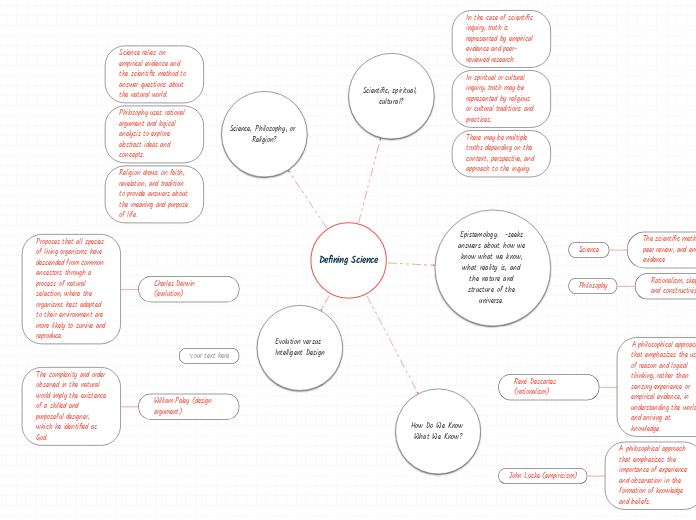
In the case of scientific inquiry, truth is represented by empirical evidence and peer-reviewed research.
In spiritual or cultural inquiry, truth may be represented by religious or cultural traditions and practices.
There may be multiple truths depending on the context, perspective, and approach to the inquiry.
Science
The scientific method, peer review, and empirical evidence
Philosophy
Rationalism, skepticism, and constructivism
René Descartes (rationalism)
A philosophical approach that emphasizes the use of reason and logical thinking, rather than sensory experience or empirical evidence, in understanding the world and arriving at knowledge.
John Locke (empiricism)
A philosophical approach that emphasizes the importance of experience and observation in the formation of knowledge and beliefs.
Science relies on empirical evidence and the scientific method to answer questions about the natural world.
Philosophy uses rational argument and logical analysis to explore abstract ideas and concepts.
Religion draws on faith, revelation, and tradition to provide answers about the meaning and purpose of life.
Charles Darwin (evolution)
Proposes that all species of living organisms have descended from common ancestors through a process of natural selection, where the organisms best adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Your text here
William Paley (design argument)
The complexity and order observed in the natural world imply the existence of a skilled and purposeful designer, which he identified as God.