Negative Effects of Computers:
The Environment
By: Isabella Gu
Production
Fossil Fuel & Chemical Consumption
Harmful chemicals/pollutants are
released into the atmosphere.

Poses a threat to all
inhabitants in vicinity.
Components of Phone
Phone contains gold, silver,
platinum, and palladium.

Phone batteries are
made from lithium-ion,
as well as cobalt.

1/2 of the world's supply
of cobalt is sourced from
Democratic Republic
of Congo.

Child labor is often used.
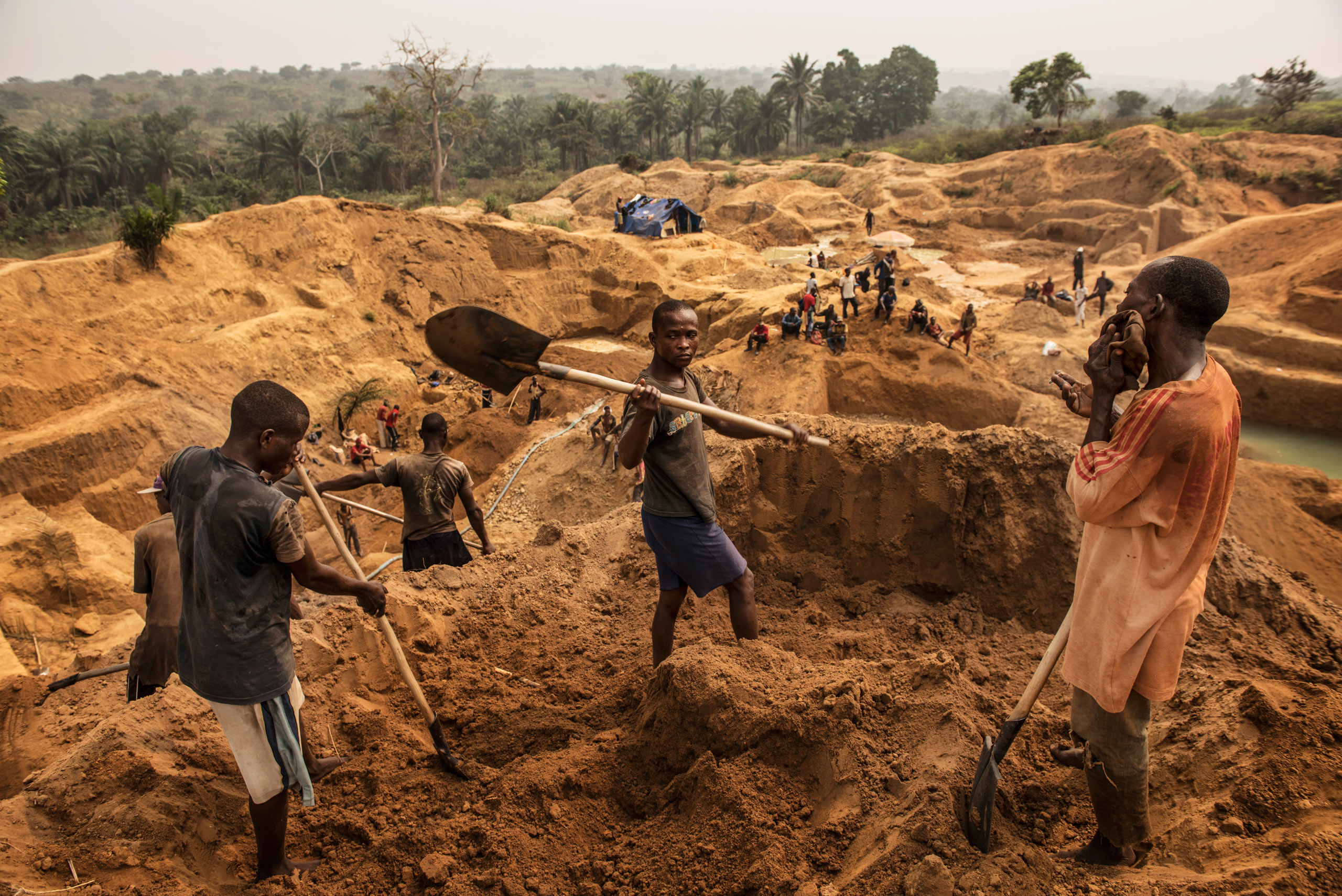

Even if child labor is not
used, mining conditions
are very poor and there
is a lack of proper
protective equipment.
Waste
Landfill Waste
With rapid releases of the
newest models of phones
and computers, obsolescence
rates of older models has
significantly increased.

