Physical Geography Map

Geologic Time
Era's
Precambrian
Began 4600 million years ago and ended 570 million years ago
It lasted 4.6 billion years, and took up 87.6% of geologic time
Geological Events
Canadian Shield, Brazilian Shield, and the Australian Shield were all formed.
Biological Events
The first multi celled and single celled organisms were formed on earth.
Paleozic
Began 570 million years ago and ended million years ago
It lasted 325 million years, and took up 7.06% of geologic time
Geological Events
Large parts of North America were covered by shallow seas.
Also the Appalachian Mountains were formed.
Biological Events
This was the age of amphibians and fish...
...the first insects
...and the first plants and animals
There were lots of large swamps...
Coal formed from this vegetation.
Mesozoic
Began 245 million years ago and ended 66 million years ago
It lasted 180 million years, and took up 3.89% of geologic time
Geological Events
The Rocky Mountains were formed. Along with the Innuitian Mountains.
At this point in time, there were still shallow seas in the interior of North America.
Biological Events
This was the age of reptiles (dinosaurs)...
...the first flowers
...and the first birds
Cenozoic
Began 66 million years ago and hasn't ended
It has been about 66 million years, and it has taken up about 1.43% of geologic time.
Geological Events
Ice sheets cover some of North America.
Biological Events
This is the age of mammals...
... Humans started to(and now are) develop

Soil
True Soil
To make true soil you need all 4 of these...
Minerals
Air
Moisture
Bacteria (Organic)
Top Soil
The top most layer of soil
Humus

"Nutrient rich" soil made up of compost
Leaching
Is when all of the "left over" precipitation sinks down below the surface and holds moisture for all of the bigger plants.
Subtopic

