Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Investment
2 ATP + 1 Glucose
Payoff
2 NADH + 4 ATP
2 Pyruvate
Aerobic
Occurs in Cytoplasm
Anaerobic
Alcohol or Lactic Acid Fermentation
Liver
Oxidized into Pyruvate

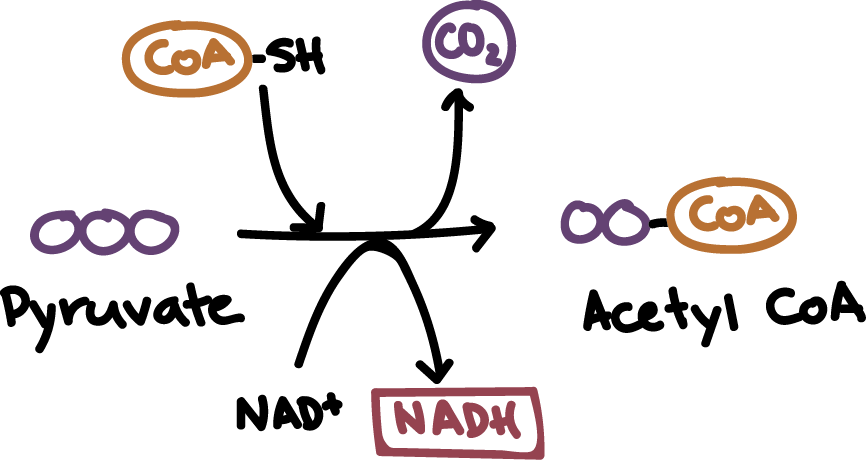
Pyruvate Oxidation
Step1: Carboxyl group removed
Released as 1 CO2 per pyruvate
Step 2: Oxidized
Step 3: Acetyl group transfered to coenzyme A
2 Acetyl CoA
Krebs Cycle
Occurs in mitochondrial Matrix
2 acetyl CoA enter for every glucose molecule
Oxaloacetate
Citric Acid
Loses carbons as CO2
REDOX Reaction
NADH and FADH2 carry hydrogen
Spins Twice
2 CO2+ 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 +1 ATP produced for each spin
NADH, FADH2
Releases waste CO2

Electron Transport Chain
Complex I
NADH
8 Protons pumped out
Q
Complex II
FADH2
12 Protons pumped out
Complex III
12 Protons pumped out
C
Oxygen
Water
Occurs across inner mitochondrial membrane


Chemiosmosis
Complex IV

Mitochondria
Intermembrane Space
Concentration Gradient