Constructivism
What is learning?
Learning is the alteration of behaviour as a result of individual experience.
The knowledge is constructed by the learner.

Example
The learner has his own ideas of the world.

Example
Knowledge is represented in the brain as conceptual structures.

Example
Even knowledge is individual and personal, learners inevitably interact with the world.

Example
Learner's ideas must be taken seriously by the teachers.

Example
Origins
Takes the stance of the Geneva School, therefore it is constructivist and interactionist.

Example
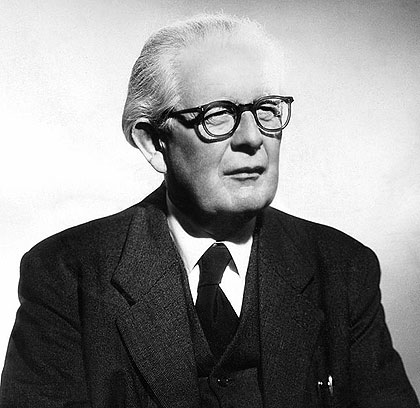
During the 1980's. Jean Piaget was one of the founders of this school of thought in education. The followers of this approach said that the learner had to be active in the knowledge acquisition process.

Example
Other key theorists: John Dewey, Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky, and Jerome Bruner
Nature
In contrast to Behaviorism, the Constructivism is of an active and constructive nature.

Example
The learner gets closer to the object of knowledge, he knows it and he creates a representation of it.

Example
There are two elements which are inextricably linked to the cognitive development process: organization and adaptation.
Example