Ancient Greece Sadeen Maghari
Legacy
The ancient Egyptians invented a variety of things that are still taken for granted in modern society. The Egyptians invented paper and ink, cosmetics, the toothbrush and toothpaste, and even the precursor of the modern breath mint
They were one of the first cultures to develop a written language

Ancient Egypt Alphabet
Any of the Egyptians' architectural skills are still in use today. Huge temples and monuments, such as massive pyramids, were built by the Ancient Egyptians, and the majority of them are still standing today
it is known that Ancient Egyptians were possibly the first civilizations to practice art. The egyptians constructed some of the worlds largest monuments without using technology.
Ancient Egyptians had also invented items that include the use of measured time such as, the sun dial, water clock, and calendar. They also developed a unit of measuring length which is the cubit.
The Egyptians also made further developments in astrology, astronomy, sience and medicine.
Geography
Located in the North-Eastern corner of Africa
Egypt's geography affected every aspect of Ancient Egyptian life, including the Nile River, which provided food, water, and transportation, as well as the desert, which provided a natural defense
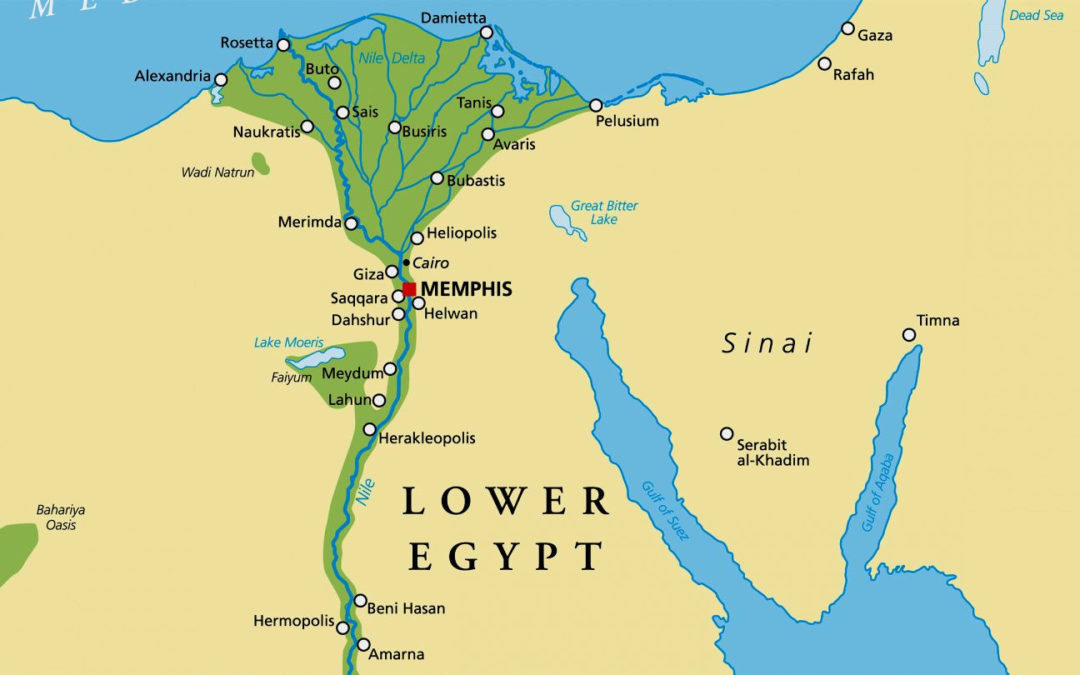
Map of Nile River
The Nile River flooded every year, making the land fertile and suitable for farming along its banks. Egypt's agriculture became one of the most prosperous in the Near East as a result of this
Despite the flooding on the Nile River, Egyptians thought of this as a good thing because it brought back the rich black soil and renewed farmlands.
There were some brief rainy periods, but the climate became increasingly dry, and resources and people started to congregate along the Nile, leading to the huge social stratification and hierarchy that became synonymous with Egyptian society
The Nile River also provided The Ancient Egyptians with Fertile Land as most of Egypt was dessert. Along the Nile River the soil is rich and was a good location for growing crops. Wheat, Flax, and Papyrus were the most important crops.
In Ancient Egypt, people thought of it as being divided into two different lands. The first one being " The Black Land" which was the fertile land located on the banks of the Nile. This land was used to grow their crops. The second land was the "Red Land" which was the barren desert. This land was to protect Egypt by separating Ancient Egypt from neighbouring countries and armies that might invade.
Beliefs
Were polytheists who claimed that gods and goddesses presided over the human, natural, and supernatural realms
Egyptians used faith to make sense of their surroundings, such as the annual Nile floods
Religion in Ancient Egypt
Another belief was the importance of cats. Ancient Egyptians believed that cats were gods. Thus, being cats worshipped and treated as royalty.
Used to describe everyday activities such as the sun setting and rising. Gods were modeled after humans in the sense that they lived and died and needed food to survive
Fun Facts
During the European Middle Ages, mummies were in high demand as medicine. Europeans, for example, will boil a mummy and use the resulting oils to treat swelling, stomach aches, and a number of other ailments

