Threads communicate with each other
through functions which are implemented
as final and called within synchronized context-
wait()
Tells calling
thread to
give up monitor
and go to sleep.
notify()
Wakes up first
thread that
called wait().
notifyAll()
Wakes up all
the threads
that called
wait().
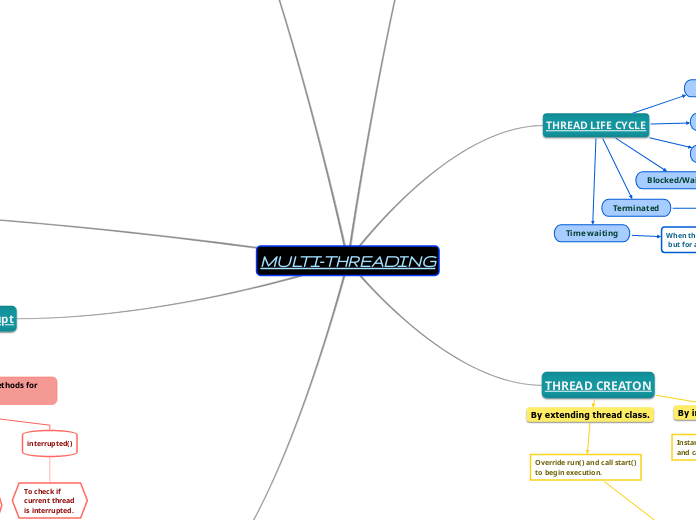
New
Born thread in new state- before invoking of start().
Runnable
When new born thread is started.
Running
A thread scheduler selects the thread, it becomes running.
Blocked/Waiting
When the thread is inactive for a span of time.
Terminated
Run() exits normally or any unusual error occurs.
Time waiting
When the thread is waiting for a resource
but for a given time interval.
By implementing runnable interface
Instantiate object of type thread
and call start() to execute run().
Common Methods of runnable interface
Run()
To perform actions
for a thread.
By extending thread class.
Override run() and call start()
to begin execution.
Common Methods of thread class
getPriority()
Obtain a threads priority
start()
Start a thread by calling
run().
sleep()
Suspend thread for a
period of time.
run()
Entry point for thread.
join()
Wait for thread to
terminate.
isAlive()
Determine if
thread is still
running.
getName()
Obtain a threads name.
The capability to control the access of
multiple threads to any shared resource.
Leads to Deadlock
Use join().
Avoid nested locks.
Avoid unnecessary locks.
Why use Synchronization
To prevent race condition.
To prevent consistency problem.
To prevent thread interference.
Types
Process
Synchronization
Thread
Synchronization
Types
Mutual Exclusive
Achieved using
Synchronized Method
Used to lock an object
for any shared resource.
Static Synchronization
To make any static method,
as synchronized lock will be
on the class not object.
Synchronized block
To lock an object for any
shared resource, scope is
smaller than method.
Uses synchronized keyword.
Cooperation
Networking
Games
Image Processing
Websites
Animations
Data Processing
Thread class provides three methods for interrupting a thread
interrupt()
To set the
interrupt
flag for a
thread.
isinterrupted()
To check if
interrupt flag
has been set for
a thread.
interrupted()
To check if
current thread
is interrupted.
Execution of multiple threads
(tasks) at same time
Advantages
1) Greater CPU utilization.
2) Improved throughput.
3) Utilization of multiprocessor
architecture.
4) Better resource utilization.
5) Improved user experience.
Disadvantages
1) May lead to deadlock.
2) Increases code complexity.
3) Synchronization overhead.
4) Increased memory usage.