2018: Apple admitted to
deliberately slowing down
older iPhone models. Their
reasoning was that they
wanted to extend the life
of older phones as their
batteries worsened.
Contributes to consumers' desire to
buy the latest models of phones
and computers when they see their
device performance in declination.
People, especially youth,
want to change their phones
frequently to stay up to date
with trends and feel cool.
Increased demand for new
technologies results in more
waste ending up in landfills.

50 million tons of technological
waste is generated each year.
Only 20% of this waste is
properly recycled.
Location of landfill waste ties in
with socioeconomic impacts.

Most electronic and electrical
waste gets sent to landfills
in developing or poorer
countries (ex. Ghana, India,
Vietnam, Philippines).
As a result, the pollution
worsens in these countries,
especially considering general
waste from other countries is
already constantly being exported
on top of electronic/electrical
waste.
Potential Solutions
Trade-in programs.
Helps with electronic waste
that results from people
upgrading their electronics.
Certified e-waste haulers/recyclers.

Individuals can take broken
electronics and drop off at
specified centers (ex.
government building,
organization).
Electricity
Electrical Grid Strain
2019: 1.3 billion people in the world
possessed personal computers, and
164 million people collectively in the US.
PC typically uses up 764 kilowatts of
power each year.

764 kilowatts of
power is more than
the amount of power
required to power a
fridge.
Inevitable for power plants
to be strained by the ever so
growing demand of energy.
Production of Electricity
Information technology takes up 2%
of the world's net energy consumption.
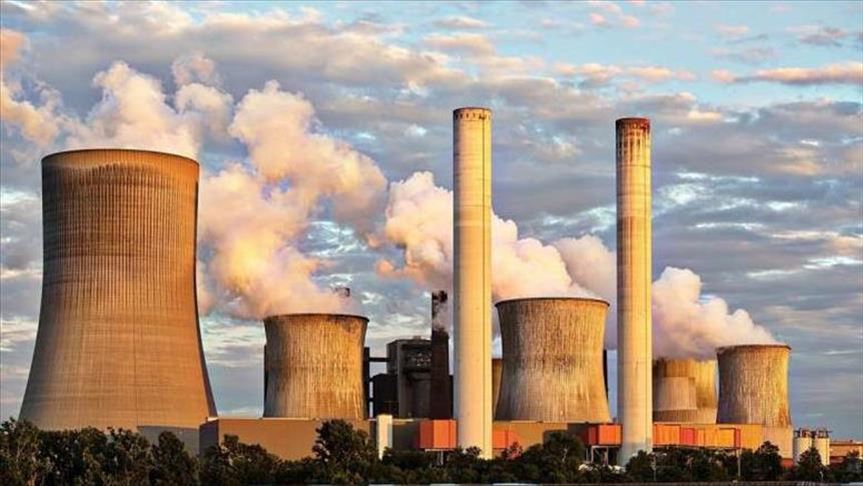

