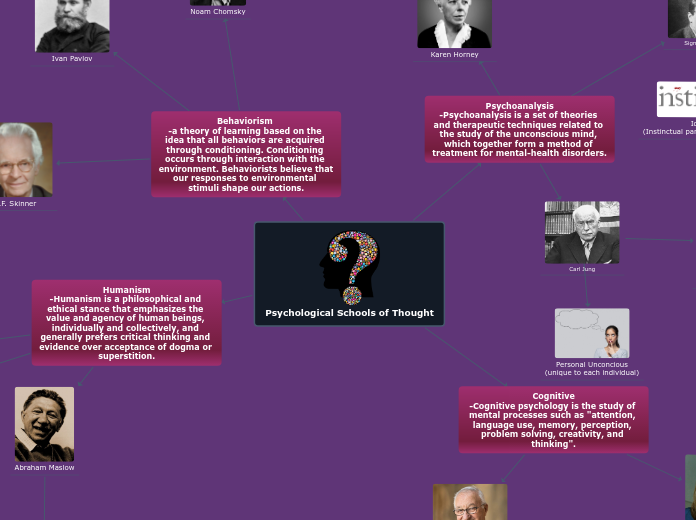
Psychological Schools of Thought
Behaviorism
-a theory of learning based on the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning. Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment. Behaviorists believe that our responses to environmental stimuli shape our actions.

Ivan Pavlov

Conditioning
Experiment

B.F. Skinner
Operant Conditioning

Skinner's Box

Noam Chomsky

States we learn language
through association, imitation,
and reinforcement.
Psychoanalysis
-Psychoanalysis is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques related to the study of the unconscious mind, which together form a method of treatment for mental-health disorders.

Sigmund Freud

Id
(Instinctual part of the mind)
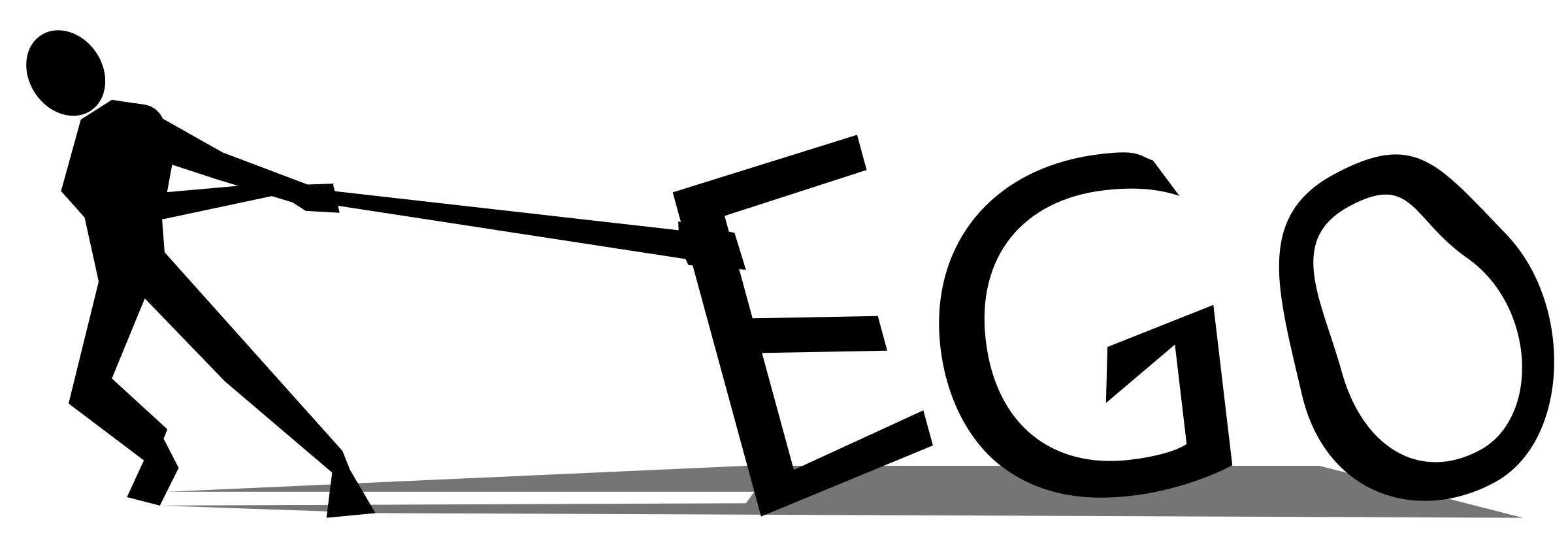
Ego
(Rational part of the mind)

Superego
(Morals of the mind)

Karen Horney

Founder of feminine psychology

Carl Jung

Personal Unconcious
(unique to each individual)

Collective Unconscious
(inherited pool of memories from
our ancestors)
Humanism
-Humanism is a philosophical and ethical stance that emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, individually and collectively, and generally prefers critical thinking and evidence over acceptance of dogma or superstition.

Abraham Maslow

Self-Actualizing

Viktor Frankl

Logotherapy
(A form of psychotherapy that
tries to help the patient find the
meaning to their life)

Carl Rogers

The Client-Centered Model
(focuses on the potential of
each person to realize their
own growth in self-awareness
and self-fulfillment.
Cognitive
-Cognitive psychology is the study of mental processes such as "attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and thinking".

Albert Bandura

Studied how people
learn behavior by
watching and imitating
others

Bobo Doll Experiment

Elizabeth Loftus

False Memories

Mall Story Experiment

Laura Melnyk's book
"The development of
Metasuggestibility in Children"
provides truth to Loftus' theory