History-
Social Science
Curriculum

Content

Economics
12.1.1. Examine the causal relationship between scarcity and the need for choices.
12.1.2. Explain opportunity cost and marginal benefit and marginal cost.
12.1.3. Identify the difference between monetary and non-monetary incentives and how changes in incentives cause changes in behavior.

History
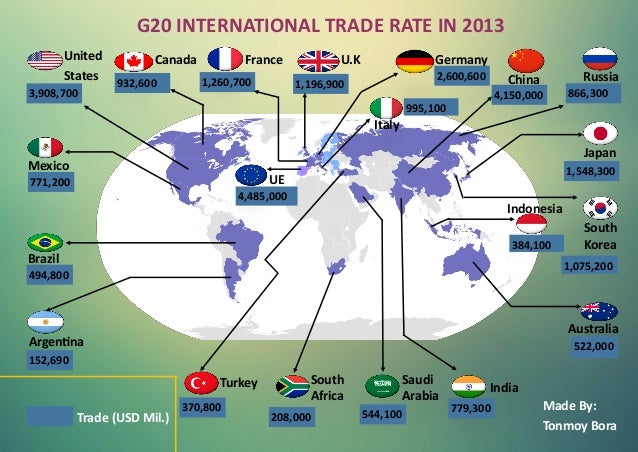
12.6.1 Identify the gains in consumption and production efficiency from trade, with emphasis on the main products and changing geographic patterns of twentieth-century trade among countries in the Western Hemisphere.
12.6.2 Compare the reasons for and the effects of trade restrictions during the Great Depression compared with present-day arguments among labor, business, and political
leaders over the effects of free trade on the economic and social interests of various groups of Americans.
12.6.3. Understand the changing role of international political borders and territorial sovereignty in a global economy.

Geography
12.2.10 Discuss the economic principles that guide the location of agricultural production and industry and the spatial distribution of transportation and retail facilities.
12.4.4 Explain the effects of international mobility of capital and labor on the U.S. economy.
12.6.4 Explain foreign exchange, the manner in which exchange rates are determined, and the effects of the dollar’s gaining (or losing) value relative to other currencies.
By: Angelica Reyes

Literacy
Reading
RH1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, connecting insights gained from specific details to an understanding of the text as a whole.
RH6. Evaluate authors' differing points of views on the same historical event or issue by assessing the author's claims, reasoning, and evidence.
RH9. Integrate information from diverse sources, both primary and secondary, into a coherent understanding of an idea or event, noting discrepancies among sources.

Writing
WHST6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information.
WHST7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.

Inquiry
12.2.6 Describe the effect of price controls on buyers and sellers.
12.2.7. Analyze how domestic and international competition in a market economy affects goods and services produced and the quality, quantity, and price of those products.
12.4.2. Describe the current economy and labor market, including the types of goods and services produced, the types of skills workers need, the effects of rapid technological
change, and the impact of international competition.
12.4.3. Discuss wage differences among jobs and professions, using the laws of demand and supply and the concept of productivity.
12.5.2. Define, calculate, and explain the significance of an unemployment rate, the number of new jobs created monthly, an inflation or deflation rate, and a rate of economic growth.

Government/Civics

Citizenship
12.1.4 Evaluate the role of private property as an incentive in conserving and improving scarce resources, including renewable and nonrenewable natural resources.
12.1.5 Analyze the role of a market economy in establishing and preserving political and personal liberty (e.g., through the works of Adam Smith).
12.3.1. Understand how the role of government in a market economy often includes providing for national defense, addressing environmental concerns, defining and enforcing
property rights, attempting to make markets more competitive, and protecting consumers’ rights.
12.3.2. Identify the factors that may cause the costs of government actions to outweigh the benefits.
12.4.1 Understand the operations of the labor market, including the circumstances surrounding the establishment of principal American labor unions, procedures that unions use to gain benefits for their members, the effects of unionization, the minimum wage, and unemployment insurance.