Final summative mind map

Lab Equipment
Glassware
Non-Volumetric Glassware Beaker,
and Erlenmeyer Flask
Volumetric Glassware, Graduated Cylinder
other Lab equipment
test tube rack used for holding test tubes.
funnel a funnels main purpose is used for liquids or fine-grained substances into containers with a small opening.
pipette a pipette is used for transporting small liquids
tongs tongs are used to pick up very hot objects
ring stand and ring clamp used for supporting lab equipment
thermometer Used to take temperature in Celsius
Forceps forceps are used for picking up very small objects
Triple Beam Balances & Digital Balances Triple Beam Balances are used to measure masses.
Bunsen Burner the bunsen burner is used Used to heat laboratory samples which are usually very hot
Goggles goggles protect you from dust liquid splash, optical radiation and high heat hazards.
Test Tube Brush is used to clean test tubes
Petri Dish is used for growing bacteria and other diseases
Mortar and Pestle is used to crush bigger objects into smaller ones

WHMIS lesson

WHMIS symbols Workplace
Hazardous
Materials
Information
System
compressed gas means and object is under pressure
Flammable and combustible Examples:
Gasoline
Butane
Aerosol Canisters
Oxidizing material Examples:
Hydrogen Peroxide
Potassium Permanganate
Poisonous & inFectious Examples:
Cyanide
Chlorine Gas
Health hazard Examples:
Asbestos
Lead
Mercury
Biohazardous it can cause diseases Examples:
Medical Waste
Sewage
Decaying matter
Corrosive materials can burn skin Examples:
Bleach
Toilet bowl cleaners
Sulphuric Acid
Explosive is very reactive and an example of this is TNT
Health/ozone layer hazard less serious then health hazards
Environment Examples:
Herbicides
Heavy metals
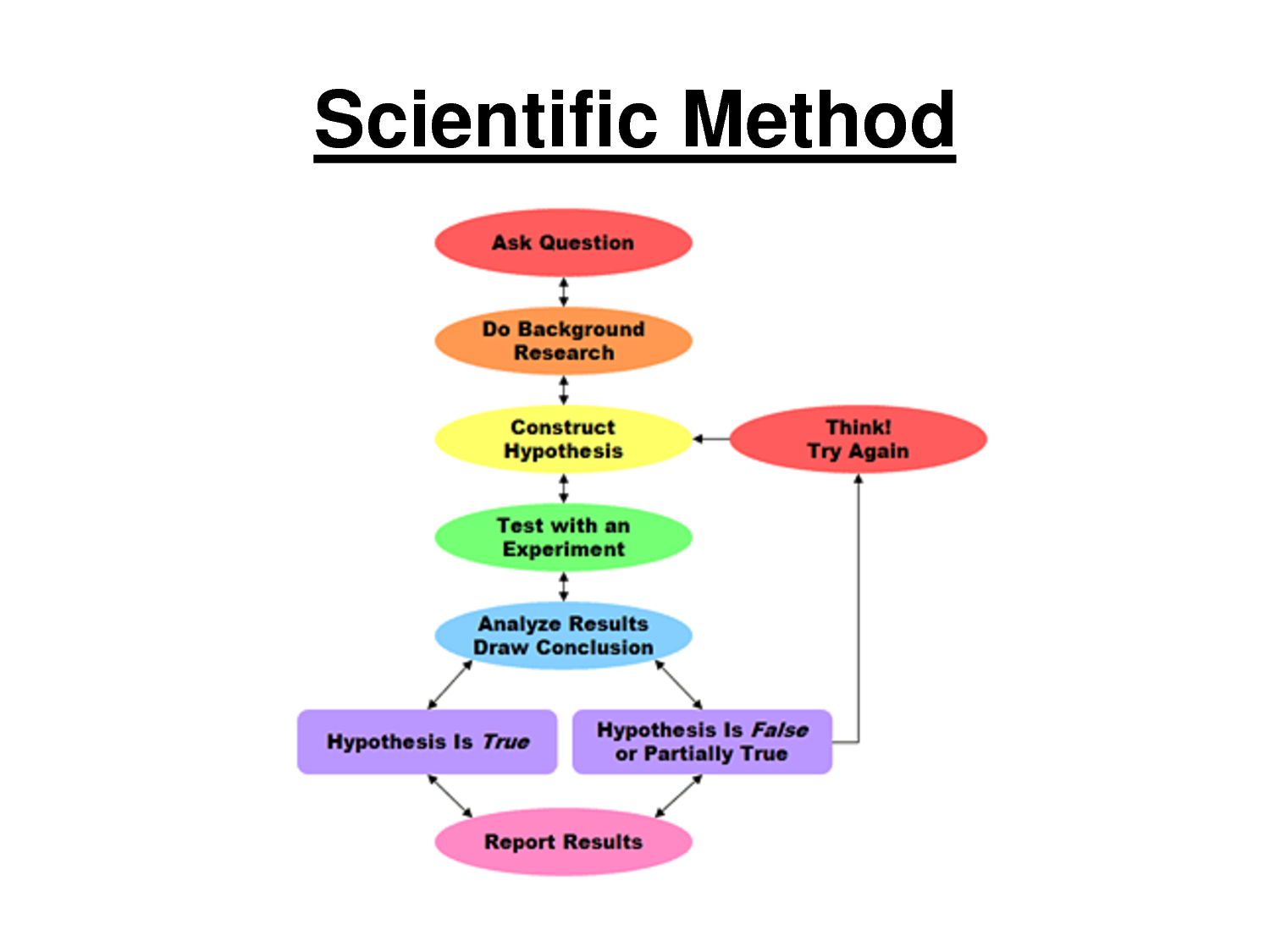
Scientific method
What is the scientific method? Scientific Method involves a series of steps that are used to investigate a natural occurrence.
Problem/question a question or problem that can be solved through experimentation.
Observation/Research Make observations and research your topic of interest.
Hypothesis: try and predict the answer
Experiment: make and create a procedure.
Collect and Analyze Results modify the results and try and make it better
Conclusion conclude your topic

