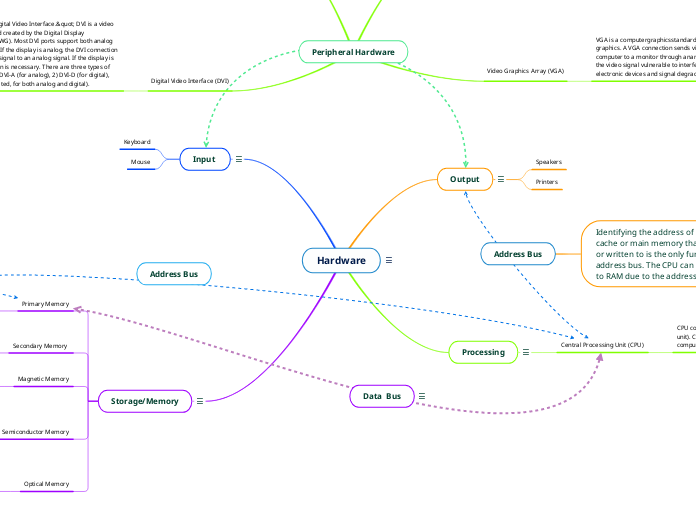
The term "hardware" separates the physical components of a computing system from "software," which is made up of written, machine-readable instructions or programmes that specify what to do and when to execute physical components. For example, Monitor, Mouse, etc.
An output device is any hardware component used to transmit data from a computer to a user or other device. The majority of output peripherals are typically designed for human usage, thus they take the computer's processed data and convert it into audio, video, or physical copies.
Speakers
Printers
The four primary functions of a processor are fetch, decode, execute and store. Fetch instructions from memory.Decode instructions into computer language.Execute the instructions.Store the result to memory.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
CPU consists of ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) and CU (control unit). CU interprets and directs the instructions. ALU does computations.
Arithemetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Performs arithmetic, comparison, and other
operations. Arithmetic operations include +, - , x, /
Comparison operations include >, <, =
Control Unit (CU)
Directs and coordinates most of the operations in the computer. Like a traffic cop: it interprets each instruction issued by a program and then directs the action to be carried out
Data entered into or received by a computer is referred to as an input. This could involve the user tapping a touch pad, clicking a mouse to pick an item on the screen, or pressing a key on a keyboard.
Keyboard
Mouse
A computer's ability to store information, either temporarily or permanently.
Primary Memory
Volatile Memory (except ROM) that is directly accessed by the CPU. Examples: RAM, Cache, Registers.
Secondary Memory
Non-Volatile Memory that is used to store data and instructions for later retrieval. Examples: HD, SSD, flash drive, floppy disk etc.
Magnetic Memory
Technology that uses magnetic field to record data on disk . Floppy disk, Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
Semiconductor Memory
Technology that uses silicone or other semiconductor to record data on an integrated circuit. Example; RAM, cache, flash drive, SSD.
Volatile Memory
Temproary storage that is lost of power is off. Examples: RAM, Cache, Registers.
Non-Volatile Memory
Type of memory that stays stored even if power is off. Examples: ROM, HDD, Flash Drive, etc.
Optical Memory
Technology that uses laser to record data on disk. Example; CD, DVD, Blue Ray.
Primarily used for streaming media (video & sound) from computer to television or projector or DVD/blue ray player. HDMI connectors are available in three sizes: standard, mini and micro.
USB ports allow Peripheral Devices to be connected to each other with and transfer digital data over USB cables. Peripheral devices such as cameras, camcorders, printers, scanners, and more.
VGA is a computergraphicsstandard for displaying color graphics. A VGA connection sends video signals from a computer to a monitor through ananalogconnection, making the video signal vulnerable to interference from other electronic devices and signal degradation over long cables.
Stands for "Digital Video Interface." DVI is a video connection standard created by the Digital Display
Working Group (DDWG). Most DVI ports support both analog and digital displays. If the display is analog, the DVI connection converts the digital signal to an analog signal. If the display is digital, no conversion is necessary. There are three types of DVI connections: 1) DVI-A (for analog), 2) DVI-D (for digital), and 3) DVI-I (integrated, for both analog and digital).
The data bus is in charge of bringing the data from the primary memory to the CPU