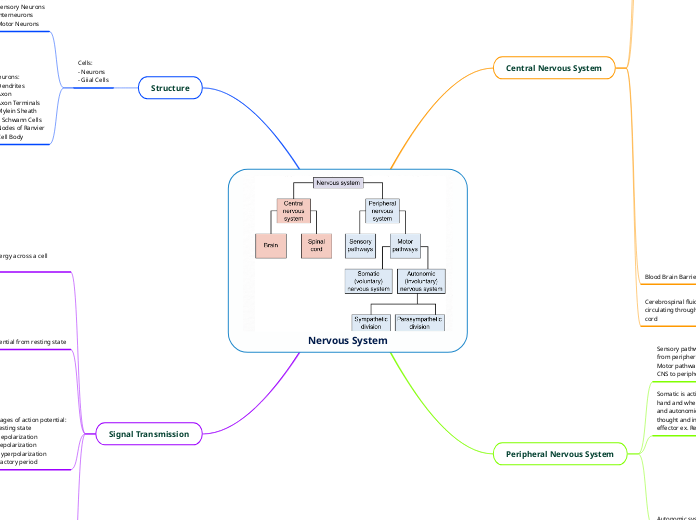
Nervous System
Central Nervous System
Spinal cord is a nerve tissue that extends from the skull throught the backbone
relays infor between body and brain, is protected by mengies, cerebrospinal fluid and vertebrae
Brain
GREY matter of the brain is unmyelinated
WHITE matter of the brian is myelinated
Skull and mengies protect it
1. Forebrain
2. Midbrain
3. Hindbrain
Midbrain processes sensory input from eyes and ears and relays info the other areas of brain
Hindbrain is used for coordination and maintaining homeostatic functions
Cerebellum is used for controlling limb movements, balance, fine motor skills and reflexes
Pons passes info btw neurons of left and right halves of brain
Medulla Oblongata joins the spinals cord to the cerebellum Nd the PNS and CNS; coordinates homeostasis
Forebrain is used for through, learning and emotions
Thalamus is located at baseof forebrain and provides connection btw parts of the brain
hypothalamus located below thalamus contains neurons that control homeostasis
Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two hemispheres and 4 lobes
Right lobe controls sensory stimilus and motor control of/from left side of body
Left lobe controls stuff on right side of body
Frontal Lobe:
integrates info from other parts of brain and controls reasoning, critical thinking, memory and personality
Temporal Lobe:
shares processing of visual info main function is auditory reception
HIppocampus: used in learning and memory
Parietal Lobe:
receieves and processed sensory info from the skin and processes info about orrientation
Occipital Lobe:
analyzes visual info and recognition of what is being seen
Blood Brain Barrier
Selectively controls the diffusion of substances into the brain from the blood
Cerebrospinal fluid is a liquid derived from blood plasma circulating throught the spaces between the brain and spinal cord
provides shcok absorbtion and transports hormones, wbc and nutrinets across the BBB
Peripheral Nervous System
Sensory pathways include afferent transmissions of impuses from peripheral organs to the CNS
Motor pathways are efferetn transmissions of impulses from CNS to peripheral organs
Somatic is action which requires conscious thought before hand and when the signals take a longer path to the effectors and autonomic is for all actions which do not require conscious thought and in which the signal goes straight from stimilus to effector ex. Reflexes and homeostasis
Autonomic system
Sympathetic nervous system is for all fight or flight responses and falls beloww the autonomic division
Parasympathetic is responsible fro rest and digest functions which is used to maintain homeostasis (acetylcholine is used to commence this function) this also falls under autonomic system
Reflex arc:
nerve pathway containing 5 components
- receptor
- sensory neruon
- interneuron in spinal cord
- motor neuron
- effector
All occurs without the signal going to the brain
ex. touching a hot stove, knee jerk,
Structure
Cells:
- Neurons
- Giial Cells
Types of Neurons:
1. Sensory Neurons
2. Interneurons
3. Motor Neurons
Motor neurons relay information form the CNS to PNS and effectors
Sensory neurons sense and relay info from PNS to CNS for processing
Interneurons link sensory and motor neurons and exisit only in the CNS
Neurons:
- Dendrites
- Axon
- Axon Terminals
- Mylein Sheath
- Schwann Cells
- Nodes of Ranvier
- Cell Body
Dendrites Recieve information from receptors or nerve cells
Axons and Axons terminals carry nerve impulses away from cell body to other neurons/effectors
Cell body contains the genetic info, specialized organelles, nucleus and maintains the structure of the neuron
Mylein Sheath is a fatty layer surrounded the axon allowing nerve impluses to travel faster
Schwann Cells are a type of gilal cell that produces the mylein sheath
Nodes of ranvier are gaps in the mylein sheath which allow nerve impulses to jump from on node to another
Signal Transmission
Membrane potential is the potential energy across a cell membrane
Resting membrane potential:
nerves are not transmitting brain impluses
membrane potential of -70mV is fored as a result of the chemical gradient formed by the constant pumping of Na+/K+
3 factors play a part in maintaing the resting potential:
1. negative proteinss inside the cell
2. ion specific channels allowing passive movement
3. sodium/potassium pump brining 3Na+ out and 2K+ in resulting in a positive charge OUTSIDE of the cell
Action potential is a change in potential from resting state
when signal is recieved in dendrites gates open in the neurons membrane allwing Na+ to move into the cell. if the charge reaches above approx. 55mV the neuron becomes active and the action potential begins
All or nothig principle reffers to wheter the signal from a neuron is sufficient enough to reach the threshold of excitation
4 stages of action potential:
1. resting state
2. Depolarization
3. Repolarization
4. Hyperpolarization
refractory period
Resting State:
Lots of sodium inside lots of potassium inside
-70mV
Depolarization
Na+ channels open and na moves in
K+ channels are closed
-50mV
Repolarization:
+40mV
na channels close
k+ channels open and k moves out of cell
Hyperpolarization:
K+ continues moving out of the cells until it becomes -90mV then K+ channels close
Refractory period:
both channels are closed and protein retores -70mV
Synapse:
can be chemical and electrical
signal transmission occurs at the junction between two neurons (place where neurons communicate with each other
NEUROTRANSMISTTERS carry neutral signal from one neuron to another
exictatory ion channels open to allow Na+ in to depolarize
Inhibitory allow k+ to flow out to hyperpolarize cell