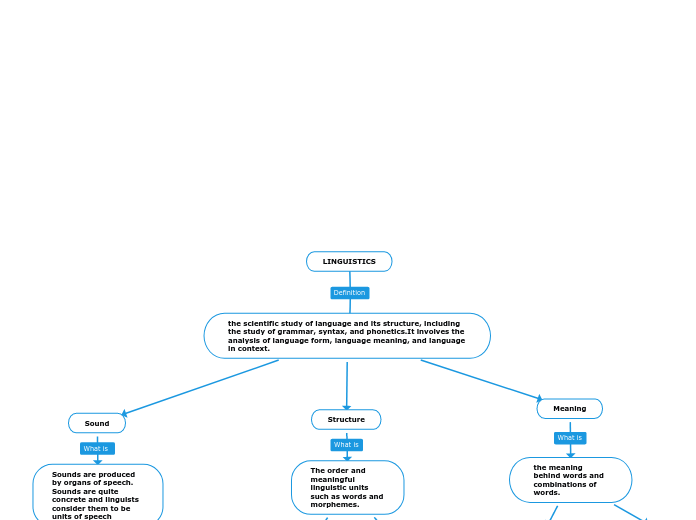
Sound
Sounds are produced by organs of speech. Sounds are quite concrete and linguists consider them to be units of speech
Phonology
Phonology is concerned with the linguistic abstractions and categorizations of sounds.
Phonetics
Phonetics is largely concerned with the physical aspects of sounds such as their acoustics, production, and perception.
Structure
The order and meaningful linguistic units such as words and morphemes.
Morphology
Morphologists study similar rules for the order of morphemes—sub-word units such as prefixes and suffixes—and how they may be combined to form words.
Syntax
The study of sentences and their order. How sentences are formed out of words.
Meaning
the meaning behind words and combinations of words.
Semantics
Examines meaning that is conventional or "coded" in a given language, pragmatics studies how the transmission of meaning depends not only on structural and linguistic knowledge of the speaker and listener but also on the context of the utterance. Homophones-homonyms
Pragmatics
Pragmatics encompasses speech act theory, conversational implicature, talk in interaction and other approaches to language behavior in philosophy, sociology, linguistics and anthropology