Chemistry
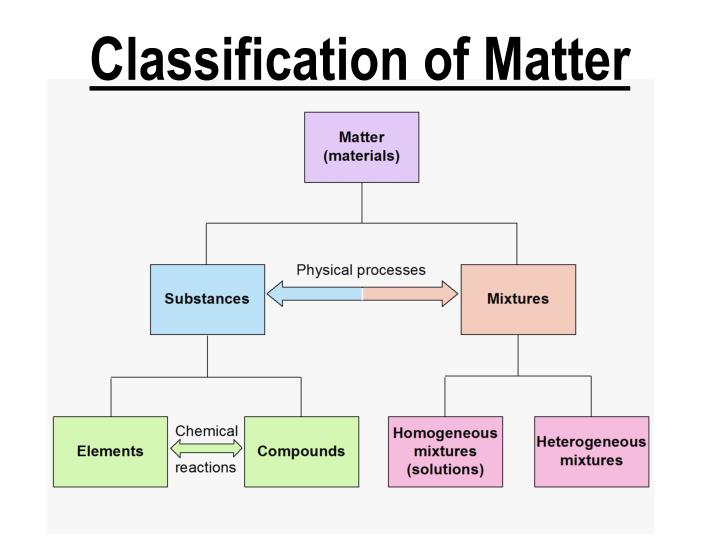
Classification of Matter
What is Matter? matter is what make up all of the universe
Properties of Matter Color
white, green.
Hardness
hard, soft.
Texture
smooth, rough, slippery.
crystal, powder.
Shape
square, no shape.
State of Matter
solid, liquid, gas
Temperature
by observation only!
hot, cold.
Kinds of Matter Elements
Compounds
Mixtures
Compounds are two or more objects chemically combined
Mixture a mixture is a add of two or more substances
Solutions are Some mixtures involve solids being dissolved in a liquid
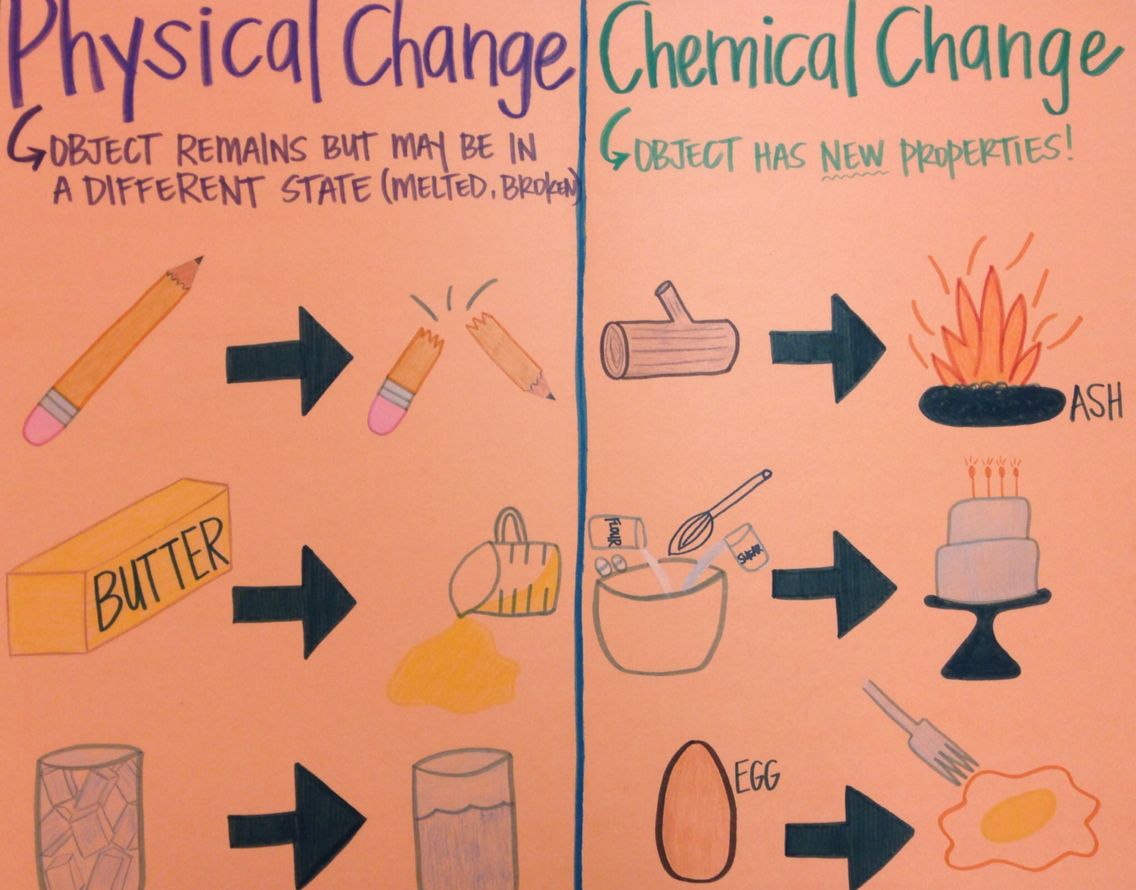
Physical and Chemical Changes
Physical Properties can be changes without changing the composition of matter
states of matter
appearance (size, shape, color)
texture
smell
density
a change in matter which makes one or more substances.
examples of chemical changes:cooking an egg
a nail rusting
burning wood
fireworks
/chemical-properties-of-matter-608337-v33-5b6334d346e0fb0082054666.png)
Chemical Properties
Examples:combustibility, reactivity with oxygen, flammability and reactivity with acids
/TC_608336-examples-of-physical-changes-5aa986371f4e1300371ebebb.png)
Physical Change
A physical change is a change where the form of matter is not changed
Physical change examples Changing the state of matter
the size the temperature and the shape
/123535121-58b5b3173df78cdcd8ac81de.jpg)
chemical reactions
Example Calcium and chlorine react to produce calcium chloride
Acid and base
ACID a compound which dissolves into water to produce hydrogen ions
PROPERTIES OF ACIDS: Sour taste
React with some metals to produce H2
Electrolytes
BASE
A compound that dissolves in water to produce hydroxide ions
PROPERTIES OF BASES: Bitter taste
Slippery and soapy to the touch
Electrolytes

