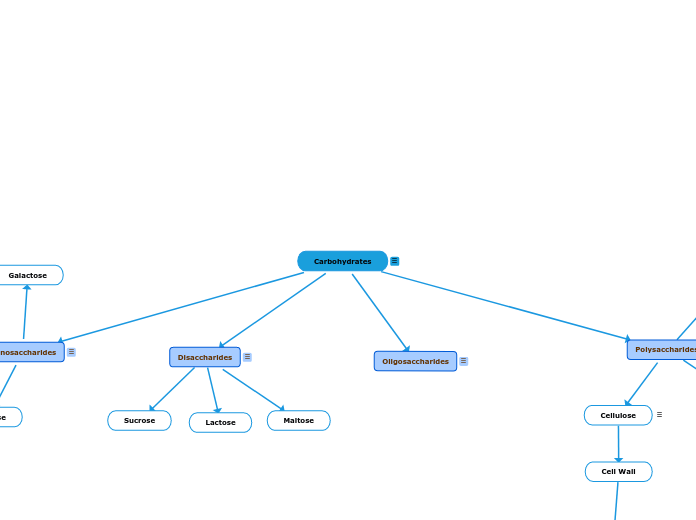
There are four major classes of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (simple sugars)– the smallest units that makeup carbohydratesConsists of a single polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone unit, meaning they cannot be further hydrolyzed to simple sugarThe most abundant monosaccharide in nature is the six-carbon sugar D-glucose, aka dextroseThe three main monosaccharides in the human diet are: glucose, galactose, fructose
Fructose
Galactose
Disaccharides– made up of two monosaccharidesThe three common examples of disaccharides is sucrose, maltose, and lactose
Maltose
Oligosaccharides– consists of short chains of monosaccharides, typically less than 20 monosaccharides, joined by linkages called glycosidic bondsGlycosidic bonds– join monosaccharides or longer sugar chains to other carbohydrates
Polysaccharides (glycans)– sugar polymers containing more than 20 or so monosaccharide units, some having hundreds or thousands of unitsMost carbohydrates found in nature occur as polysaccharidesEx. starch There are two types based on their function and composition: storage and structuralStorage polysaccharide (ex. starch)Structural polysaccharide (ex. cellulose)Homopolysaccharide– a polysaccharide is made up of one type of monosaccharide unitHeteropolysaccharide– a polysaccharide that’s made up of more than one type of monosaccharide
Cellulose is found in plantsIt makes up the structural component of plant cell wallsHelps support the plant wall
Glucose is converted into ribose and deoxyribose which is needed for building RNA and DNAIt is also the main source of energy production in cells
A polysaccharide composed of glucoseProduced by the fermentation of sucrose
A polysaccharideFound in starch, one of the components that make up starchStarch– a complex polysaccharide made up of a large number of glucose as monomeric units joined together by glycosidic bondsFunctions as secondary long-term storage in animal cells
A polysaccharide of glucose that functions as energy storage in animalsThe main storage form of glucose in the body