Science
Chemistry
Table of Elements
The periodic table, created by Dmitri Mendeleev, is a compilation of the foundations of what everything around us is made of. There are currently 118 known elements on the table.
Element
A pure substance that can't be broken down by regular chemical means
Compound
A pure substance made of 2 or more different elements
Patterns
The metals are at the left of the periodic table, while non-metals are at the right.

Eg: The Periodic Table
Alkali Metals
An element in group 1 of the periodic table, they are highly reactive.
Alkaline Earth Metals
An element in group 2 of the periodic table, they are shiny and silvery metals. They are also highly reactive but not as much as the alkali metals.
Halogens
An element in group 17 of the periodic table, they are very reactive and rarely found in elemental form.
Noble Gases
They are unreactive non-metals. They contain full Valence shells and are mostly non-toxic
Metalloids
They are found along the "staircase" of the periodic table, and contain characteristics of metals and non-metals.
Hydrogen
Non-metal, but put in the alkali metal column, but put into the alkali group because of their atomic number. Hydrogen has no neutrons.
Theories of the Atom
An Indivisible Particle - The Atom
Made around 400 BC by Greek philosopher Democritus, talked about all matter being able to be divided into smaller pieces until an indivisible particle is reached (atom). He proposed atoms are of different sizes, in constant motion and separated by empty space
Aristotle
Created around 450 BC by Greek philosopher Aristotle. The theory was that all matter is made up of 4 substances, earth, water, air and fire and have 4 qualities dry, wet, cold and hot. This theory was accepted for almost 2000 years.
Billiard Ball Model
Created by John Dalton in 1807, he proposed that all matter is made up of tiny indivisible particles called atoms, all atoms of an element are identical. Atoms of different elements are unique and atoms are rearranged to form new substances in chemical reactions, but are never created or destroyed
Thompson's experiments-the electron
Created by J.J Thompson in 1897, he proposed that particles could be emitted by very hot materials. He concluded that particles must be negatively charged and they were called electrons. His theory was that atoms contain negatively charged electrons, and the rest of the atom is a positively charged sphere since atoms are neutral, negatively charged electrons are evenly distributed throughout the atom
The Gold Foil Experiment
Created by Ernest Rutherford in 1909. He theorized that the centre of an atom has a positive charge (nucleus), it contains most of the atoms' mass but occupies a very small space. The nucleus is what made some particles bounce back. The nucleus is surrounded any a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Most of the atom is empty space.
Explain the Periodic Table
Atomic number
Is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus
Atomic mass/Mass number
Is the mass of an atom in atomic mass units (u)/the number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus
Finding the number of neutrons
x= Atomic Mass - Atomic Number
Bohr-Rutherford Diagram

Eg: Bohr-Rutherford Diagram
Properties of Matter
Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical Properties
A characteristic we can determine using our 5 senses and/or measuring instruments
Gives us info of what a substance is like
Qualitative Properties
A property of substance that isn't measured by numerical values, such as colour, odor, texture, etc

Eg: Tasting a Powder
Quantitative Properties
Freezing, Melting, & Boiling Point
Freezing Point: The point where the temperature turns a liquid into a solid
Melting Point: The point where the temperature turns a solid into a liquid
Boiling Point: The point where the temperature turns a liquid into a gas
A property of substance that is measured by numerical values, such as temperature, height, mass, etc

Eg: Measuring Energy Particles of a Bulb
Chemical Properties
A characteristic of a substance that we know has changed if its composition is also changed.
How one substance chemically reacts with another

Eg: Rusting in Iron
The Particle Theory of Matter
All matter is made up of tiny particles that have empty spaces between them
Different substances are made up of different kinds of particles
Particles are in a state of constant motion
The particles of a substance move faster as the temperature increases
Particles attract one another
Matter
Pure Substances
A substance that is only made up of 1 type of particle

Eg: Pure Water
Mixtures
A substance that is made up of 2 or more different particles
Solutions
Alloys
A solid solution of 2 or more metals

Eg: Solder (Tin and Lead)
A uniform mixture of 2 or more substances

Eg: Orange Juice
Mechanical Mixtures
A mixture where you can see the difference between the types of matter

