Non-polar
Insoluble in water
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
Energy Sources
Fats
Unsaturated
Liquid at room temperature
short chains
Polyunsaturated
Multiple double bonds
(looks more bent that mono)
Monounsaturated
One double bond
A bent structure
Saturated
Solid at room temperature
Long, straight chains
Triglycerides
Three fatty acids chains
which are linked to a
glycerol molecule
Phospholipids
Steroids
4 hydro carbon rings
Wax
Good for water proofing
Protection
Soft and is made up of
long fatty acid chains
Linked to carbon rings or
alcohols
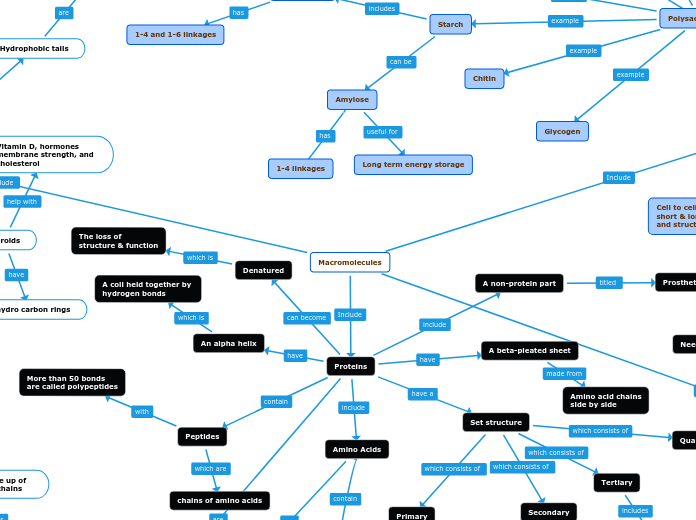
Vitamin D, hormones
membrane strength, and
cholesterol
Plasma Membranes
Groups of polar lipids
Hydrophilic heads
Soluble in water
Hydrophobic tails
Insoluble in water
Fatty Acids
Of a carboxyl group linked
to a hydrocarbon chain
Trans
One or more double bonds in
a trans configuration
Straight structure
The assembly instructions
for all proteins in living organisms
A "backbone"
made up of alternating
sugar and phosphate groups
Nucleotides
H bonds
Complementary stands
of nucleotides
Phosphodiester bonds
Building blocks
of nucleic acids
5-carbon sugar
Nitrogenous base
1-3 Phosphate groups
Can be either
Purine
Adenine and Guanine
As ATP and GTP
Transport chemical
energy
Pyrimidine
Uracil, Thymine and Cytosine
Linked with covalent bonds
Linked with a Phosphate bridge
5' carbon
Is the phosphate group end
3' carbon
Is the deoxyribose sugar end
RNA
Single stranded molecule
DNA
Double stranded
Double helix shape
By base pairs of 2 nucleotides
Amino Acids
A carboxyl group and an
amino acid group
Connected by peptide bonds
Set structure
Secondary
Hydrogen bonds
in the peptide
Amino acids to fold into a
repeating pattern
Tertiary
A 3-D folding pattern
Quanternary
More than one amino acid
chain
Held together by ionic bonds,
sulpher-sulpher covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions
Primary
A sequence chain of amino
acids
Denatured
The loss of
structure & function
A non-protein part
Prosthetic groups
Needed for protein function
Peptides
chains of amino acids
More than 50 bonds
are called polypeptides
A beta-pleated sheet
Amino acid chains
side by side
An alpha helix
A coil held together by
hydrogen bonds
Structural
Aids in framework support
Ligaments
Polysaccharides
Through Hydrolysis
Glucose
An energy source
Multiple bases including sugars
Branching chains/long chains and
beta/alpha linakages
Determine the function
Energy source, cell to cell communication
and structural support
Starch
Amylopectin
Alpha glucose
1-4 and 1-6 linkages
Amylose
1-4 linkages
Long term energy storage
Chitin
Cellulose
Glycogen
Monosaccharides
In the simplest form
consisting of one sugar unit
Pentose sugar
5 carbon atoms
Deoxyribose/ribose
Hexose sugar
6 carbon atoms
Glucose
A ring structure in water
Alpha glucose
Starch in plants
1-4 linkages
Hydrogen bonds
Glycogen in animals
1-6 linkages
A branching structure and leads to
long term energy storage
Beta glucose
Cellulose in plants
the OH- group placement
Fructose
Galactose
Glycosidic bonds
Quick energy
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
atoms.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides joined together
Two sugar bases
A dehydration synthesis reaction/condensation reaction
Quick energy
Sucrose, Maltose, and Lactose
Glycosidic linkages
1-6
A branching structure
Beta
Orientation of the OH- groups
1-4
Linear structure
Alpha
Cell to cell communication,
short & long term energy storage
and structural support.