Physics
Chapter 13
Lenses
a curved transparent object that is smooth and regularly shaped so that when light strikes it, the light refracts in a predictable and useful way
Lenses are used in: Telescopes, microscopes, cameras etc

Camera

Telescope
Converging Lenses
A lens that is thicker in the middle and thinner on the edges
Principal Focus
Point where rays converge after refraction
Optical Centre
Point at the centre of the lens
Principal Axis
Line through the optical centre and focal point
Normal Line
Imaginary Line perpindicular to principal axis
Diverging Lenses
A lens that is thinner in the middle and thicker on the edges
Principal Focus
Point where extended light rays meet after refraction
Optical Centre
Point at the centre of the lens
Principal Axis
Line through the optical centre and focal point
Normal Line
Imaginary Line perpindicular to principal axis
Parts of the human eye
Cornea
outer surface if the eye where light enters and it is completly clear
Pupil
is the dark hole in the eye that allows light to pass into th eye
Iris
A circular band of muscle that controls the pupil
Eye Problems
Hyperopia
can see distant objects clearly but not nearby objects clearly
Can be helped by converging lenses
Presbyopia
a form a far sightdness where the eye lens looses its elasticity
can be helped by converging lenses
Myopia
can see nearby objects clearly but not distant objects
Can be helped by diverging lenses
Chapter Summary
In this Chapter we learned how different types of lenses work abd how our humans eye work and why we have different problems with our eyes and why some people need lenses
Chapter 11 & 12
Concave Mirrors
the reflection is made from the inner surface of the sphere
the center caves inward, away from you
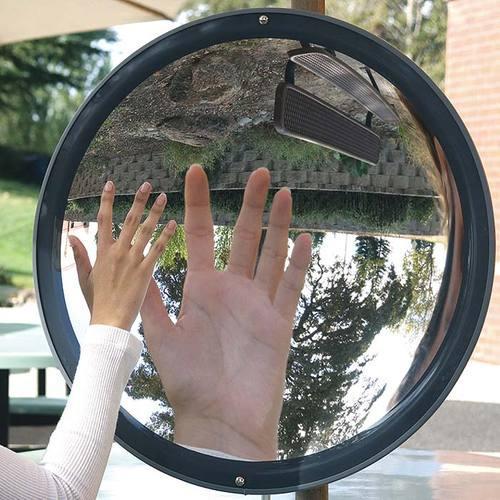

Convex Mirrors
the reflection is made from the outer surface of the sphere
the center sticks out, toward you

Real Image
image is in front of the mirror
Virtual Image
image is behind the mirror
Light from incandescene
Producing light by heating a material up
Light from electric discharge
Produced by electricity passing through gas
Light from fluorescence
Produced by asborbing UV light and emitting it
Light from chemiluminescene
Producing light from the reaction of two chemicals
Refraction
The bending of light as they pass through different media
Unit Summary
In these chapters we learned different ways light works and how the light we use everyday is produced we also learned different types of mirrors and why certain mirros look different and act different