
Geometric Concepts

Geometric Content

Polygon

Circle
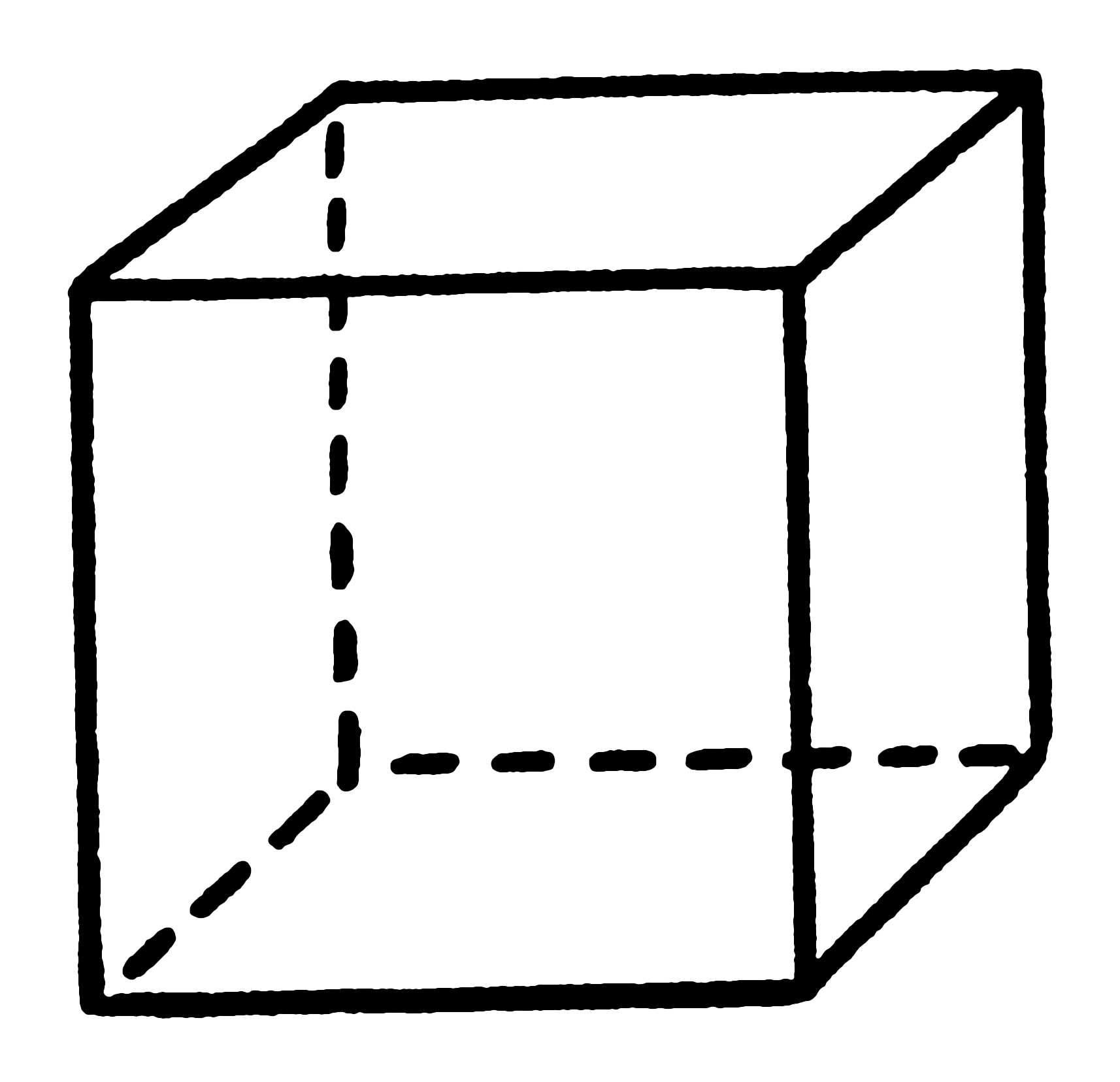
Box, Cylinder, and Cube
Coordinate geometry
Main topic
Level 0: Visualization
Level 1: Analysis
Level 3: Deduction
Level 4: Rigor
Characteristics of the van Hiele Levels:

Goal:The student will demonstrate the ability to solve mathematical and real-world problems using measurement and geometric models and will justify solutions and explain processes used. The student will represent and analyze two- and three-dimensional figures using tools and technology when appropriate.


Polygon
Area of a Polygon: A=bh (base X height)perimeter: all sides added together

Circle
The Area of a Circle is: A = π × r2

Box, Cylinder, and Cube
Box or Cube:V=l X w X hCylinder:V = πr2h
Coordinate geometry
To introduce the idea, consider the grid on the right. The columns of the grid are lettered A,B,C etc.The rows are numbered 1,2,3 etc from the top. We can see that the X is in box D3; that is, column D, row 3.D and 3 are called the coordinates of the box. It has two parts: the row and the column.There are many boxes in each row and many boxes in each column. But by having both we can find one single box,where the row and column intersect
Figures shown in the same color are similar Two geometrical objects are called similar if they both have the same shape, or one has the same shape as the mirror image of the other.
Level 1: Analysis
The objects of thoughts at level 1 are classes of shapes rather than individual shapes.
Level 2: Informal Deduction
The objects of thought at level 2 are the properties of shapes.*Students can develop relationships between these poperties
Level 3: Deduction
The objects of thought at level 3 are relationships between properties of geometric objects.
Level 4: Rigor
The objects of thought at level 4 are deductive axiomatic systems for geometry.
Characteristics of the van Hiele Levels:
Levels are not age dependentadvancement through the levels requires geometric experiences.