Organic chemistry
Phospholipids

phosphoglyceride
glucerol + 2 fatty acids + PO4 + amino alcohol

spingolipids
glycerol + 1 fatty acid + PO4 + amino alcohol
hormones
Steroid

Cholesterol
most abundant steroid in body
Cause clogged blood vessel

Polymer
Polymers are materials made of long, repeating chains of molecules.
ex) DNA, clothing, fibers

condensation
Nyloin, Dacron, etc
addition
teflon, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride
Nucleic acid

DNA
hold genetic code
2 nucleic acid through hydrogen bond
A-T, G-C
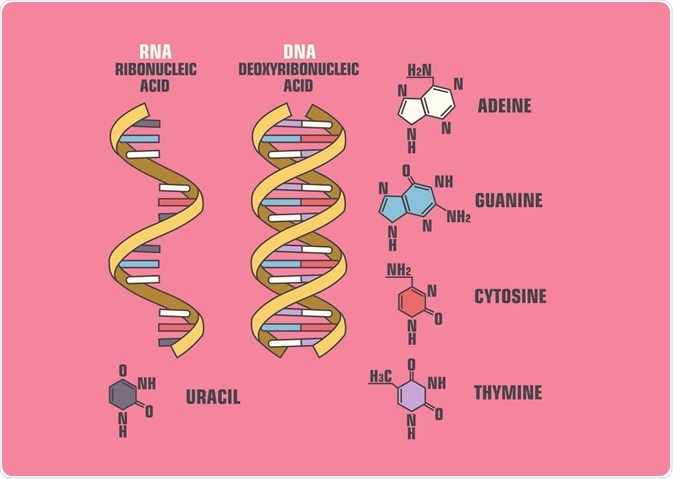
RNA
hold genetic code
decomposes once it was used
help synthesis of proteins
References
Elcias, A. (2019). Matter and sustainability. Presentation, Mexico.
Alina. B. (2017, Oct 13). What is polymers?. Retrieved April 28 from https://www.livescience.com/60682-polymers.html
Benedette. C. (2019, Feb 2). What is RNA?. Retrieved April 28 from https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-is-RNA.aspx
Macromolecule
huge molecules
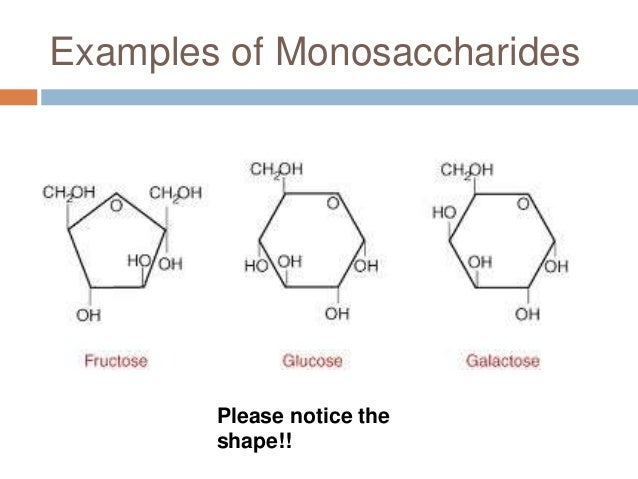
ex) fructose, glucose, galactose
Proteins
Bigger chain than peptide bonds
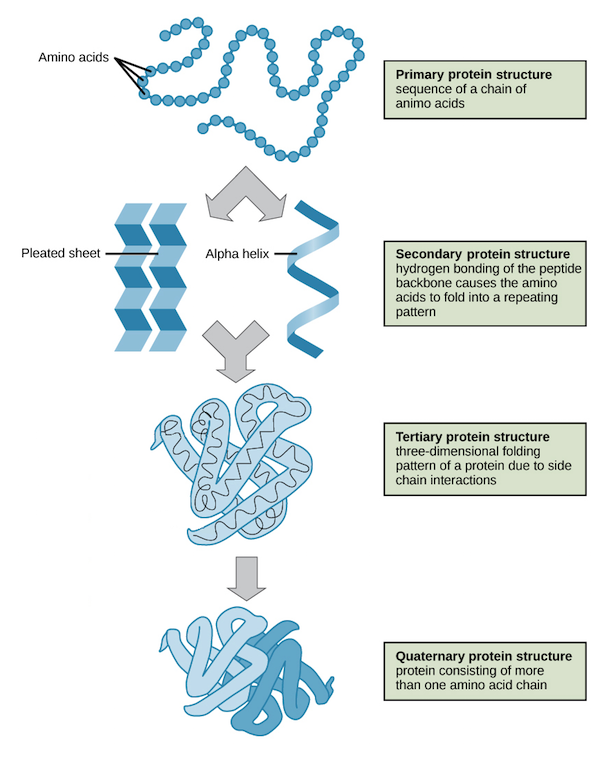
primary-secondary-teritary-quaternary
Example: fibruous,globular, and membrane
amino acids

Peptide
have 50 or less amino acids
amino acid+amino acids
Amine + carboxylic acids
ex) serine, lysine, phenylalanine
Carbohydrates
polysaccharides
ten, hundreads, thousands of simple sugars connected
Monosaccharides
simple carbohydrates
sugars in fruits, milk, vegetables
complex carbohydrate
bread, cereal, starch
Lipids
Fatty Acids
Unsaturated fatty acid: low melting point, liquid at room temperature, fewer interaction between bonds
saturated fatty acid: high melting point, solid at room temperature, strong interaction between bonds
long chain carboxylic acids: typically 12 to 18 carbon atoms
Cis and trans
isomerism through the hydrogenation of fats
triglyceride
3 fatty acids + glycerol

ex) butter, oil, cholesterol