Diversity of Living Things

Archaebacteria - Euryarchaeota
Nutrition: heterotrophic which means it turns sulfur, hydrogen and carbon dioxide into methane
Shape and Size: Cocci, bacilli, cell wall made of pseudopeptidoglycan or protein, some cells do not have a cell wall
Reproduction: binary fission but mostly depend on the condition of the environment. The better it is, the more they reproduce
Environment: live in extreme condition such as really cold or hot or deep in the ocean
Genetic Material: RNA tightly wounded together inside of the cell with the DNA
Classification: it can be either gram positive (purple) or gram negative (pick) depending if the cell wall has pseudomurein

Eubacteria - Cyanobacteria
Size and Shape: round shape, 1/10 or 1/20 size of a eukaryotic cell, may live single or in pairs, larger then a virus
Organelles: no mitochondria, no chloroplast, no golgi, presence of only ribosomes
Reproduction: Binary fission, multiple fission, spore and fragmentation
Binary Fission reproduction
Nutrition: autotrophic, photosynthetic and chemosynthetic
Genetic Material: the DNA in cyanobacteria
Taxonomy: Kingdom: Eubacteria Phylum: Cyanobacteria Class: Cyanophceae Order: Nostocales Family: Nostocaceae Genus: Cyanobacterium
Protista
Protozoa - Sarcodine (animal like protists which are classifed by their movements)
Taxonomy: Kingdom: Protozoa Phylum: Sarcodine Class: Rhizopoda Family: Amoebidae
Genus: Amoeba
Species: Proteus
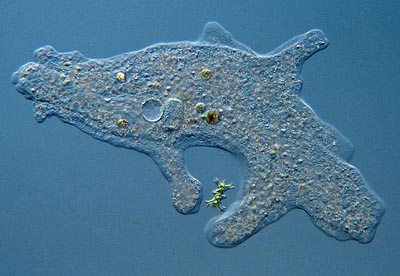
Characteristics: Move with ( false feet) pseudopodia, some have shell or covering called a test
Reproduction: binary fission or conjugation
Illnesses: malaria, diarrhea, fever, infection
Nutrition: heterotrophic which means they eat smaller bacteria
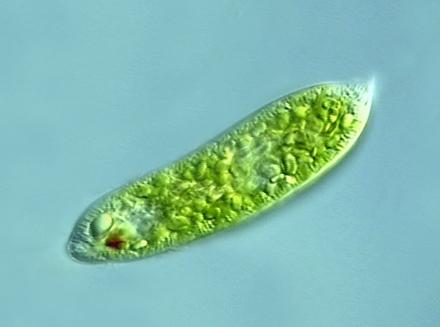
Algae - Euglenoids (Plant like protists)
Characteristics: found in fresh water ( toxic to fish), protein rich cell membrane, eye spot, they have animal like features
Nutrition: Autotrophic during day and heterothrophic during dark
Reproduction: Binary fission
Cell makeup:
reservoir,nucleus,contractile vacuole, pellicle, chloroplast,nucleolus, stigma, flagellum

Fungi - Myxomycota
Characteristics: not true fungi ( lack a cell wall), like plants and animal protista
Reproduction: formation of spore which is moves by an insect or wind to fertilize
Nutrition: Engulfing small plants into their cytoplasm, heterotrophic
Taxonomy: Kingdom: fungi
Phylum:amoebozoa
Class: Myxomycetes
Order: Liceales
Family:Reticulariaceae
Genus: lycogala
Species: Epidendrum
Plant kingdom
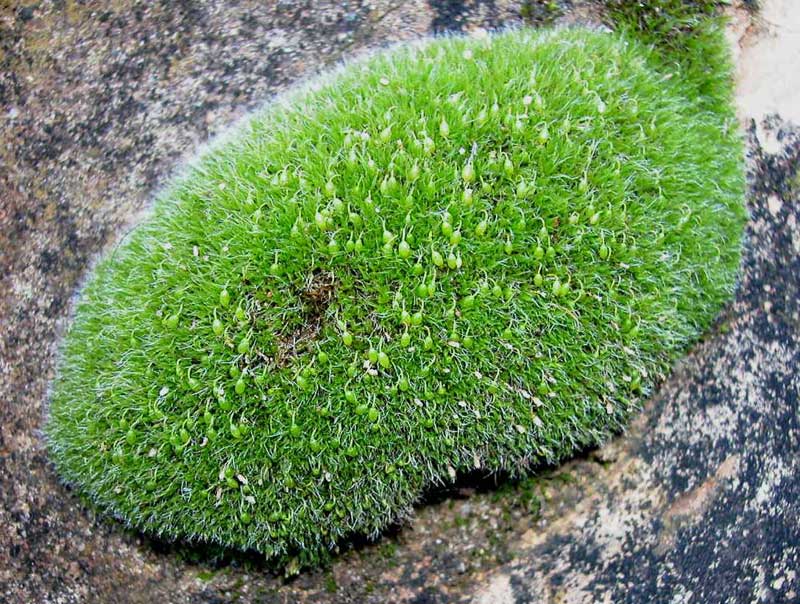

