Optics
Production & Reflection of Light
Light
Types of Light Production
Incandescence
Light Produced by very hot objects
Electric Discharge
Light Produced by an electric current
passing through a gas
Phosphorescence
The process of absorbing UV light,
and remitting it later as visible light
Fluorescence
The process of absorbing UV light
and instantly remitting it as visible light
Chemilumiescence
Light produced through a chemical reaction
Bioluminescence
Light produced from a chemical reaction
happening within a living organism
Triboluminescence
The production of light through rubbing to crystals together
Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
Light produced through an electric current
flowing through semiconductors
Photons
Particles of light that travel at 299,792,458 m/s
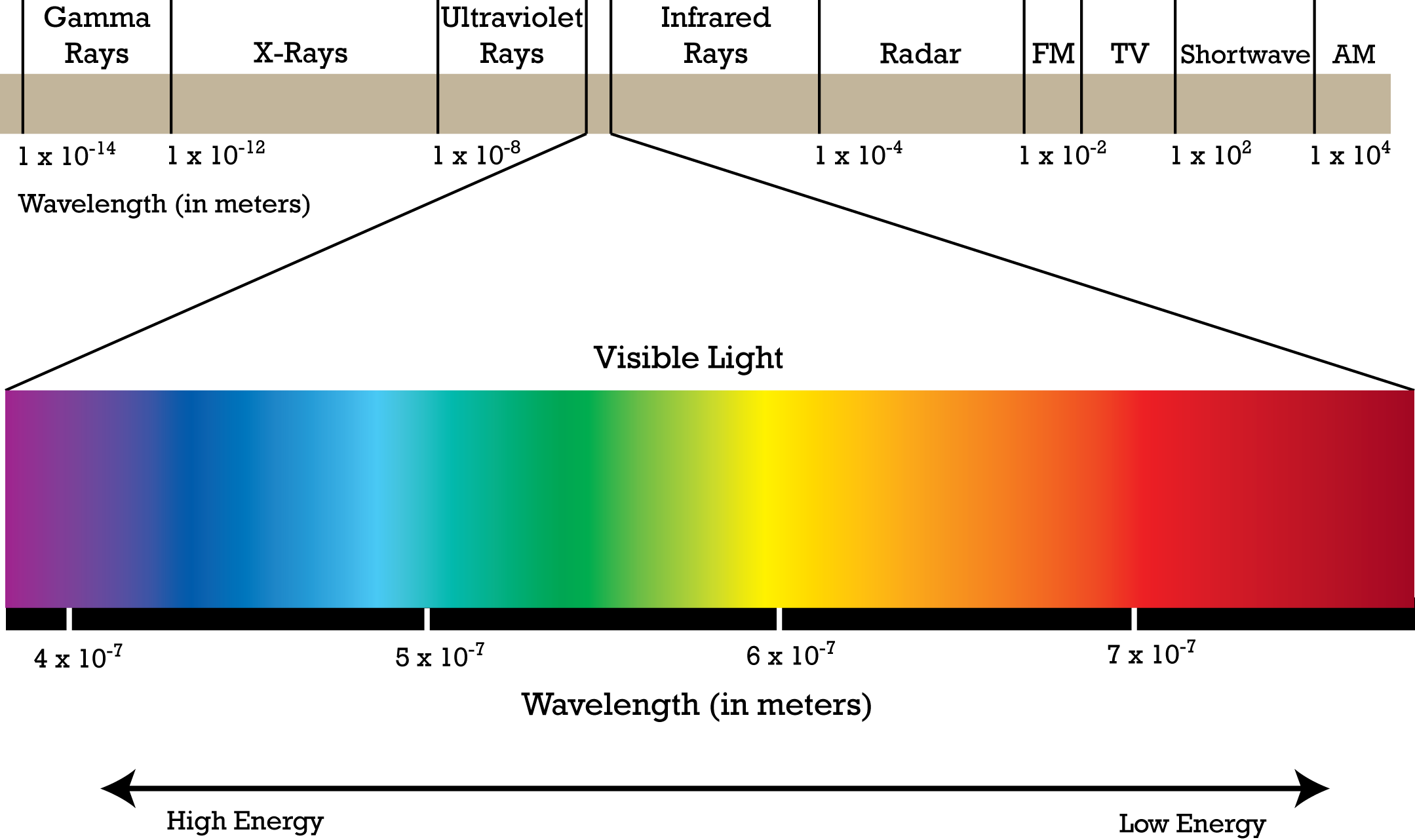
Electromagentic Waves
Waves that move at the speed of light, with different energies at different wavelengths
Radiation
Energy transfer that does not require a medium
Types of electromagnetic waves
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infared Light
Visible Light
Ultraviolet Light
X-Rays
Gamma Rays
Reflection
Normal
The line that is perpendicular to the mirror's surface
Incident Ray
The incoming light ray that hits the surface
Reflected Ray
The ray that bounces off of the surface
Mirror types
Plane Mirror
A flat mirror
Curved Mirror
Concave
A curved mirror that converges light rays onto the focal point
Usually creates an inverted, real image
Convex
A curved mirror that diverges light rays away from the focal point
Usually creates an upright, smaller, virtual image
Image
Virtual
An image that appears to come from behind the mirror
Real
An image that can be shown on a screen in front of the mirror
S.A.L.T.
Size
The apparent size of the image
Attitude
Whether the image is upright, or inverted
Location
Where the image is in relation to the mirror
Type
Whether the image is real, or virtual
Lenses and Optical Devices
The Refraction of Light
Incident Ray
The incoming light ray that transfers between mediums
Refracted Ray
The light ray after it changes mediums
Normal
The line perpendicular to the line separating the two mediums
Angle of incidence
The angle between the incident ray and the normal
Angle of Refraction
The angle between the refracted ray and the normal
The bending of light as it travels between two materials
Index of refraction
n=c/V
equation for calculating the index of refraction (n)
Speed of light in a Vacuum (c)
Speed of light in a medium (V)
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum,
to the speed of light in a medium
The index of refraction for different mediums
Air/Vacuum: 1.00
Water: 1.33
Glass: 1.52
Diamond: 2.42
Total Internal Reflection
Critical Angle
The angle of the incident ray when the
angle of refraction is 90*
Occurs when the angle of incidence is
greater than the critical angle
Only happens when light is transfering from a medium with
a greater index of refraction, to a medium with a lower index of refraction