Eg: Cereal and Milk
Chemical Compounds
Molecule
2 or more atoms that are chemically joined in a unit.
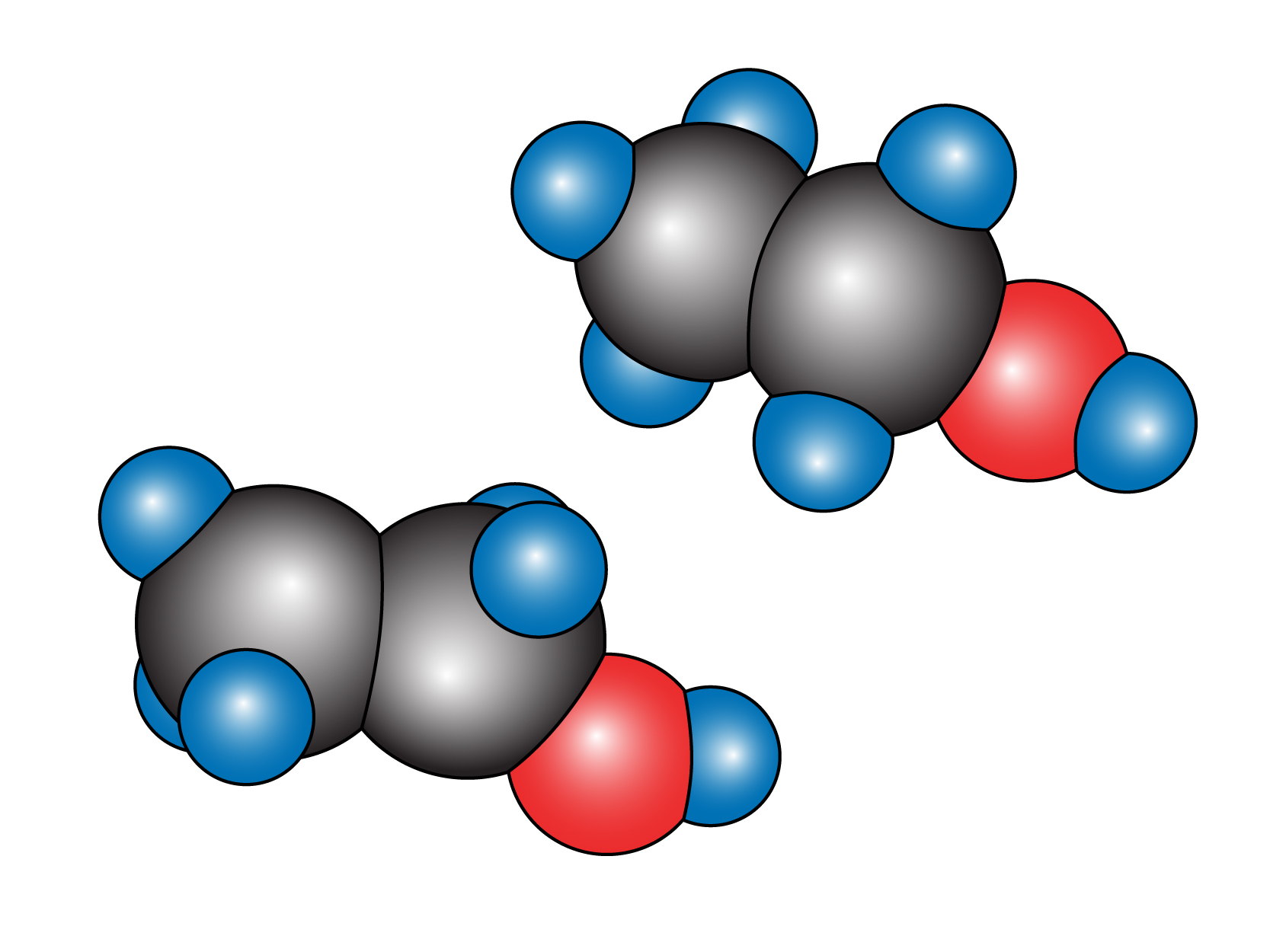
Eg: Molecule
Chemical Formula
A notation that indicates the type and number of atoms in pure substances
How Atoms Combine
Elements combine to become more stable and fill their shells
Metals form mixtures with other metals (alloys)
Metals bond with non-metals to form compounds (ionic)
Non-metals bond with non-metals to hold atoms together (covalent bond)
Biology
Understanding Ecosystems
Spheres
Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding Earth
Lithosphere
Earth's solid outer layer
Hydrosphere
Earth's water in its 3 forms
Biosphere
Zone where life can exist on Earth
Ecosystems
All living organisms and their physical and chemical environment
Factors
Biotic
Living things and their remains and features associated with their activities

