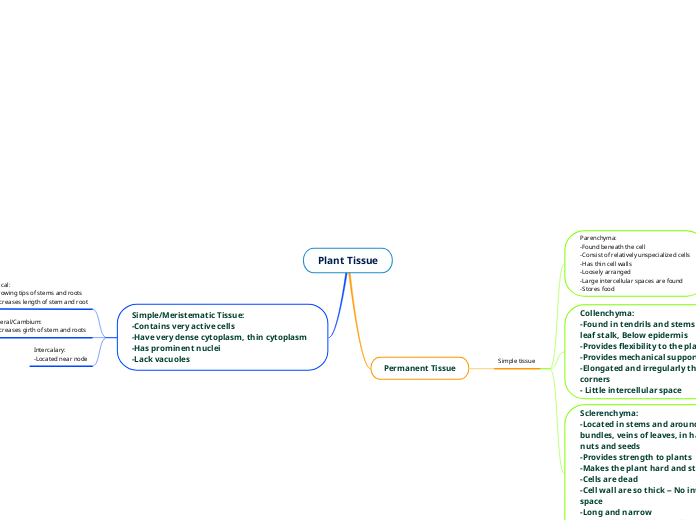
Plant Tissue
Permanent Tissue
Simple tissue
Parenchyma:
-Found beneath the cell
-Consist of relatively unspecialized cells
-Has thin cell walls
-Loosely arranged
-Large intercellular spaces are found
-Stores food
Chlorenchyma:
-Parenchyma that contains chlorophyll ad performs photosynthesis
Aerenchyma:
-Parenchyma with large air cavities, allowing them to float
Collenchyma:
-Found in tendrils and stems of plants or leaf stalk, Below epidermis
-Provides flexibility to the plants
-Provides mechanical support
-Elongated and irregularly thickened at corners
- Little intercellular space
Sclerenchyma:
-Located in stems and around vascular bundles, veins of leaves, in hard covering of nuts and seeds
-Provides strength to plants
-Makes the plant hard and stiff
-Cells are dead
-Cell wall are so thick -- No intercellular space
-Long and narrow
- Walls thickened due to *lignin*
-Example-- Husk of cocunut
Simple/Meristematic Tissue:
-Contains very active cells
-Have very dense cytoplasm, thin cytoplasm
-Has prominent nuclei
-Lack vacuoles
Apical:
-Growing tips of stems and roots
-Increases length of stem and root
Lateral/Cambium:
-Increases girth of stem and roots
Intercalary:
-Located near node