1]Sets is a collection of well
defined elements in its own right
N : the set of all natural numbers
Z : the set of all integers
R : the sets of all realnumbers
Z+ : the set of all positive integers
Q :the set of all rational numbers
Q+ :the set of al l positive rational numbers
R+ : the set of all positive real numbers
1]Sets are usually denoted by capital letters A S D E F L P
2]The elements of a sets are denoted by small letters a d e k
3] If 'a' is a element of set A then we say "a belongs to A" if no we say 'not belongs to'
SETS can be represented in to forms
*Roster form or Tabular form {12345}
*Set builder form{x:x is a positive integer}
in roster form the order in which elements are isted are immaterial
In roster form elements ae not generally repeated ex: SCHOOL={S,C,H,O,L}
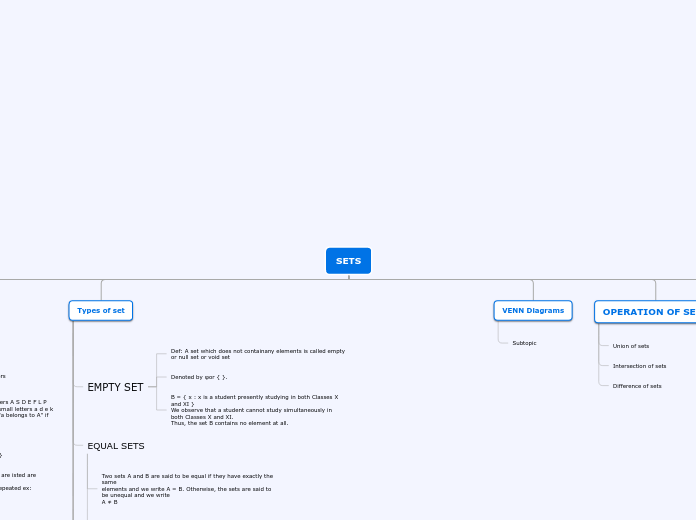
EMPTY SET
Def: A set which does not containany elements is called empty
or null set or void set
Denoted by φor { }.
B = { x : x is a student presently studying in both Classes X and XI }
We observe that a student cannot study simultaneously in both Classes X and XI.
Thus, the set B contains no element at all.
EQUAL SETS
Two sets A and B are said to be equal if they have exactly the same
elements and we write A = B. Otherwise, the sets are said to be unequal and we write
A ≠ B
A set does not change if one or more elements of the set are repeated.
For example, the sets A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {2, 2, 1, 3, 3} are equal, since each element of A is in B and vice-versa. That is why we generally do not repeat any
element in describing a set.
SUBSETS
Definition 4 A set A is said to be a subset of a set B if every element of A is also an
element of B.
In other words, A ⊂ B if whenever a ∈ A, then a ∈ B. It is often convenient to
use the symbol “⇒” which means implies. Using this symbol, we can write the definiton
of subset as follows:
A ⊂ B if a ∈ A ⇒ a ∈ B
If A is not a subset of B, we write A ⊄ B.
A ⊂ B and B ⊂ A ⇔ A = B,
INTERVALS OF SUB SET
Open interval
the interval which not contain end points
Roster form: (a, b)
set builder form:{ y : a < y < b}
Close interval
the interval which contain end points
Roster form:[ a, b]
set builder form:{x : a ≤ x ≤ b}
POWER SETS
The collection of all subsets of a set A is called the power set of A. It is
denoted by P(A). In P(A), every element is a set
Thus, as in above, if A = { 1, 2 }, then
P( A ) = { φ,{ 1 }, { 2 }, { 1,2 }}
Also, note that n [ P (A) ] = 4 = 22
In general, if A is a set with n(A) = m, then it can be shown that
n [ P(A)] = 2m
UNIVERSAL SET
The universal set is usually denoted by U, and all its
subsets by the letters A, B, C, etc.
FINITE and ININITE SETS
A set which is empty or consists of a definite number of elements is
called finite otherwise, the set is called infinit
CMPLEMENT OF SETS
Let U be the universal set and A a subset of U. Then the complement of
A is the set of all elements of U which are not the elements of A. Symbolically, we
write A′ to denote the complement of A with respect to U. Thus,
A′ = {x : x ∈ U and x ∉ A }. Obviously A′ = U – A
Subtopic
Union of sets
Intersection of sets
Difference of sets