Chemistry
Physical Properties
Malleable
Ability to be hammered and shaped
Ductile
Ability to bee shaped into a wire
State
Different forms that matter can exist

Solubility
Ability to dissolve in another substance
Conductivity
Ability to conduct electtricity
Matter
Pure substance
Consists of one type of atom. Can be an element or a compound
Compound
Two or more elements chemically combined together
Bond
Ionic Compound
st
Ion
An atom with a charge by giving or receiving an electron
Cation
Positively charged ion
Anion
Negatively charged ion
Polyatomic Ion
A polyatomic ion is different elements that act as a single ion
Ion Tests
Techniques to test for specific ions within a substance
Covalent bond
A chemical bond between atoms by sharing electrons
Diatomic Atom
Consists of only 2 atoms bonded together
Acids and Bases
Acid
An acid is a compound with special properties. Some acids can be harmful to humans while others can be useful or essential. Acids have a pH rating of less than 7
Base
A base is a compound with special properties. Some bases can be harmful to humans while other can be useful or essential. Bases have a pH rating of more than 7
pH Scale
A pH scale is a number scale that measures the acidity or basicity of a substance
Neutral
Substances with a pH ratting of 7 is neither an acid or a base

Indicator
An acid-base indicator is a substance that changes colour if acid or base is present.

Mixture
A combination of pure substances
Homogenous mixture
A homogenous mixture looks visibly the same throughout
Heterogenous mixture
A heterogenous mixture has visible different parts

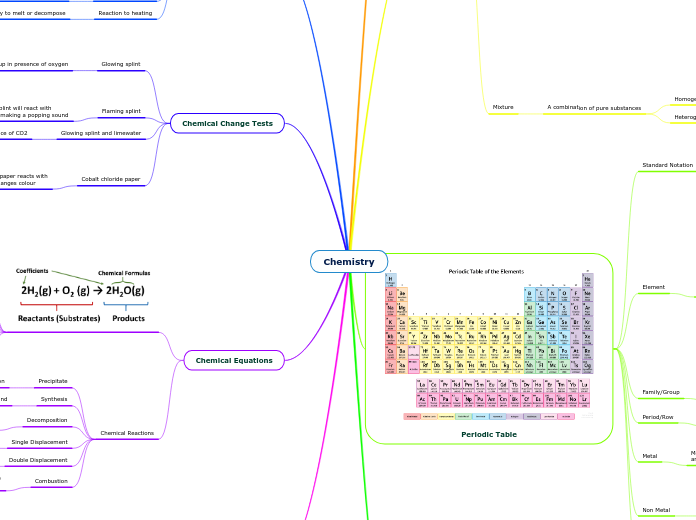
Periodic Table
Standard Notation

Atomic Number
The number of protons in an element
Atomic Mass
The average weight of an element
Chemical Symbol
One or two letters that represent an element
Element
Substance that can not be broken down into a simpler substance
Proton
Subatomic particle with a positive charge
Neutron
Subatomic particle with a neutral charge
Electron
Subatomic particle with a negative charge
Bohr diagram
Represents an elements orbiting electrons around a nucleus

Shells
Group of electrons orbiting around a nucleus
Valence electron
Number of electrons in the outer shell
Family/Group
Elements in a family/group have similar characteristics and same number of valence electrons
Period/Row
Elements in a period are organized in an order increasing in valence electrons
Metal
Metals are lustrous, good conductors of electricity and heat, malleable, and ductile elements
Alkaline Metal
Soft, silver-grey metals that react easily with water and with oxygen in the air in group 1 of the periodic table.
Alkaline Earth Metal
Silver-grey metals that are harder and less reactive than group 1 metals in group 2 of the periodic table.
Non Metal
Non metals lack the characteristics of metals
Halogen
Coloured non-metals that are very reactive in group 7 of the periodic table.
Noble Gas
Non-metals that are colourless, odourless gases and very unreactive in group 8 of the periodic table.
Metalloid
Metalloids have a mixture of properties of metals and non metals
Nomenclature
Binary
Composed of 2 different ions metal and non metal.
The cation is written first and the anion is written second
The name of the cation is the same
The suffix- ide is added to the root name of the anion element
Multivalent Metals
Multivalent metals are atoms that can have multiple ions
The name of a multivalent metal has a roman numeral indicating the charge
Molecular/Covalent
Formed when a non-metal combines with a non-metal. A molecule is a group of atoms formed by a covalent bond.
Numerical prefixes are used to indicate the number of each element present in a compound
The suffix- ide is added to the root of the second element
Chemical Properties
Ability to burn
Combustion (flame, heat, light)
Flash point
The lowest temperature at which a flammable liquid in the air ignites
Behaviour in air
Ability to degrade, react, or tarnish
Reaction with water
Ability to corrode or dissolve
Reaction to heating
Ability to melt or decompose
Chemical Change Tests
Glowing splint
Glowing ember will light up in presence of oxygen

Flaming splint
Flaming splint will react with hydrogen making a popping sound
Glowing splint and limewater
Glowing splint will go out in presence of CO2
Cobalt chloride paper
Blue cobalt chloride paper reacts with water vapour and changes colour

Subtopic
Chemical Equations
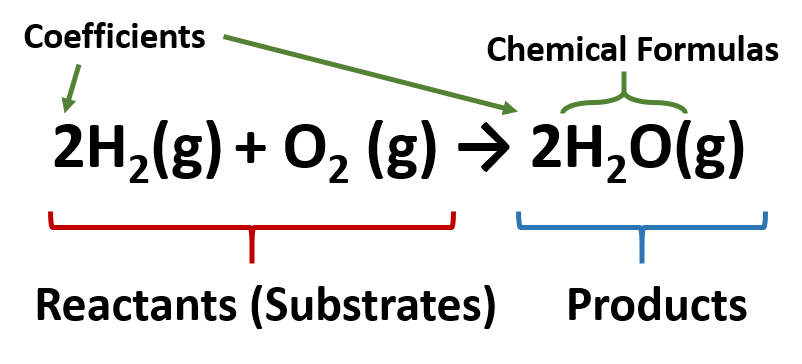
Reactant
Reactants are starting materials that undergo cheemical change
Product
Products are the ending materials that have different properties than the reactants
Coefficient
Coefficients are numbers before a chemical symbol that represents the number of atoms or molecules in a reaction.
Law of Conservation Mass
Matter cannot be created or destroyed
Skeleton Equation
Skeleton equations use formulas to represent the substances in a reaction
Balanced Equation
Balanced equations have an equal amount of atoms and molecules on the right and left side of the equation
Chemical Reactions
Precipitate
Process that forms a solid from a solution
Synthesis
Two or more elements combine to form a compound
Decomposition
A compound breaks down into elements and/or simpler compounds
Single Displacement
An element replaces another element in a compound
Double Displacement
Two compounds switch parts with one another
Combustion
A fuel reacts with oxygen to release carbon dioxide, water, and heat
Water
Water Quality
Water quality is the condition of the water. It includes the physical and chemical characteristics.
Hard water
High in dissolved minerals mainly calcium and magnesium
Soft Water
Low in dissolved minerals mainly calcium and magnesium
Filtration
Process that removes physical particles and contaminants to create safe and clean drinking water.
Coliforms
Coliforms are bacteria that is found in digestive tracts of animals.
Dissolved oxygen
Dissolved oxygen is the amount of oxygen in the water