Bryophyte
Reproduction: male and female gametophte knows as archegonium (f) and antheridium (m) fertilizes to make zygote in archegonium
Characteristics: non-vascular, thin or short leaves and grows in shady or moist places
Other kinds of the phylum can be moss, liverworts and hornworts
Nutrition: get food from environment or the soil
Taxonomy: Phyum: Bryophyta
Class: Bryophyta (mosses)
Order: Bryales
Family: Bryaceae
Genus: Bryum Hedw. – bryum moss
Species: Bryum caespiticium Hedw. – dry calcareous bryum moss

Gymnosperm
Nutrition: photosysthesis, CO2 and H2O which they turn into glucose by the help of sun
Characteristics: nakes seeds whch means no outer coverings parts for the seeds, no flower and no fruit
Reproduction: pollinates by the winds which reproduces diploid zygote
Phyla: Coniferophyta, Ginkgophyta, Gnetophyta
Animalia Kingdom

Chordate
Nutrition: they are predictors which means they feed on other animals and they are called heterotrophic
Taxonomy: Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum:Chordata
Class:Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish)
Order:Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays)
Family:Selachii
Genus:Carcharodon
Species:carcharia
Reproduction: Sexual and asexual where they buddy a part of themselves called parthenogenesis
Characteristics: vertebrates, mammals, fishes and bilateral symmetry
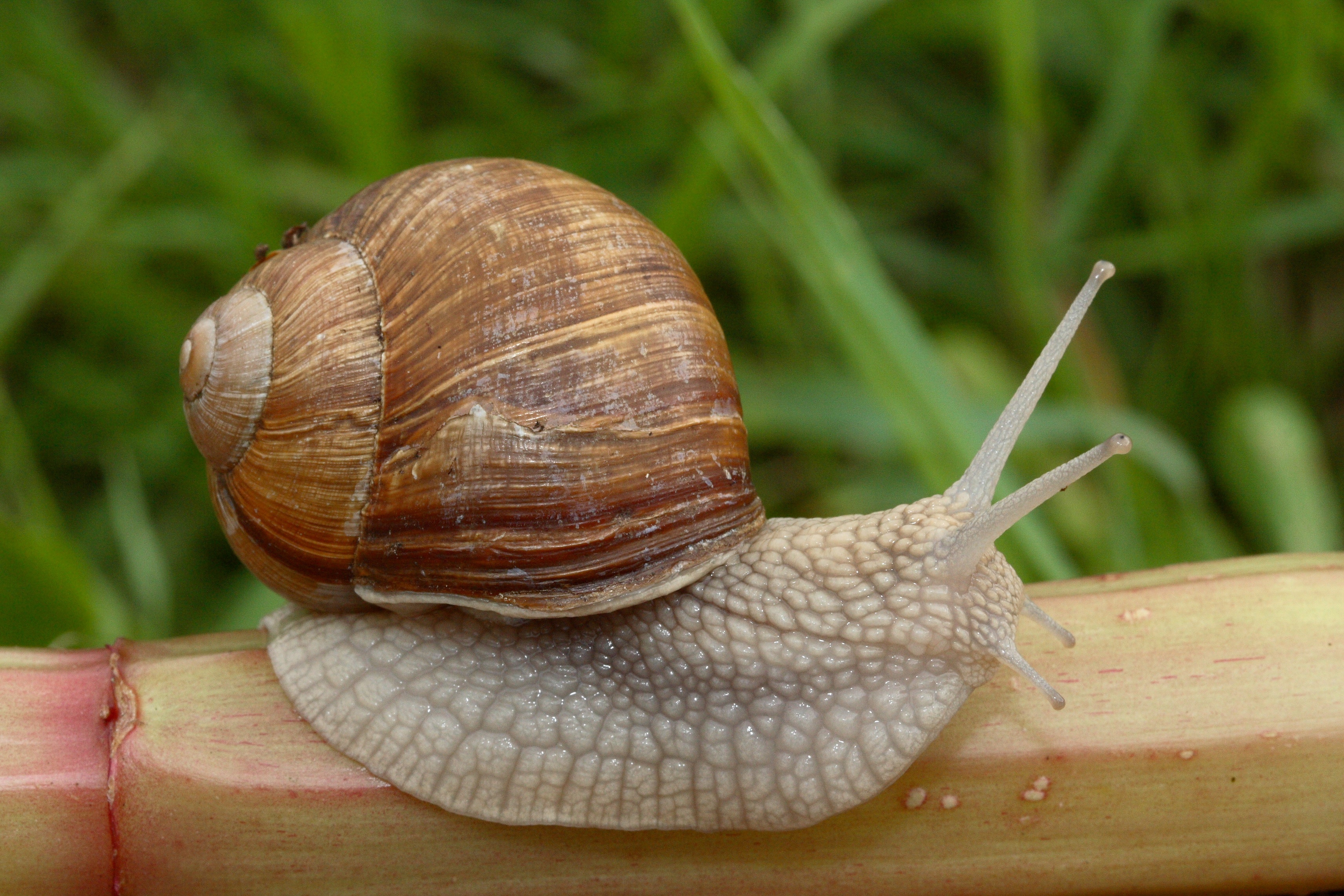