Rocks
Rocks
Sedimentary
Clastic
Conglomerate
Breccia

Sandstone
Slitstone
Mudstone
Shale
Chemical

limestone
Qolostone
Evaporites
Biological
Coal

Chert
Igneous
Intrusive
Gabbo
Diorite

Gandorite
Granite
Extrusive

Basalt
Andesite
Dacite
Rhyolite
Metamorphic
Foliated

Slate
Schist
Gneiss
Non-Foliated
Quartzite

Marble
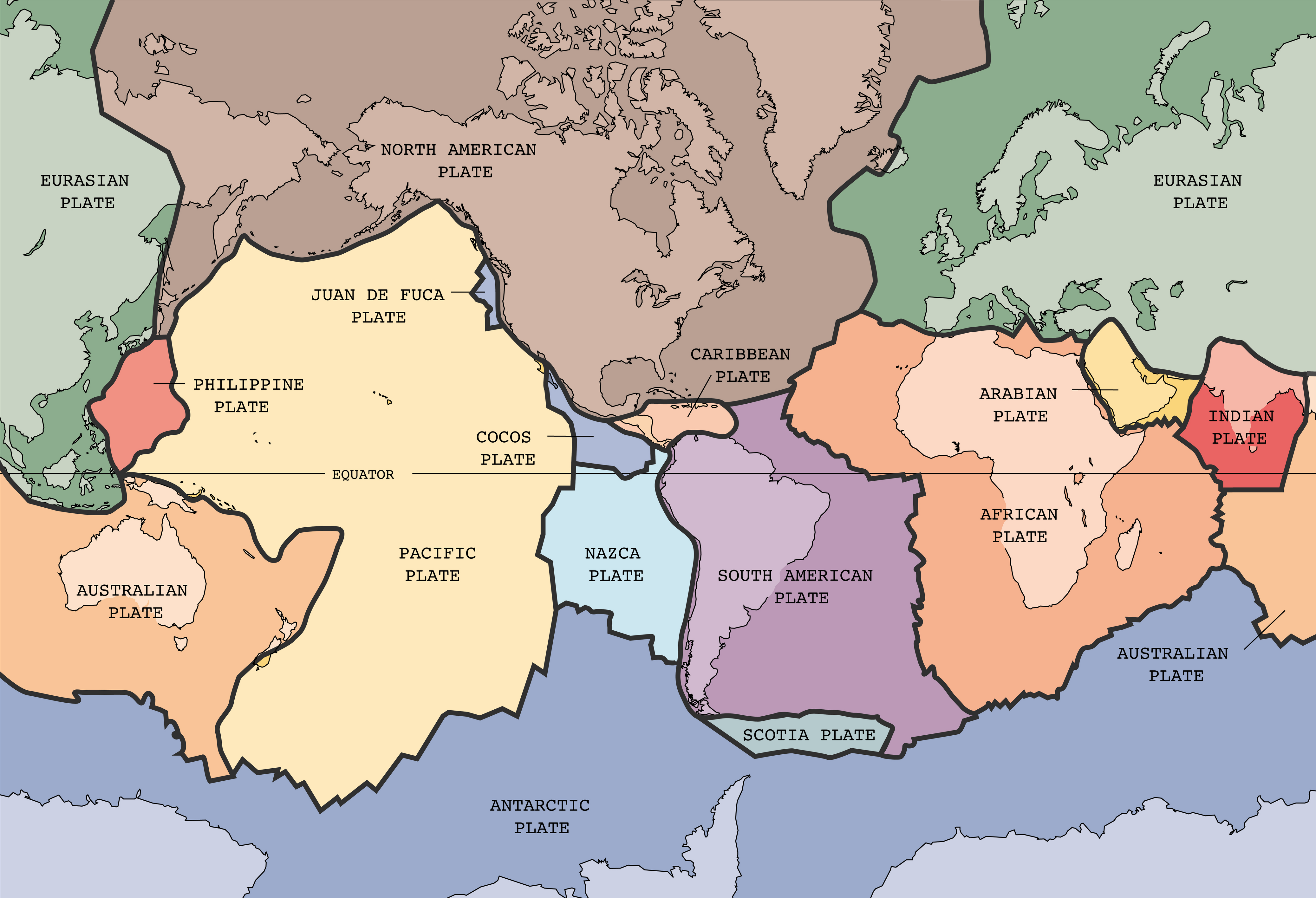
Plate Tectonics
Who?
Alfred Wegener, a German scientist back in the early 1900's,
(1905-1930) born in 1880, died in 1930, came up with the original theory about plate tectonics.
Theories?
Alfred Wegener thought that all of the countries used to be connected.
1. All of the countries fit together like puzzle pieces
2. There is fossil remains of different plants and animals in the wrong countries they are supposed to be in
3. Mountain ranges (in different countries) fit together as if connected a long time ago
What?
There are about 20 different tectonic plates on earth.
There is both land and water on very thick layers of molten rock. (700 kilometres beneath earth's crust)
Where?
The plates move along special boundaries
Divergent
Move away
Convergent
Move toward one another
Transform
Slide past
Pangea
Pangea was the last super continent the world had and it broke apart 50-200 million years ago.
Scientist at Yale believe that the next super continent will be formed in the next few hundred years.
They also believe that the plates are moving because of magnetic forces that are pushing and pulling them together

Climate
Factors that influence climate
Latitude
Extends from a great distance - distance away from the equator,means more or less sunlight, means different temperature.
Ocean Currents
Water takes longer to heat up and cool down - changes temperature on land.
Wind
Westerlies and eastward winds - colder where wind is blowing.
Elevation and Relief
Refers to elevation of earths surface - farther up you go the colder it gets - because the atoms in the air are farther spread apart.
The difference between weather and climate
Weather= mixture of precipitation, cloud cover, and winds
Climate= average precipitation and weather conditions

Natural Vegetation

Natural Vegitation
Is when humans do nothing to help the vegetation
Picking, Planting, Trimming, Watering, Fertiliser, etc...
NO:
Trees
Deciduous

