ACCOUNTING
Fundamental Accounting practices
Ledger’s
Trial Balance
Income Statement
Net Loss
Net Income
Expanded ledger
O.R.E.O
DR/CR Theory
T Accounts
Debit/Credit
Debit = left
Credit = Right
account Balances
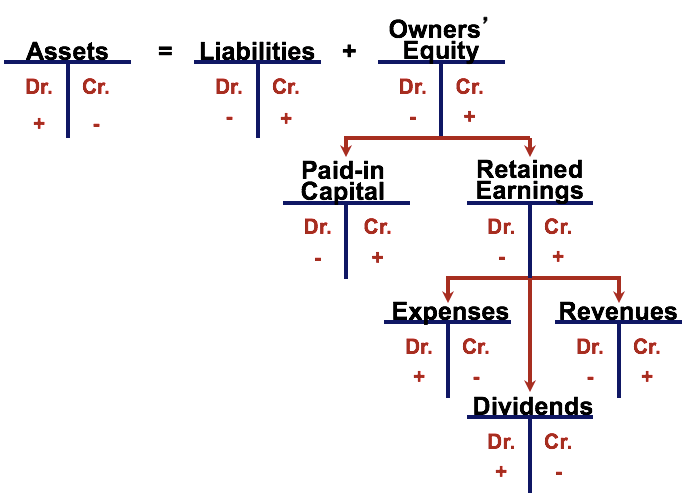
Assets = debit; increase credit; decrease
Liabilities & owner’s equity = credit; increase debit; decrease,
exceptional Balances
Asset = credit
Liabilities & Owners equity = debit
Balance sheet
Steps to creating balance sheet
1. Determine the Reporting Date and Period
2. Identify Your Assets
3. Identify Your Liabilities
4. Calculate Shareholders' Equity
5. Add Total Liabilities to Total Shareholders' Equity and Compare to Assets
Balance sheet conventions
order of liquidity
Order in which you need to pay first
Fundamental accounting equation
owner’s equity
Owner's Capital, Revenue, Drawings, Expenses
Assets
Current assets and Fixed Assets, Liquid-non liquid
Liabilities
Long-term Liabilities, Accounts payable,
Business transactions
Source Documents
Transaction Analysis
Equation Analysis Sheets
Transactions on Account
Purchase on account
Sale on account
Payment on account
Receipt on account
Introductory Accounting Concepts
Types of businesses
Manufacturing
Service
Merchandising
Not -for-Profit
Types of ownership
Sole-Proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
Financial Position
Bankruptcy
User’s of accounting Information
Managers of the company
Shareholders
Bankers/Creditors
CRA
General public
Competitors
Claims against the assets
The claim by the owner or creditor is against the
assets of a business (and not just cash)
GAAPS: Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, commonly referred to as GAAP, are a set of 11 standards, rules, practices or procedures that Accountants must follow
Group’s Compromising GAAPS
FASB & GASB
Business entity’s
AICPA
CICA
Preparers
IFRS
CPA’s/accounting firms
Financial community
Government(SEC)
CICA HANDBOOK
Principles of GAAPS
prudence
consistency
materiality
objectivity
basic principles of modern accounting
Revenue Principle
Expense Principle
Matching Principle
Cost Principle
Objectivity Principle