Atoms and Ions
Parts of an Atom Nucleus: the center of the atom
Orbitals (shells): the shells are around the atoms
Ionic bonding or electrovalence Like a magnet - uses positive and negative charge to attract.
Elements elements cannot be broken down into smaller kinds of matter.
Orbital
A three dimensional region around a nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron
Ionic Compounds
What is an ion? Ion: a charged atom or molecule (+ or -)
Cation: positive ion
Anion: negative ion
Why do ions form? atoms tend to lose ,gain and share to fill there valence shell
molecular compounds
a compound formed by two atoms that are of different elements
Polyatomic Compounds
Groups of atoms that are stable and have a net charge
Counting atoms and Balancing
you multiply coefficients with subscripts
parentheses If elements or compounds are inside of then everything behind the subscripts count inside

Indicators
Common Indicators
Red litmus paper,Blue litmus paper, pH paper and Cabbage Juice
Biology

Introduction to the Microscope
Typer of microscopes Light Microscope are models found in most schools.
Stereoscope This microscope allows for two eyes viewing of larger specimens.
Scanning Electron Microscope allows scientists to view a universe too small to be seen with a light microscope
goes through Electron Microscope also uses electrons, but instead of scanning the surface electrons are passed through very small specimens.
Microscope Viewing Field the view can be changed from the microscope
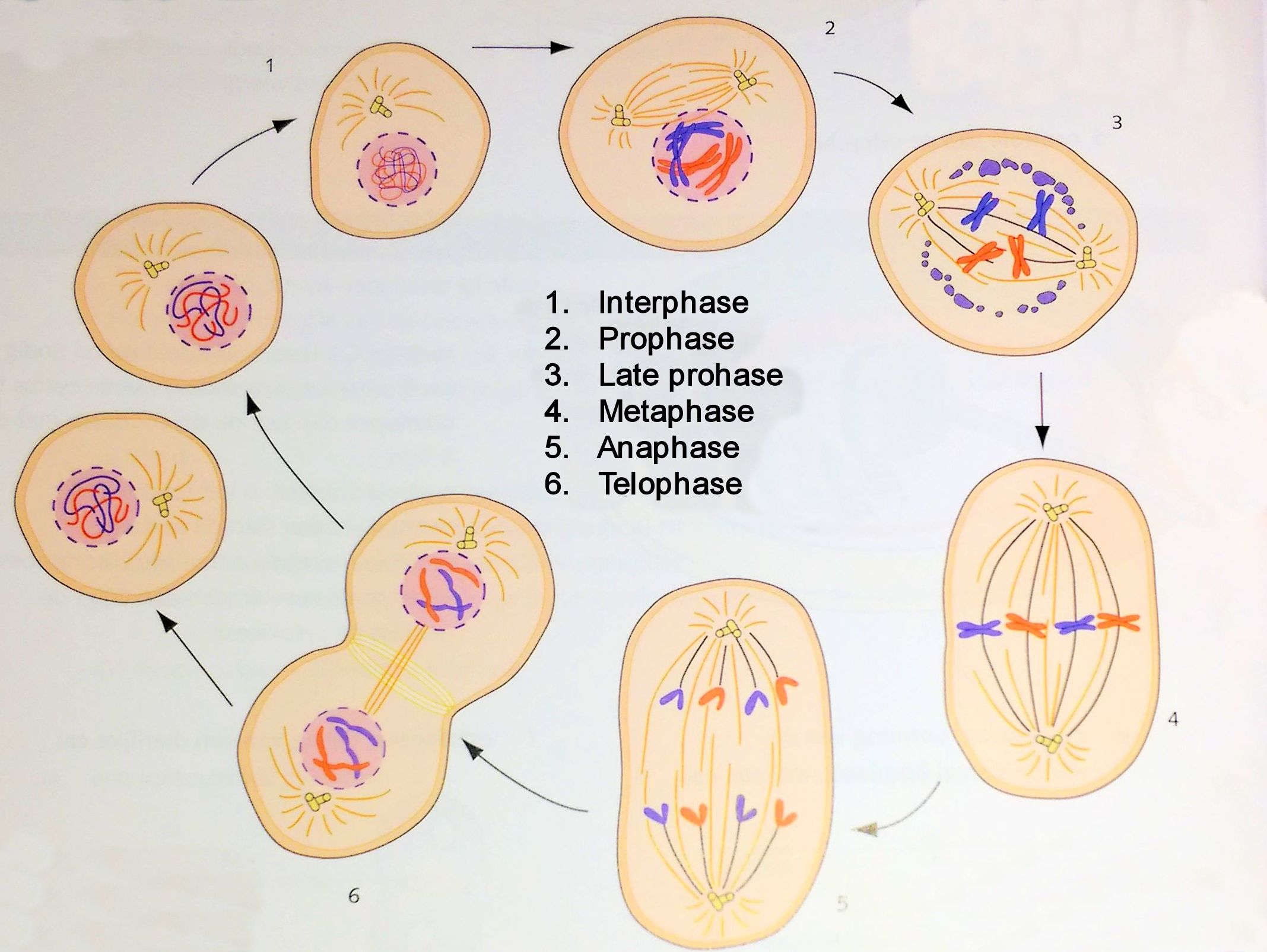
Mitosis
Why do cells divide? ells divide because when you skin your knee, cells divide to replace old, dead, or damaged cells.
How do cells divide? Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei.
interphase cell grows to its mature size, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares to divide into two cells.
Prophase Chromosomes and Spindle Fibers Appear
Chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes.
Metaphase Chromosomes Line Along Equator
The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell.
Anaphase Chromosomes Split and Move to Opposite Ends
The centromeres split and the two chromatids separate.
Telophase Cytoplasm Begins to Divide
The chromosomes begin to stretch.
Cytokinesis Cytoplasm Divides The cell membrane pinches in around the middle of the cell.

