Structure: C, H, O
Polysaccharide
Structural
Cellulose
Cell Wall
Storage
Starch
Function
Energy source
Monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Disaccharide
Sucrose
Active Transport
Cell Membrane
Structure: C, H, O, N
Function
Enzyme
Lysosomes and Peroxisomes
Muscle Development
Carrier
Cell Membrane
Faciliated Diffusion
Amino Acids
Amino Group
Carboxyl Group
R Group
Polar
Nonpolar
Acidic
Basic
Ribosomes
Rough ER
Mitochondria:(along w/DNA)
Structure: C, H, O, N, P
Nucleotides
Phosphate Group
Nucleoside
Nitrogenous Base
Purines
Adenine & Guanine
Pyramidines
Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
Pentose Sugar
Deoxyribose
DNA
Ribose
RNA
DNA
Nucleus
Nuclear Envelope
Centrosomes
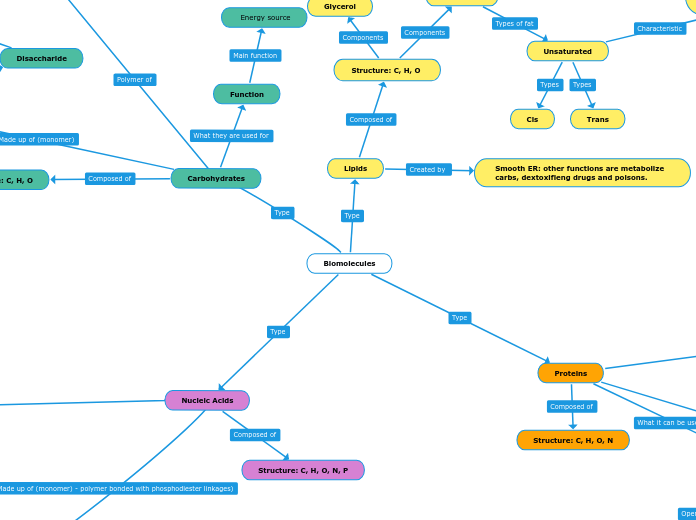
Structure: C, H, O
Glycerol
Fatty Acid
Saturated
Unsaturated
Cis
Trans
Prescence of unsaturated fats (due to their double bond) can increase membrane fluidity
Smooth ER: other functions are metabolize carbs, dextoxifieng drugs and poisons.
Phospholipid Bi-layer
Plasma membrane: the cells barrier
Synaptic Signaling
Paracrine Signaling
Hormonal Signaling
Receptors
Membrane Receptors
GCPR
Signal mlcl binds to receptor
Which swaps out GDP for GTP
G-protien
Adenyl Cyclase (enzyme)
Cyclic AMP
Protein Kinase Cascade
Activates a Cellular Response
AMP
Tyrosine Kinase /RTK
Ion channel
Signal molecule binds to the receptor
Gate allows specific ions (Na+ and Ca+) through a channel in the receptor
Voltage across the membrane is changed
Action potential is triggered
Intracellular Receptors
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Membrane
Reception
Transduction
Activated receptor activates a molecule
More molecules are activiated
A response may occur in the cytoplasm or nucleus
Gene Expressions
Cell growth or Division
Change in Motility
Change in cell shape or size
Activation for a protein
Response
Extracellular Signals
Intracellular Signals
the Signal to Nucleus
patterns of protein transciptions
binds to enzyme, uses a phosphate from GTP(ATP) to produce cAMP^
cAMP^
1st protein kinase activated
Subtopic^
Protein Kinase 3,4,5
2nd signal molecule messenger
anti-parallel strands
complimentary base pairings
complimentary base pairings
elongation
large ribosome
P-peptidyl transferase
5-AUG-3'
small ribosomes
E-Exit
release Codon
A-Amino Acyl Transferase
adds Codon
continuous Codon cycle added
initiation
Termination
peptide bonds
RNA is used to produce proteins
Polypeptide
Ribosomes
always in Cytoplasm START+Complete
starts in Cytoplasm
START only
Semi conservative
ORI Origin of Replication
separates two strands of DNA
Keeps DNA strands single
primer binding
Elongation
Termination
make mRNA
occurs in Cytoplasm
mRNA that is ready
for TRANSLATION
occurs in Nucleus
needs to be modified before
it can be translated
RNA Processing
addition 5' G-CAP
splicing
addition Poly AAA tail
initiation
promoter binds to 3'-5' template
Elongation
mRNA made to 5'-3' direction
Termination
mRNA synthesis stops at
the terminator sequence
Transcription Factors
Specific
Activators
Repressors
General
Active CAP
cAMP
Operator Sequence
Repressor
Allolactose
30 nm and 300 nm
300 nm metaphase chromosome
signal recognition particle binds to signal peptide that comes from the ribosome
particle brings ribosome to the ER which is around other proteins
ribosome goes back to translating which feeds the polypeptide through the pore and goes into the ER
signal peptidase cuts the signal peptide off
translation continues and the amino acid enters the ER lumen
completed polypeptide is sent into the ER where it floats around freely
Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, plasma membrane, etc.
Protein transport/Endomembrane Process