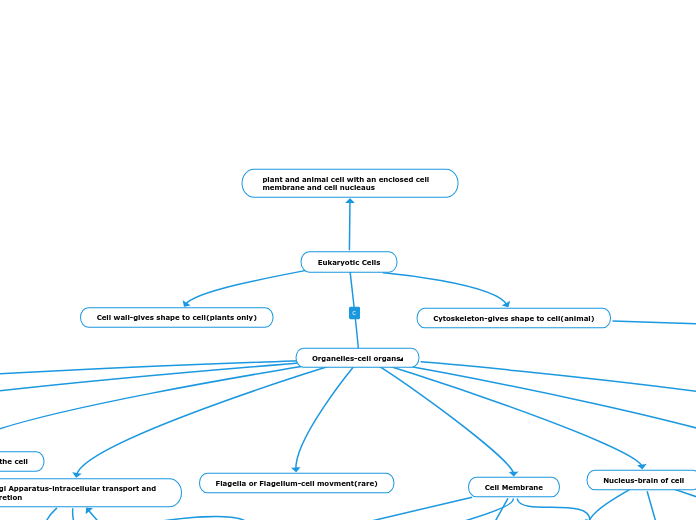
Nucleus-brain of cell
Chromosomes-holder of genetic information
Chromatin-what makes up Chromosomes
DNA-genetic information
Nuclear Membrane-encloses nucleus contains Chromosomes
Nucleolus-a structure surrounding the nucleus during interphase
Ribosomes-made up of RNA, it is responsible for protein synthesis
Proteins-make up Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum-responsible for things like protein synthesis, protein folding, lipid and steroid synthesis.
Rough ER-ribosomes attach
Smooth ER-ribosomes cannot attach
ribosomes leaving in vesicles from ER to cause protein synthesis and combination with products like carbohydrates and lipids
Golgi Apparatus-intracellular transport and secretion
Vacuole-cavity containing fluid(plants only)
Lysosome-waste management
lipids proteins and one enzyme make up Lysosomes
Mitochondria-powerhouse of the cell
Cellular Respiration-chemical reactions that cause glucose to breakdown into ATP causing cell energy production
ATP-energy in the cell
Chloroplast-photosynthesis(plants only)
Chlorophyll-cellular solar panels
Flagella or Flagellum-cell movment(rare)
Microfilaments-the equivalent to muscle contractions
protein
Microtubules-made up of a-tubulin and b-tubulin. also takes part in cell growth and intracellular movement
Diffusion-movement from a high concentration to a power concentration. both solute and solvent molecules move freely
Centriole(only active during cell division in animal cells)
carbohydrates-found in Golgi Apparatus and Cytoplasm
lipids-found in Golgi Apparatus and Cytoplasm
Cytosol-a component of the cytoplasm where organelles and particles are suspended
Vacuoles-space in Cytoplasm
Channel Protein-water and small ions pass through
Gated Channel Protein-a gate must open for a molecule to pass through
Carrier Protein-a protein which has a substance it transports across the cell