Eg: Biotic Organisms
Abiotic
Non-living physical and chemical factors of an ecosystem
Eg: An Abiotic Object
Sustanibility
The ability to maintain an ecological balance
Sustainable Ecosystem
An ecosystem that is maintained through natural processes
Energy flow
Types of energy
Radiant energy
Energy that travels through empty space
Light energy
Radiant energy that is visible to the human eye
Thermal energy
Energy transferred during heating or cooling
Cycles
The carbon cycle
The biogeochemical cycle in which carbon is cycled within the 4 spheres.
Photosynthesis
The process in which the sun's energy is converted into chemical energy
carbon dioxide + water = sugar + oxygen
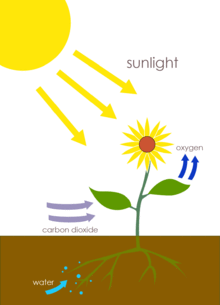
Eg: Photosynthesis
Cellular respiration
The process in which chemical energy is converted into useable energy
sugar + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy
Eg: Cellular Respiration
Food Chains and Food Webs
Food chains
A sequence of organisms each feeding on the next

Eg: Terrestrial Food Chain
Food webs
A representation of the feeding relationships within a community

Eg: Aquatic Food Web
Ecological niche
The function a species serves in an ecosystem
Trophic levels
First Trophic Level
Producers
An organism that goes through photosynthesis
Second Trophic Level
Primary Consumers/Herbivores
Organisms that only consume plants
Third Trophic Level
Secondary Consumers/Carnivores
Organisms that only consume other animals
Fourth Trophic Level
Tertiary Consumers/Omnivores
Organisms that consume both plants and animals
The Water Cycle
The series of processes in which water cycles through the environment

Eg: Water Cycle
The Nitrogen Cycle
The series of processes in which nitrogen compounds are moved through the biotic and abiotic environment

Eg: Nitrogen Cycle
Biotic and Abiotic Influences
Carrying Capacity
The maximum population size of a particular species in a sustainable ecosystem
Tolerance Range
The abiotic factors in which a species can survive
Limiting Factors
Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the size of a population
Natural Ecosystems and Stewardship
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is important because species are dying out or going extinct in an unnatural way affected by human activity. Biodiversity ensures that we have a more diverse food web in which the negative impact of one species doesn't effect the entire ecosystem as much.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in a particular ecosystem
Habitat Loss
Is one of the most serious threats to Earth's ecosystem
Fragmentation
Reduces ecosystem's sustainability
Is the dividing up of a region into smaller fragments
Native Species
Organisms that originated in a specific area
Non-Native Species
Organisms that came in from another area
Non-native species are a concern because you don't know how they will react or take over with a native species and can disrupt the entire food web.
Ecosystems by Design
Pesticides
Pesticides have benefits such as more food and better health
Pesticides have a big environmental cost
Managing soil
Use natural and synthetic fertilizers
Natural fertilizers may not have as many benefits with growing crops, but have less environmental cost
Synthetic fertilizers have more benefits with growing crops, but also have more environmental cost
Bioaccumulation
The concentration of a substance in the body of an organism
Bioamplification
The increase in concentration of a substance as it moves through the food web

Eg: Bioamplification in an Aquatic food Web
Space
Astronomy
The scientific study of what is beyond Earth
Celestial object
An object that exists in space
Universe
Everything that exists
The Origin and Evolution
The universe is always expanding
The Big Bang Theory
The theory that the universe began in an incredibly hot, dense expansion, approximately 13. 7 billion years ago
Stars
A massive collection of gases held together by its own gravity and emitting huge amounts of energy
Luminosity
The total amount of energy produced by a star per second
Magnitude
Apparent Magnitude
The brightness of stars in the night sky as they appear from Earth
Absolute Magnitude
The brightness of stars as if they were located 33 ly from Earth
Star Colour
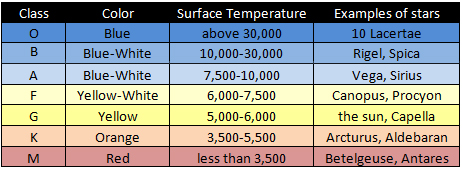
Eg: Colour/Temperature Ranges
Solar Mass
A value used to describe the mass of stars and galaxies other than the sun (2 x 10^30 kg)
Life Cycle of Stars
Nebula
A massive cloud of interstellar gas and dust (beginning of the star)
Protostar
A massive concentration of gas and dust that is thought to eventually become a star after the nebula collapses
Star
Nuclear fusion helps turn the core of a protostar into a star
Supernova
The death of a star as it burns out
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram

Eg: Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
Planets
A large round celestial object that travels around the star
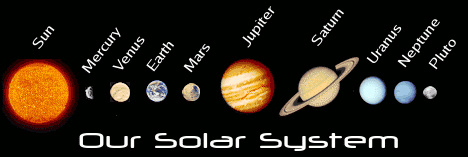
Eg: The Planets in Order
Satellites
A celestial object that travels around a planet or dwarf planet
Galaxies
A huge rotating collection of gas, dust, and other celestial objects
Sun
Electromagnetic Radiation
Energy emitted from matter that travels at the speed of light
The Structure of the Sun