Trees with leaves
Coniferous

Trees with needles
Better able to handle harsh conditions

Land Form Regions
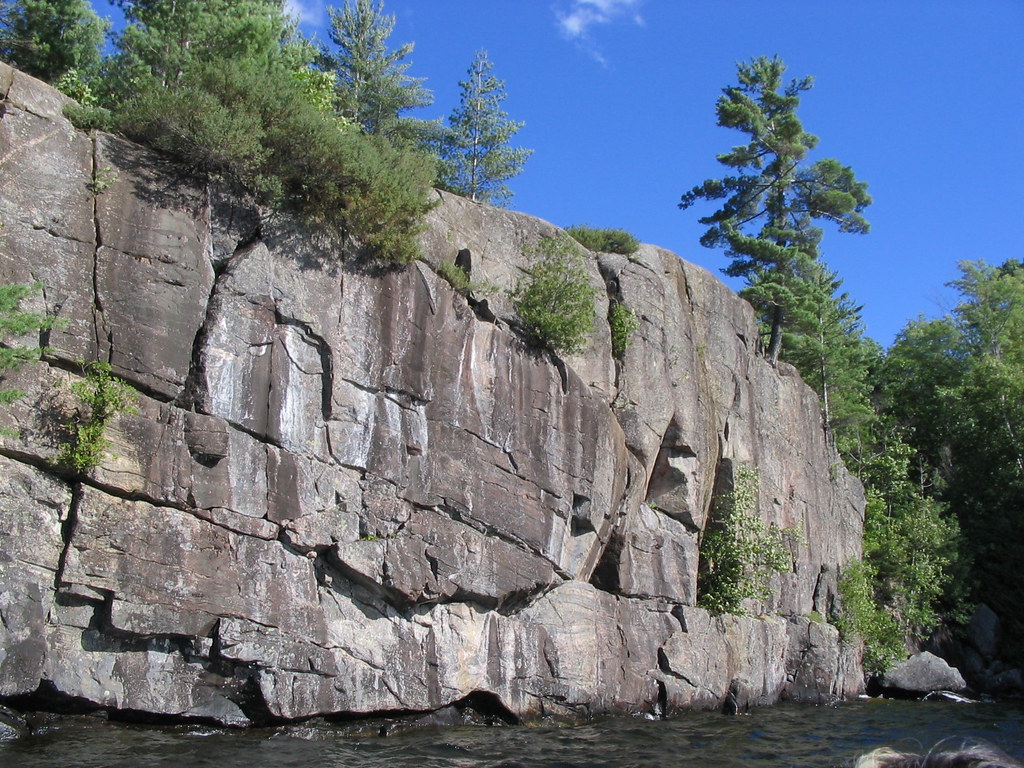

Canadian Shield
General Appearance
Fairly Flat
Rocky
National Park
Pukaskwa
Outstanding Natural Features
"Dotted" with lakes and rivers.
Multiple spots with exposed granite.
Activities
Canoeing and Kayaking
Portaging
Backpacking
Suspension Bridge

Interior Plains
General Appearance
Fairly Flat
Some Small Hills
National Park
Riding Mountains
Outstanding Natural Features
Escarpment
Lakes with islands and beaches.
Activities
Swimming
Camping
Horseback Riding

Great Lakes/ St.Laurence Lowlands
General Appearance
Flat Plains
Rolling Hills
Glacial Hills
Deep Valleys
abundance of water
Natural Park
Point Pelee
Outstanding Natural Features
Very Small
Part of lake Erie
Composed of large marsh
Activities
Butterfly and Bird watching
Swimming/Skating
Canoeing/Kayaking

Arctic Lowlands
General Appearance
Somewhat flat/Some hills
Surrounded by water
National Park
Wapusk
Outstanding Natural Features
Subarctic Climate
Large marsh area
Activities
Polar bear watching
Snowshoeing
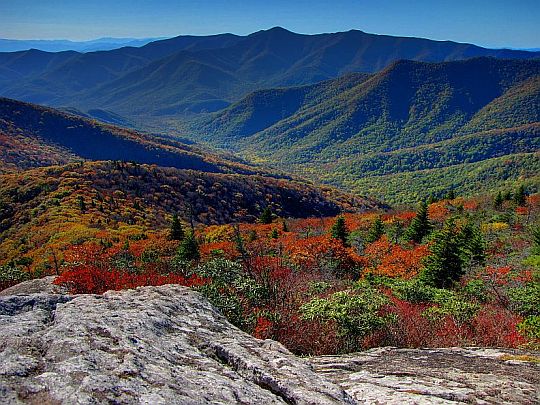

Appalachians
General Appearance
Rounded Mountains
and hills
Wide glacial hills
Long bays
National Park
Cape Breton Highlands
Outstanding Natural Features
All three types of rocks are visible
Mountains "rolling" into the sea
Activities
Camping
Seal and whale watching

Innuitian
General Appearance
Mountains surrounded by water
Covered by glacial Ice
National Park
Ellesmere Island
Outstanding Natural Features
Covered in frost
"Frozen Desert"
Ice is over 100 00 years old
Very big
60x The size of Toronto
Activities
Backpacking
geo and eco studies
Extreme sports

Western Cordillia
General Appearance
Mountains
Sharp, ridged, and pointy
Some valleys
National Park
Banff
Outstanding Natural Features
Oldest national park
Hot springs
Rockies
Activities
Ski
Snowboard
Mountain biking
Rock Climbing
