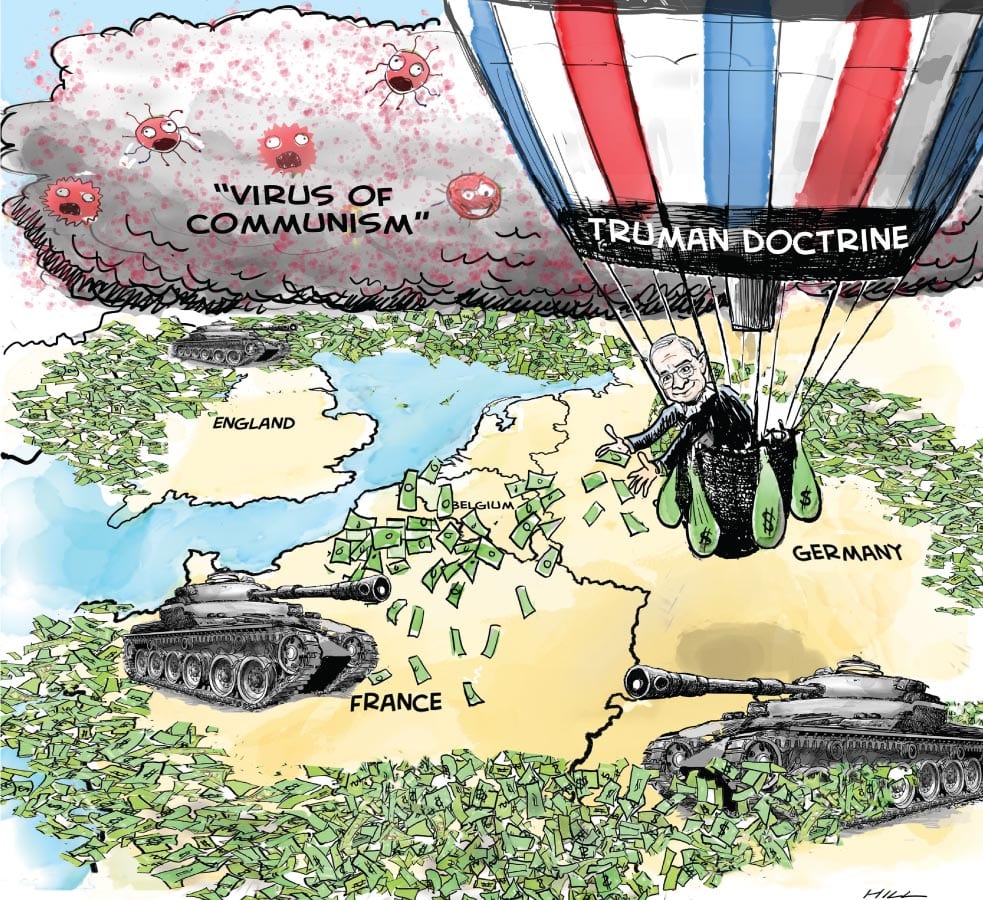
Cold War Documents
Truman Doctrine
Summary:
- Supported free people who were facing exterior pressure
through the subjugation of arms or other forceful acts
- Maintained a regime that strayed away from totalitarian regimes, ultimately preventing evil from coming into the United States or any of its allies
- Provided resources through financials and materials/support to Greece and Turkey to prevent the spread of communism in their territories
- Supplied $400 million dollars towards stopping the spread of communism
Totalitarian Regimes: Nations led by dictators who
assume total control over the social, economic and
political lives of their people (ex: Hitler, Stalin).
Subjugation: To force people under the
authority of a cruel leader or government
Goals:
- Contain the Soviet Union from the entire world to
ensure that communism does not continue to spread
- Help people through economic and financial aid in
order to maintain the economic and politics
- Prevent coercion and the force of political powers
preventing other people's decision making
- Keep people's hope to live better lives than they
currently do alive and support those who are vying
for their freedom
Coercion: To persuade people to do something using force
The Truman Doctrine was successful because it contained communism and prevented its spread into several previously struggling countries. They directly stopped the idea of Soviet Union expansionism by promising to aid those who fought against communism, ultimately allowing them to gain allies.
Soviet Union: Communist nation formerly known as
Russia. This transition occurred at the end of WWI

NSC-68
Summary: NSC-68 recommended that the United States focused on military expansion of conventional forces and the nuclear arsenal, including the development of the new hydrogen bomb. It also outlined a variety of possible courses of action, including a return to isolationism, war, or continued efforts to negotiate with the Soviet Union. The U.S feared the Soviets would cut them off from the allies and resources they needed to fight off further Soviet intrusions. But, the Soviet Union argued that the United States could contain them through political and economic measures, rather than purely military ones.
Nuclear Arms: Weapons made using nuclear fission
(atomic bombs) or fusion (hydrogen bombs), usually
in the form of missiles ("Nukes")
Goals: The U.S thought the best course of action was a massive build-up of the U.S. military and its weaponry. The U.S also wanted to attain sufficient strength to decrease Soviet aggression. America sought to protect their land and its allies from Soviet air and land attacks, maintain lines of communications, and enhance the technical superiority of the U.S.