Eg: Labelled picture of the sun
Solar Flare
Gases and charged particles expelled above an active sunspot
Sunspots
Dark spots appearing on the sun's surface that are cooler than the area surrounding them
Solar System
The sun and all the objects that travel around it
Astronomical Unit
Approximately 150 million km
The Solar Nebula Theory
Explains that the solar system was formed around 5 billion years ago from a massive cloud of gas and dust (the solar nebula) that began to contract
Asteroids
Small celestial objects composed of rock and metal
Asteroid Belt
Located between Mars and Jupiter
Motions of Earth, the Moon, and Planets
Earth's Rotation
Takes 24 hours to complete 1 rotation around Earth's axis
Earth's Revolution
Takes 1 year for Earth to revolve around the sun
Motion of the Moon
Rotates around it's axis and revolves around the Earth, in the same time
Gravity
Gravitational Force
The force of attraction between all masses in the universe
Earth's Tilt
23.5 degrees from the vertical
Contributes to different seasons
Phases of the Moon

Eg: The Lunar Cycle
Patterns in the Night Sky
Constellations
A grouping of starts as observed from Earth
Electricity
Static electricity
The imbalance of electrical charge on the surface of an object
Electric Charge
A positive or negative charge that exerts an electric force
Charged/Neutral Objects
Neutral Objects
An object that has an equal number of protons and electrons
Negatively Charged Objects
An object that has more electrons than protons
Positively Charged Objects
An object that has fewer electrons than protons
Detecting Static Electric Charge
The Electroscope
A pith ball electroscope is a pith ball suspended by a thread and is used to test for the presence and type of electrical charge on an object.
Law of Electric Charges
Objects that have like charges repel each other
Objects that have opposite charges attract each other
Charging
Charging by Friction
When two different neutral materials come in contact and electric charges are transferred
Charging by Conduction
Charging an object by contact with a charged object
Charging by Induction
Charging a neutral object by bringing a charged object close to the original object
Grounding
Connecting an object to a large body that is capable of removing an electric charge
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors
Materials that electrons move easily through it

Eg: Silver, Copper, Gold
Insulators
Materials that electrons can't easily move through

Eg: Oil, Rubber, Silk
Electrical Discharge
The rapid transfer of electrons from one object to another
Current Electricity
The controlled flow of electrons through a conductor
Electric Circuits
A continuous path in which electrons can flow
Parts of a circuit
Load
The part of an electric circuit that converts electrons into other forms of energy
Switch
A device in an electric circuit that controls the flow of electrons by opening or closing the circuit
Electric Cells
A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
Types of Cells
Primary Cells
Can only be used once
Secondary Cells
Are re-usable

Eg: Circuit Symbols
Series Circuit
A circuit in which the loads are connected end to end
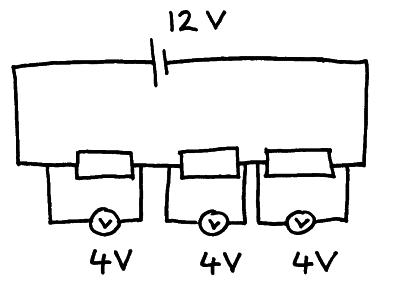
Eg: Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit

Eg: Parallel Circuit
A circuit in which the loads are connected by branches
Forms of Current Electricity
Direct Current
A flow of electrons in one direction in an electric circuit
Alternating Current
A flow of electrons that alternates in direction in an electric circuit
Measuring Current
An ammeter connected in series (amperes)
Measuring Voltage
A voltmeter connected in parallel (volts)
Resistance
The ability of a material to oppose the flow of electric current (ohms)
Measured with an ohmmeter
Ohm's Law
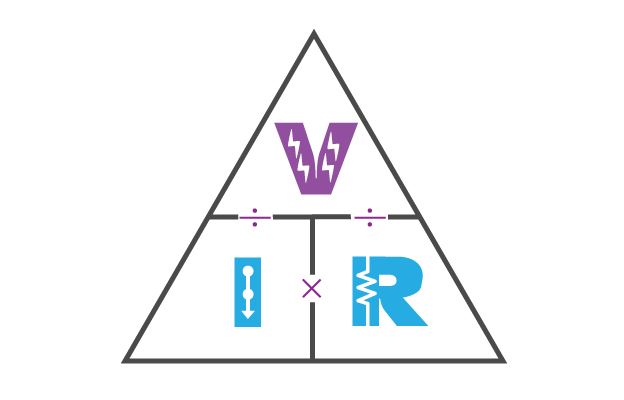
Eg: Ohm's Law's Formula
V = I x R
I = V/R
R = V/I