Mummy
Onions were often used to fill body cavities in ancient Egyptian mummification and were often used as false eyes
Most pyramids built in Ancient Egypt were for the rulers, also known as Pharaohs
Both men and women wore makeup because it was believed that makeup had magical healing powers.
Important Events
Prehistoric Egypt
A period during which the Nile's first settlers made their homes. The settlements began around 3100 BC, during what is known as the Early Dynastic Period
Construction of the Step Pyramid at Saqqara
The Step Pyramid was designed specifically for this purpose, and it acted as a tomb for Pharaoh Djoser. It was the first of the Egyptian pyramids to be built
Construction of the Pyramids of Giza
The burial tombs of Egyptian pharaohs Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure are located in the Great Pyramid of Giza and two other smaller pyramids on the site. The Great Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Pyramid of Khufu, is a 481-foot-tall structure
Ending of the Old Kingdom
This was a pivotal point in ancient Egypt's history when politics and corruption contributed to the demise of an entire empire
Influential Leaders/Important People
The pharaoh was the most important individual in ancient Egypt
The pharaoh was believed to be a divine mediator between the gods and the Egyptians. The pharaoh's function as a religious leader included maintaining religious unity and engaging in ceremonies
He owned the entire country, passed laws, raised taxes, and defended Egypt from foreign invaders. The pharaoh served the gods on Earth as the 'High Priest of Every Temple.'

Pharaoh
Ramesses the Great
Commanded the Egyptian army in battles against the Hittites, Syrians, Libyans, and Nubians. He grew Egypt's empire and fortified its borders against invaders. The Battle of Kadesh was perhaps the most famous battle fought during Ramses' reign

Ramesses the Great
Daily Life
Constructed mudbrick houses in villages and across the region
Produced some of their own food and traded for the food and products they couldn't produce in the villages. They would also farm a lot as it was one of the most common jobs
The majority of ancient Egyptians worked as laborers, fishermen, artisans, and scribes. Nobles were a select community of individuals
For fun, they'd conducted competitions in juggling, swimming, rowing, dancing, pageants, wrestling, and javelin, all of which were common spectator sports
Hunting and fishing were two of the most common sports, both of which required bravery and patience
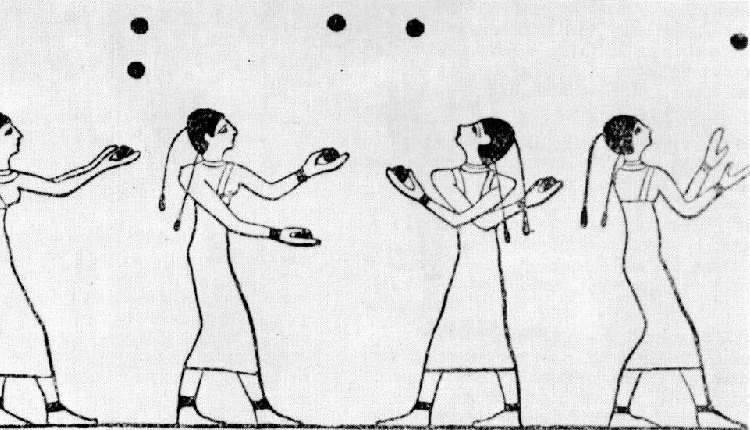
Ancient Egyptians Juggling