Production of energy &
electricity is often through
means that are not
environmentally friendly.
Traditional methods of electricity
generation (ex. burning fossil fuels)
emit millions of tons of greenhouse
gases each year such as methane.
Alternative Methods
Green energy alternatives can
also create negative impacts
for the environment.
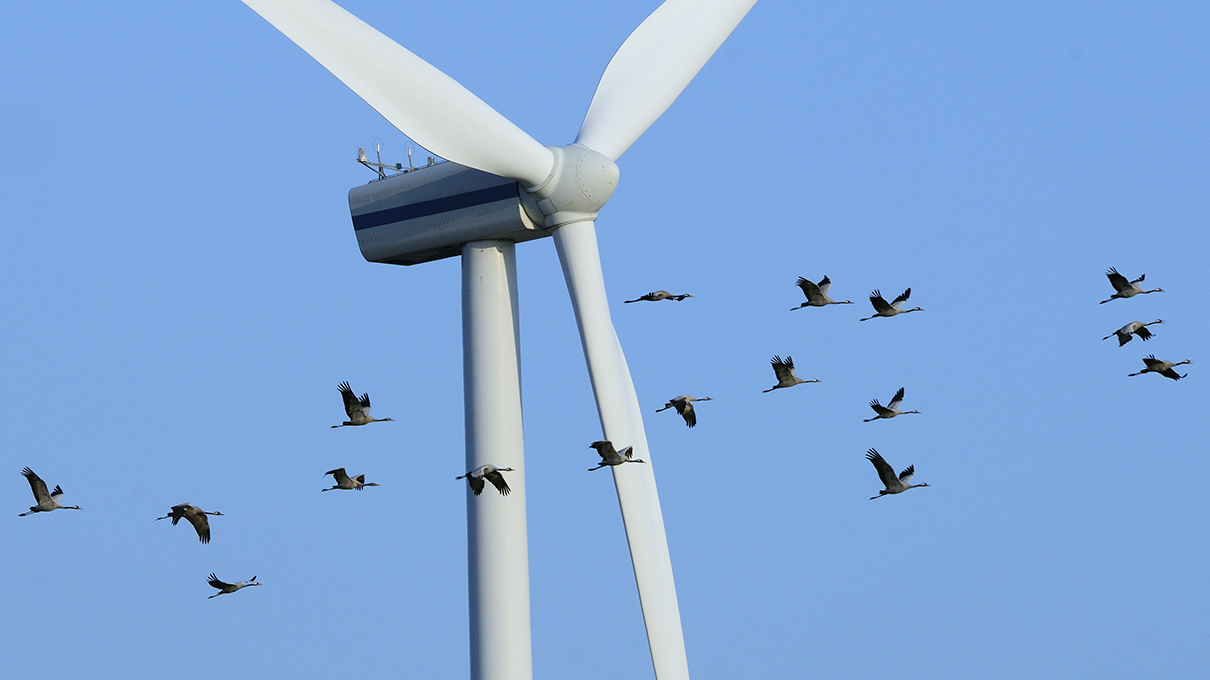

Turbines in wind farms
cause frequent collisions
in migrating birds.
Energy Wastage
Many people forget to turn off
their computers after work.

Americans were already
wasting on average $2.8
billion dollars per year on
energy wastage. This was
10 years ago.
Pollution & Contamination
Air Pollution
Incorrect disposal methods
of electronic waste causes
dust particles/toxins to
be released.

Air pollution is a threat
to respiratory health.
Even when location in which electronic
waste is burned is not close in proximity
to overall population, fine particles that
are released have the ability to travel for
thousands of miles.
Soil Contamination
Improper/illegal way of disposing
electronic waste causes heavy metals
and flame retardants to seep into
the soil.
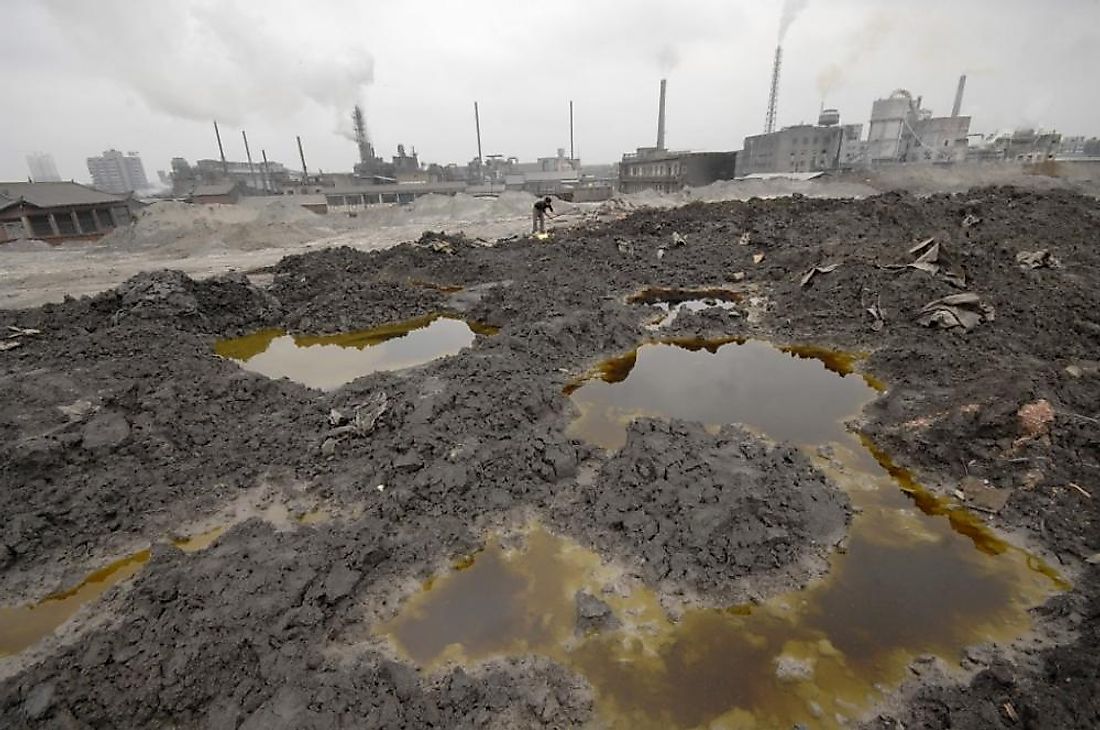