Build-up: To rapidly produce lots of something and
stockpile as much of it as possible to have it ready
for future use
Successful?- The NSC-68 was somewhat successful. It concluded that the only plausible way to take down the Soviet Union was for President Truman to support the massive build-up of both conventional and nuclear arms. But, it rejected the alternative policies of peaceful containment of the Soviet Union.

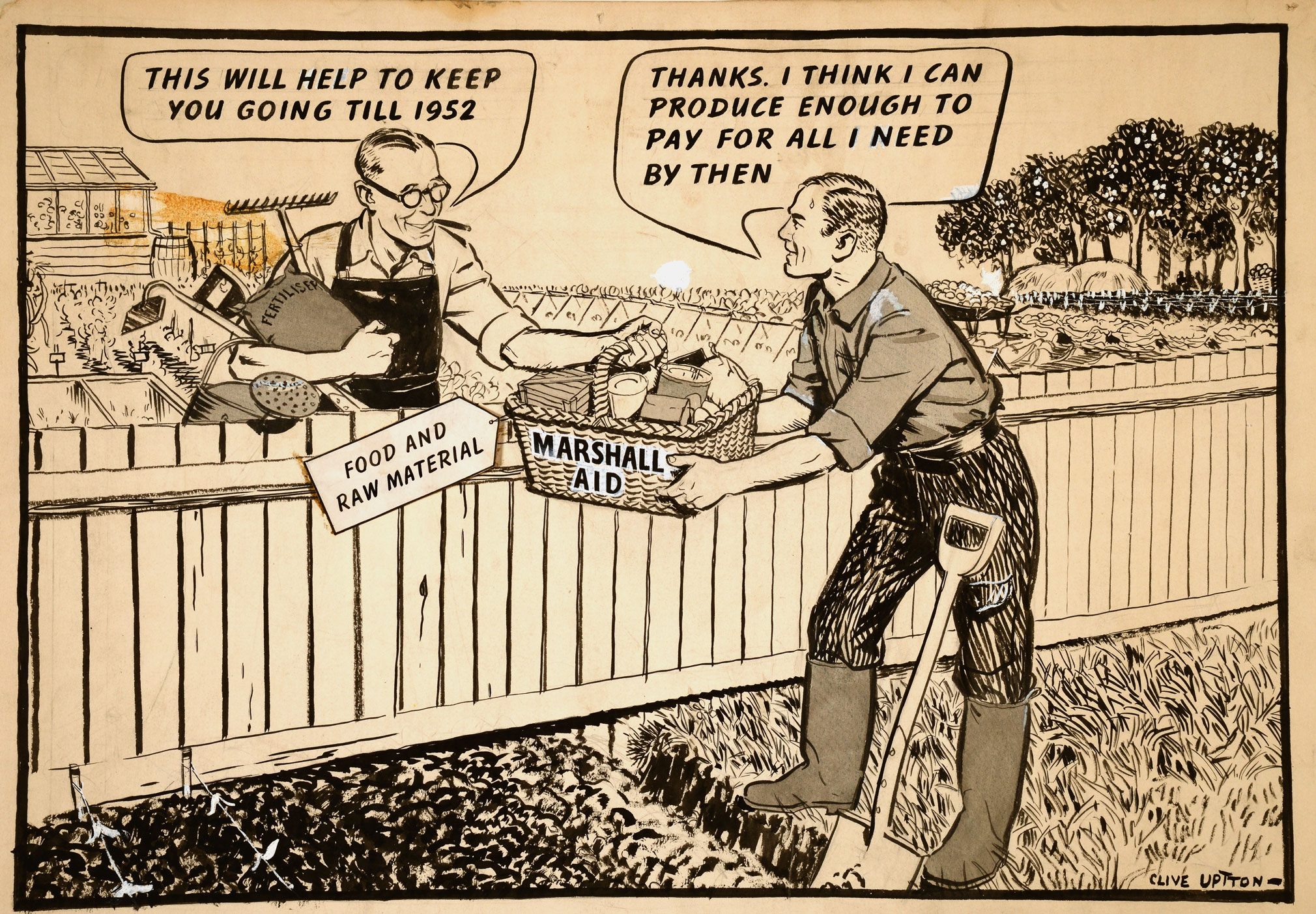
Marshall Plan
Summary:
- Provided materials and capital in order to rebuild
European's struggling economy
- Created markets to trade American goods
- Created the idea of keeping stable
Democratic governments in Western Europe
- Sent $13.3 billion to 17 countries in the span of
three years
- Greatly assisted European countries in recovery, both economically and spiritually after the war
Recovery: To aid in the return to the financial stability
of European countries after the devastation of war on
their economies in order to prevent Communist
influence and uprisings by poor people.
Goals:
- Rebuild the economies of countries in Europe,
especially those who were in the western part of
Europe
- Lift the spirits of those living in western Europe to
maintain peace and structure
- Restore the economic infrastructure in postwar
Europe
- Get rid of communism and prevent its spread to
other countries
Communism: An economic system whereby people own all resources, land and property collectively in a classless, moneyless society. All property is owned first by the government, then is distributed equally among the masses. The goal is to eliminate class differences.
The Marshall Plan was successful because it
prevented the spread of communism and
maintained a capitalist regime, while also
establishing long-standing trade relationships
between Europe and North America through
economic aid for struggling economies.
Economic Aid: Money sent specifically to help
countries recover post war.