Cellular Respiration
Mitochondria
Aerobic Reaction
Glycolysis
Pyruvate Oxidation
In the presence of oxygen after glycolysis, pyruvic acid can enter the Krebs cycle after pyruvate oxidation

There are 3 main steps; step 1: A carboxyl group is removed from the pyruvate, releasing a molecule of CO2
Step 2: NAD+ is reduced to NADH
Step 3: An acetyl group is transferred to conenzyme A, resulting in the creation of acetyl CoA.
Subtopic
In the absence of oxygen after glycolysis, pyruvic acid can take two paths; Lactic acid fermentation or Alcoholic fermentation
Latic acid fermentation occurs in animal muscle cells during excercise, it is
▪ Reversible
▪ Involves the oxidation of NADH and the reduction
of pyruvate
▪ The outputs are ATP, lactate
Alcoholic fermentation occurs in yeast cells and is used in
wine, beer, and bread making

Glycolysis is a cytoplasmic pathway set of anaerobic reactions (don't need oxygen to be performed) which break glucose down into two three-carbon compounds (pyruvate). This has the result of creating two ATP, which can release energy.

The overall equation for this pathway is:
1 glucose + 2 ATP ⟶ 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 4 ATP + 2 H2O
The inputs of Glycolysis are a glucose molecule, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP, 4 ADP and 2 P
The outputs of Glycolysis are 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, 2 ADP and 2 ATP (net gain)
This image above depicts the steps of glycolysis; hexokinase, Phosphoglucose Isomerase, Phosphofructokinase, Aldolase, Triosephosphate isomerase, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase, Phosphoglycerate Kinase, Phosphoglycerate Mutase, Enolase and Pyruvate Kinase
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
The ETC is the last stage of the respiration pathway. It is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules and involves a series of electron carriers. The ETC is made of a collection of carrier proteins found on the inner membrane of mitochondria; the cristae.
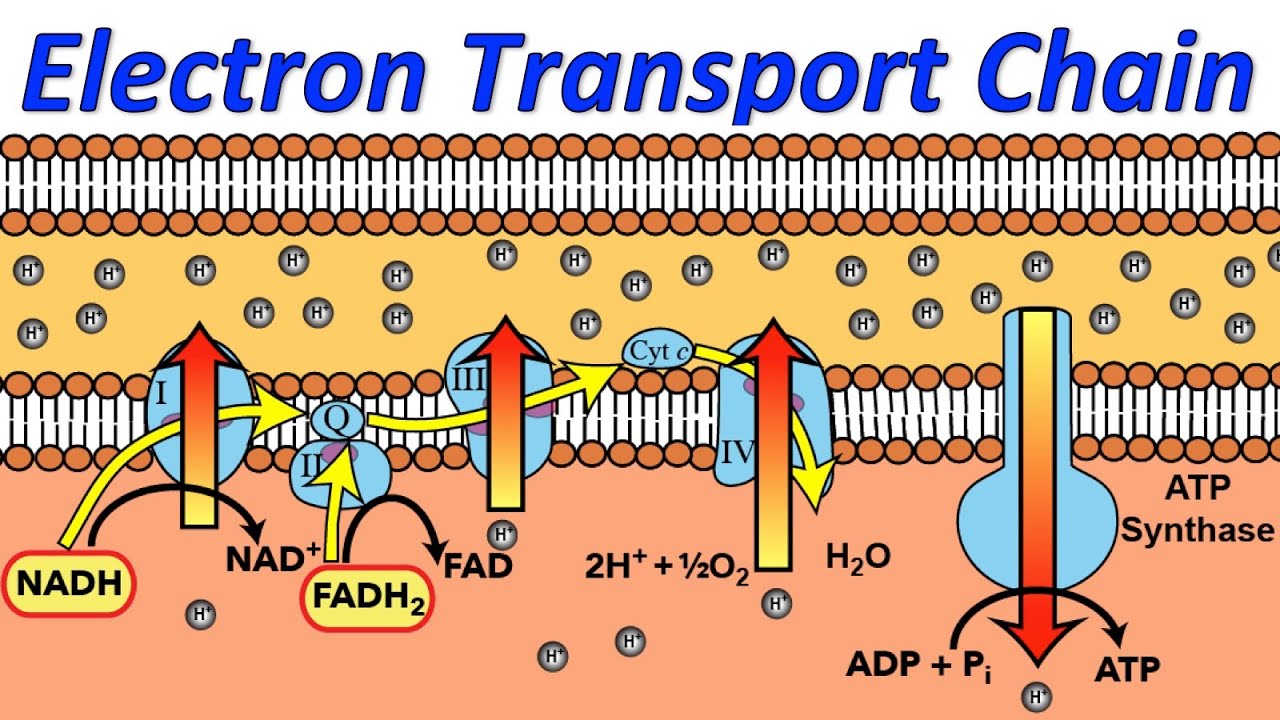
There are 5 major parts to the ETC organized by an increasing electronegativity Part 1: NADH releases hydrogen ions and electrons into the transport chain.
Part 2: The electrons transfer their energy to proteins in the membrane providing energy for hydrogen ions to be pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Part 3: NADH donates two electrons to NADH dehydrogenase and FADH2 donates them
directly to Q. They are now shuttled from one protein complex to the next until they
reach the site of water formation
Part 4: The free energy lost by the electron pair is used to pump a proton into the intermembrane space at each protein acceptor. The flow of the ions back across the membrane synthesises ATP by a protein called ATP synthase.
Part 5: NADH transfers its electrons to NADH dehydrogenase, its energy is used to pump three protons into the intermembrane space. FADH2 donates to Q, pumping two protons into the same space. 2 ATP are produced fro each FADH2, and three for every NADH.
38 ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of glucose
Chemiosmosis
The Krebs or Citric Acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. It is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate. There are 8 main steps.
The inputs being brought to the Krebs cycle are; 2 Acetyl CoA, 3 NAD+, 1 FAD, ADP, Pi
The outputs of the Krebs cycle for each spin of the cycle are 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2CO2, and 1ATP
Step 1: Acetyl CoA joins with oxaloacetate to form citrate (6 carbon molecule)
Step 2: Citrate is converted to an isomer of citrate, isocitrate
Step 3: isocitrate is oxidized releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide, leaving behind α-ketoglutarate. NAD+ is reduced to form NADH
Step 4: α-ketoglutarate is oxidized, reducing NAD+ into NADH and releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide in the process. The four-carbon molecule picks up Coenzyme A, forming the unstable CoA
Step 5: CoA of succinyl CoA is replaced by a phosphate group, which is then transferred to ADP to make ATP. One molecule of GTP is produced.
Step 6: Succinate is oxidized forming fumarate. Two electrons are transferred to FAD producing FADH2.
Step 7: Water is added to fumarate is converting it to malate
Step 8: Malate is converted into oxaloacetate. A third molecule of NADH is produced (from FAD+).
Aerobic respiration is the cellular respiration processes in which organisms use oxygen to turn fuel into ATP
Anaerobic Reaction
Anaerobic respiration is when cellular respiration within organisms can occur in the absence of oxygen
The organelle mitochondria produces ATP through all processes of cellular respiration

The mitochondria contains four main parts; the inner membrane is loaded with proteins involved in electron transport and ATP synthesis, the outer membrane has many protein-based pores that are big enough to allow the passage of ions, the matrix performs the process of aerobic respiration, and the cristae are folds of the mitochondrial inner membrane that provide an increase in the surface area.