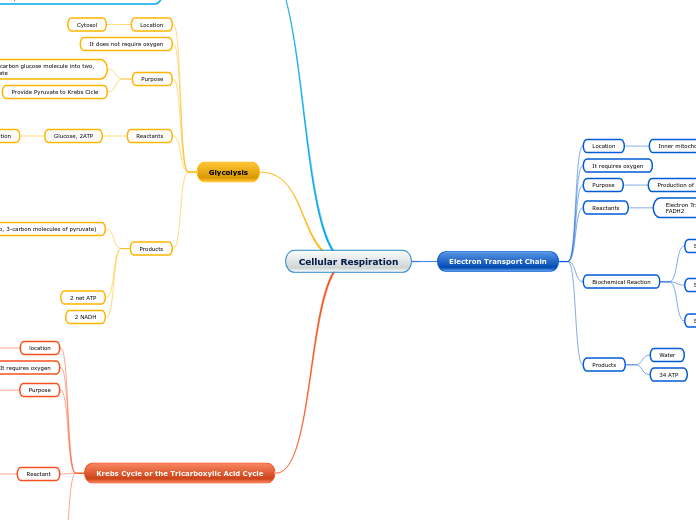
Location
Inner mitochondrial membrane
It requires oxygen
Purpose
Production of ATPs
Reactants
Electron Transport reactants: Hydrogen ions, oxygen, NADH, FADH2
Biochemical Reaction
Step 1
Electron transport
At complex I, the oxidation of NADH causes an electron to be removed. This electron is carried to complex IV. The electron combines with O2 to produce water. The potential energy stored in the electron is used to move protons at three separated complexes into the intermembrane space
Step 2
Hydrogen Ion Pumping
FADH2 is oxidized. The energy causes the flow of electrons through the inner mitochondrial membrane in an electron transport chain proteins at complex II
Step 3
ATP production
The proton gradient is used by the ATP Synthase. The potential gradient is converted to chemical potential to ATP. This reaction is called oxidative phosphorylation ( potential energy from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2.
Products
Water
34 ATP
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.
It occurs in all living organisms
Cellular Respiration : C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Three Cellular Respiration steps: Glycolysis, The Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain
Location
Cytosol
It does not require oxygen
Purpose
A partial breakdown of a six-carbon glucose molecule into two, 3-carbon molecules of pyruvate
Provide Pyruvate to Krebs Cicle
Reactants
Glucose, 2ATP
Biochemical Reaction
Step 1.Priming Reaction
Step 2. Cleavage Reaction
Step 3. Energy Harvest Reaction
Products
Piruvate (two, 3-carbon molecules of pyruvate)
Anaerobic conditions (without oxygen)
Lactate Fermentation
Bacteria- Muscles
2 ATP
2 Lactate
It generates muscle lesion
Alcohol Fermentation
Yest
Carbon dioxide as by-products
Sugars to ethanol
Aerobic Conditions
Krebs Cycle
2 net ATP
2 NADH
location
Mitochondrial Matrix
It requires oxygen
Purpose
Generate energy through the oxidization of acetate—derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins —into carbon dioxide.
Reactant
Piruvate
Biochemical Reaction
Piruvate is oxidized to Acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA
Eight Steps
Six carbon molecule formed from Acetyl CoA
One carbon is lost as CO2/NAD+ to NADH
Second Carbon is lost as CO2/NAD+ to NADH
Energy- carrying molecule equivalent to ATP
Reduced electron carrier FADH2
/NAD+ to NADH
4-carbon molecule (Oxaloacetate)
Products
Electron Carriers (NADH and FADH2)
2 ATP
Carbon Dioxide.