Mollusc
Reproduction: secxual reproduction only
Characteristics: no vertebrate, presence of mantle, two openings and bilateral symmetry
Nutrition: heterotrophic, they are preditors
Taxonomy: Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Cephalopoda Order: Teuthida Family: Loliginidae Genus: Logilo Species: brevipenna
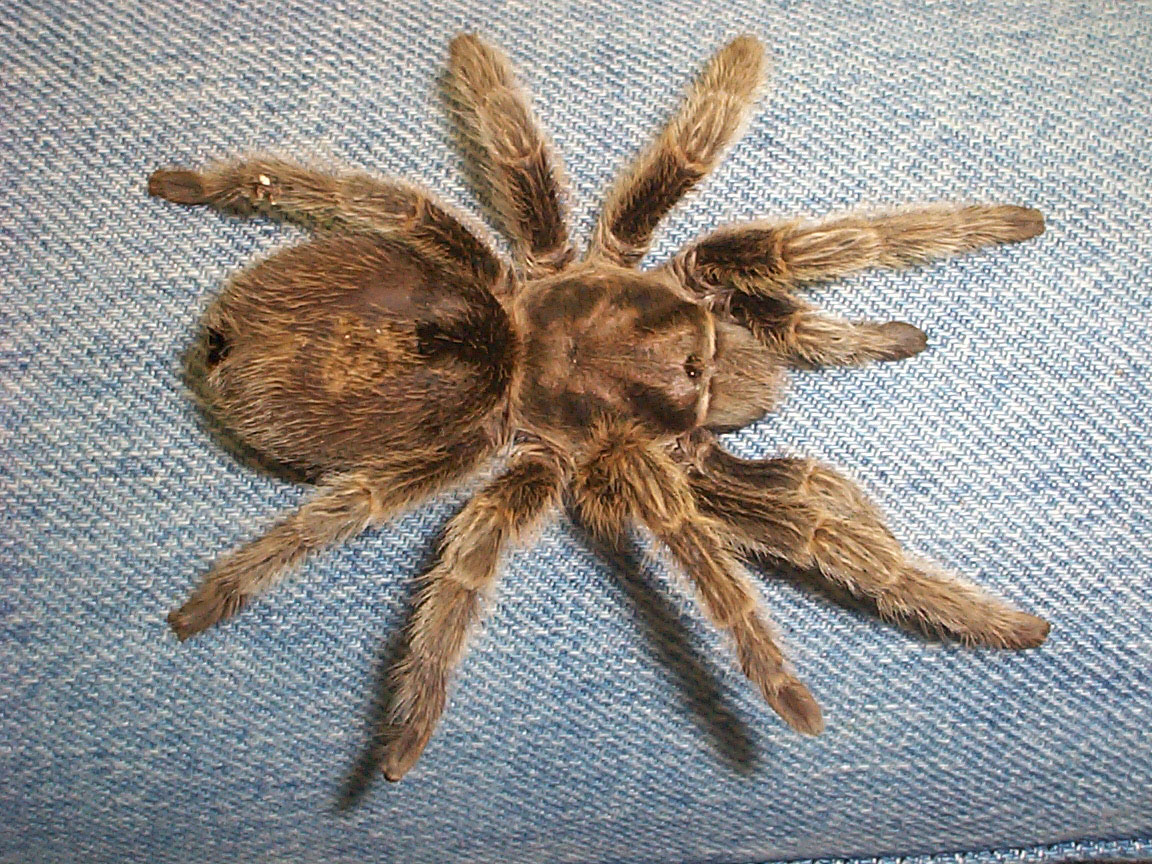

Arthropods
Reproduction: Sexual reproduction
Characteristics: they breathe through organs that are called book lungs and they are exoskeleton creatures
Nutrition: They are predictors, they use their fangs to catch the prey
Taxonomy: Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Arachnido Order: Araneae Family: Sicariidae Genus: Loxosceles redusa
Fungi Kingdom

Deuteromycota also knows as Fungi Imperfecti
Nutrition: heterotrophic and our food can be excellent nutrition for them
Reproduction: Asexual reproduction by spores
Characteristics: the size vary in size and shape from small (2-3 microns long) to large (250-300 microns long)

Chytrids
Characteristics; unicellular and can be found in fresh water and marine ecosystem
Reproduction: sexually ( spores with flagella) and axesually
Indirect impact on human is Synchytrium endobioticum, parasite that effects potatoes.
Potatoes can not be sold afterwards
An example for chytrid species can be Allomyces