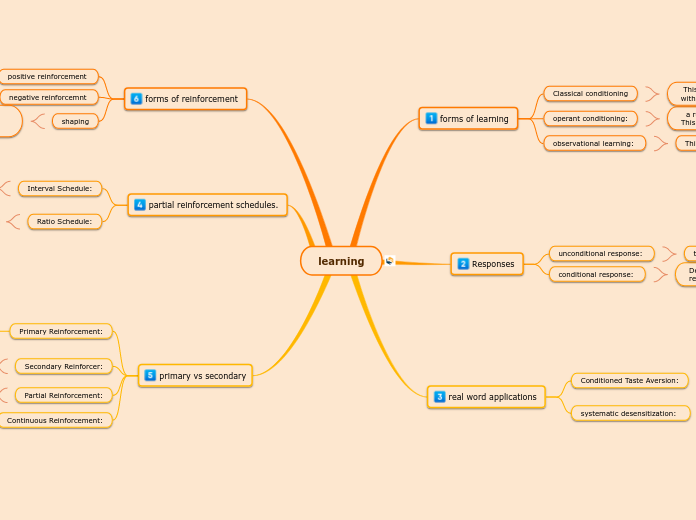
Conditioned Taste Aversion:
systematic desensitization:
partial reinforcement schedules.
Stimulus that is reinforcing its own right. this is mostly related to biological needs. such as food water or sex
Continuous Reinforcement:
This is when neutral stimuli become associated with a stimulus that produces a behavior/action.
a relation between behavior and consequence. This can be negative or positive reinforcement
This is learning through watching others.
Depends on something else, and has
requirements
the response is automatic.
its a type of classical conditioning that causes animal and humans to assoicate food with illness.
this is when a feared stimulus is paried with a different stimulus that causes an incompatible emotional response
Stimulus that has acquired its own value. like when a reinforcer is paired with another to get an action ,
this is when you reinforce only some behaviors. this is usually after the acquisition phase.
this is when to reinforce all the responses. you basically reiforce a behavior every single time its done .
fixed interval : when the time of reinforcement is always the same time
variable interval: the time is the same ON AVERAGE
fixed ratio: the number of action that require a reinforcement is always the same
variable interval:
responding to an action with a positive action
responding to an action with a negative action
take small steps to get to a goal or specific actions doesnt have to be only positive or negative response.