Specialized cells
What is a specialized Cell? Plants and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular.
Palisade Cell Designed for Photosynthesis
Red Blood Cell Designed to carry oxygen
Found in blood.
/human-digestive-system--artwork-136811327-599a0ae603f4020011c410a6.jpg)
The Digestive System
the digestive system breaks down food
Salivary Glands breaks down starch into sugars
Esophagus moves food to the stomach
Stomach Lining Mucus prevents stomach from digesting itself
Pancreas breaks down fat
Small Intestine breaks down nutrients
Large Intestine reabsorbs water, contains bacteria to aid in digestion

Circulatory System
main parts Heart,
Vessels, and Blood
blood can be separated into 3 layers
White Blood Cells protects from bacteria
Platelets helps damaged blood cells
Blood Vessels 3 main parts - arteries
- veins
- capillaries
Arteries large vessels with a small diameter
Veins large small wall vessels with a large diameter
Capillaries large vessels

Cell Organelles
Two cell types Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes No Nucleus
No Membrane bound organelles.
Eukaryotes Have a nucleus
Have membrane bound organelles
the 2 Main Types of Eukaryotic Cells plant cell and animal cell
Cell Membrane
Surrounds the cell and decides what comes in and out
Nucleus Control center of the cell
Stores DNA
Ribosome Smallest organelle
NOT surrounded by a membrane
Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER: covered with ribosomes; site of protein synthesis
Smooth ER: NO ribosomes; it makes hormones & lipids
Golgi Apparatus Delivery system of the cell
Mitochondria Powerhouse” of the cell
Site of cellular respiration
Cancer
Canadian Cancer Statistics show that 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer
Cancer can develop anywhere in the body, and at any age.
What is Cancer? Benign (non-cancerous)
Does not spread; though it can eventually become malignant in some cases.
Malignant (cancerous)
Has the potential to spread to other parts of body.
Secondary Tumors To form a secondary tumour, a tumour cell needs to leave the vessel system.
Cancer treatment Three basic treatments: surgery to remove the tumor, and radiation or chemicals chemotherapy to kill actively dividing cells.
Xrays Most common medical imaging.
Fluorscopy Technique using a continuous beam of x-rays to show the movement of organs.
Radiotherapy Radiotherapy is the use of x-rays to treat cancer.
X-rays damage the DNA of the cancer cells, either killing them or preventing them from multiplying.
CT-scans Also known as computer assisted tomography scans (CAT scans).

Human Body Systems
How is the body organized? Each specific cell is grouped with other cells similar in structure and function to form tissues
Skeletal System Major Parts
Bones
Joints
Marrow
Muscular System Major Parts
Skeletal,
Smooth, and
Cardiac muscle
Cardiovascular System major Parts
Blood
Heart
Blood vessels
Nervous System Major Parts
Brain
Nerves
Spinal cord
Digestive System Major Parts
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Liver
Pancreas
Intestines
Integumentary System Major Parts
Skin
Hair
Nails
Excretory System Major Parts
Kidneys
Liver
Lungs
Bladder
Rectum
Anus
Urethra
Lymphatic System Major Parts
Lymph nodes
Thymus
Spleen
Respiratory System Major Parts
Nose
Mouth
Lungs
Trachea
Endocrine System Major Parts
Pancreas
Pituitary gland
Thyroid
Ovaries
Testes
Many others
Immune System Major Parts
White blood cells
T-cells
Antibodies
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Bone marrow

Respiratory system
Functions:
Supply oxygen to the cells
Remove carbon dioxide from cells
Defend body against invasion of microorganisms
Pharynx path for food & air
Epiglottis Prevents food from entering the trachea when eating
Larynx Air released from the lungs causes the vocal cords to vibrate & produces sound
Trachea makes a passage way for air
Ribcage protects other organs
Diaphragm moves and changes the volume of the ribcage