Contaminates groundwater,
as well as crops that are planted
in or near the area. Crops are
prone to absorbing toxins.
Pollution generates illness in plants
and can decrease the crop yield. Once
soil is infested with pollutants, it stays
for a very long time.
Water Contamination
Interconnected with soil and
air pollution.

Heavy metals that initially contaminated
the soil will travel even further underground,
until it reaches groundwater.
Continues moving onward, along
with ponds, streams, rivers, lakes
(other bodies of water).
When contamination occurs in
greater bodies of water, acidification
and toxification arise.
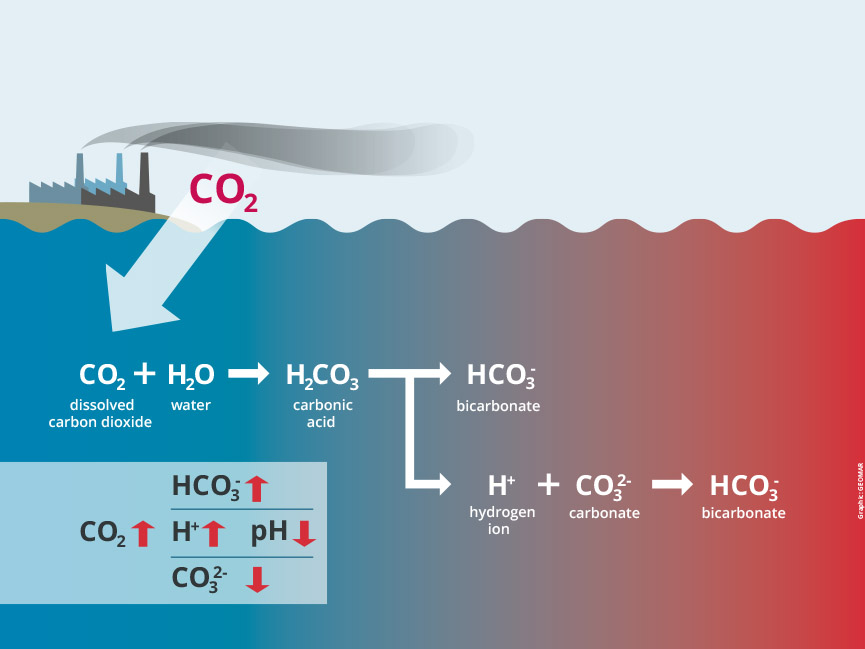
Acidification refers to the
reduction in pH in bodies of
water due to rise in levels of
CO2 (pollution).
Potent enough to kill marine
and freshwater organisms,
therefore disturbing biodiversity
and wreaking havoc in ecosystems.