Sodium azide=> Sodium + Nitrogen
Technology
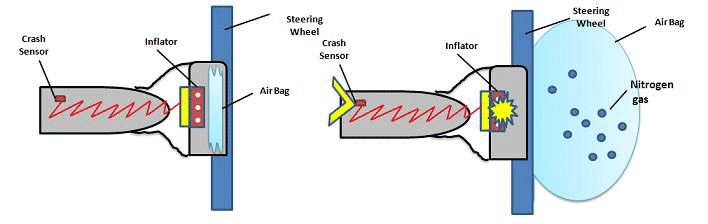
Types of technology in reaction: An electrical charge triggered by automobile impact causes sodium azide to explode and convert to nitrogen gas inside the airbag.
How technology makes reaction better: It makes the reaction better because airbags are triggered by sensors when a car is crashed to potentially protect one from dying.
Subtopic
Intro
NaN₃ => Na + N₂
Balanced: 2NaN₃ => 2Na + 3N₂
Purpose: The chemical at the heart of the airbag reaction is called sodium azide, or NaN3. CRASHES trip sensors in cars that send an electric signal to an ignitor. The heat generated causes sodium azide to decompose into sodium metal and nitrogen gas, which inflates the car's airbags.
Properties: Sodium: soft metal, reactive and with a low melting point, sodium is the most important of all the alkaline metals, sodium reacts quickly with water.
Nitrogen: nonmetallic, colorless, odorless and tasteless, nitrogen is slightly lighter than air
Sodium azide: Sodium azide is a colorless crystalline solid, it decomposes and can explode, sodium azide is highly soluble in water and other polar solvents.
Is it a part of another reaction: reaction of sodium and nitrogen is a part of the reaction of a car crash
Society
product: Sodium and Nitrogen
Is the product useful: Yes because when sodium azide decomposes into sodium metal and nitrogen gas, which inflates the car's airbags.
Annual production: Airbags
Health concerns: Airbags may injure people. Sodium azide is a rapidly acting, potentially deadly chemical that exists as an odorless white solid.
Government's policies: Government regulates sodium azide for the use of airbags
Environment
How are they disposed: depending on the accidents airbags can be fixed and disposed of
Sodium azide is toxic
Where do the get the reactants from: the reactants are the products
Making it is not harmful but when released it is
Are there environmental impacts related to the use of energy: heat may affect the sodium azide. When there is high air temperature the airbag might inflate without a warning