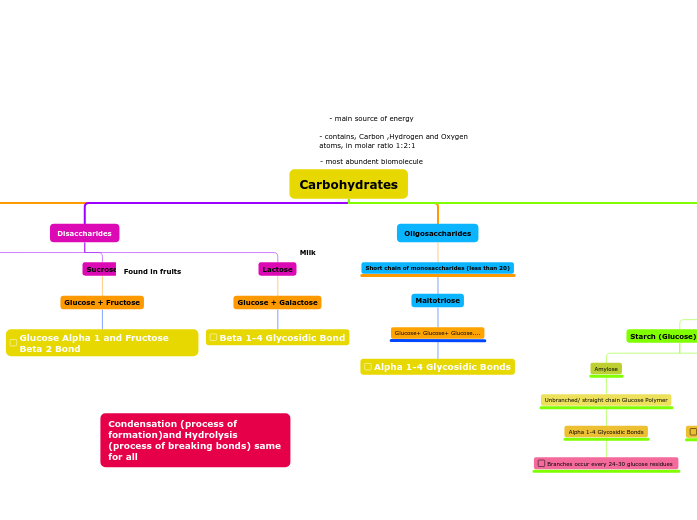
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Glucose
Alpha - Glucose
Hydroxyl (OH) group pointing in opposite directions
Beta- Glucose
Hydroxyl (OH) group pointing in same direction
Galactose
Beta - Galactose
Fructose
Beta - Fructose
Disaccharides
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
Alpha 1-4 Glycosidic Bond
Condensation
forms the bond by loosing water
Hydrolysis
looses bond by adding water
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
Glucose Alpha 1 and Fructose Beta 2 Bond
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
Beta 1-4 Glycosidic Bond
Oligosaccharides
Short chain of monosaccharides (less than 20)
Maltotriose
Glucose+ Glucose+ Glucose....
Alpha 1-4 Glycosidic Bonds
Polysaccharides
Homopolysaccharide
Only a single type of monosaccharides
Starch (Glucose)(Plants)
Amylose
Unbranched/ straight chain Glucose Polymer
Alpha 1-4 Glycosidic Bonds
Branches occur every 24-30 glucose residues
Amylopectin
Branched Glucose Polymer
Alpha 1-4 and Alpha 1-6 Glycosidic Bonds
Glycogen (Glucose)(Animals)
Amylose
Branched
Branches occur every 8-12 glucose residues
Stored in muscle and liver
Amylopectin
Unbranched
Fibers (Glucose)(Indigestible)
Soluble
Dextrans
a1-3 and a1-6 bonds
Branched
Structural component in bacteria and yeat
Insoluble
Cellulose
b1-4 glycosidic bonds
Hetropolysaccharide
Contains two or more types of monosaccharides
Branched
Unbranched