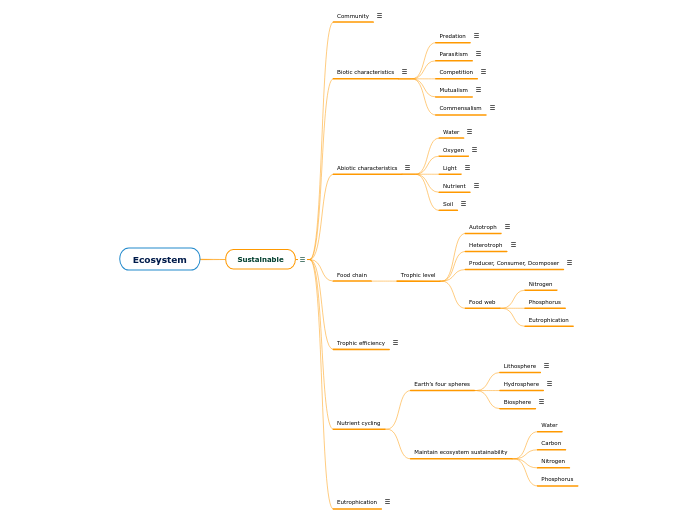
To be able to be maintained for a very long time; i.e., lots of resources for now and in the future because they arenot being overused or depleted; a stable way of life.Ex: Solar energy: Electromagnetic radiation from the sun can produce electricity and heat.Wind energy: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind energy into mechanical energy.
dCommunity
Community: Only biotic (living) populations interacting in an area.Ecosystem: Biotic & abiotic (living & nonliving) components interacting in an area.Both: Involve biotic components.
Biotic characteristics
Within ecosystems, different living species interact. Sometimes interactions benefit species, but sometimes not.
Predation
One species hunts & kills another. Ex:Wolves hunting moose, owls hunting mice.Ex: Rabbit ear grass, fox eat rabbit, bear eat fox.
dParasitism
Relationship between two species of plants or animals in which one benefits at the expense of the other. Ex:Ticks, Fleas, Leeches
dCompetition
The activity or condition of competing. Ex: Two male birds of the same species might compete for mates in the same area.
dMutualism
A symbiotic relationship in which all participating species benefit from their interaction. Ex: Pistol shrimps and gobies, Aphids and ants.
dCommensalism
An association between two organisms in which one species benefits and the other neither benefits nor suffers.
dAbiotic characteristics
Certain nonliving components are essential to ecosystem sustainability.
Water
Plants need water to make food via photosynthesis.Animals need water to allow cell reactions; rid wasteHuman affect: Pollutions, Global warming, Overuse, Rerouting of waterways
Oxygen
Most living things need oxygen to make energy via the process of cellular respiration.Global warming warms the water, which reduces dissolved gases in the water.
Light
Plants, some bacteria and some protists need light to make food.smogindustrializationGlobal warmingThe forest fireDust stormsA volcanic eruption
Nutrient
All living things need nutrients like vitamins and minerals to grow healthily.Overexploitation, deforestation and extinction mean less decayThere are so few nutrients in the soilExcessive fertilization
Soil
Plants and fungi get nutrients and water from the soil.Animals, some bacteria and some protists need soil for their homes.
Food chain
Trophic level
Autotroph
Food organism an organism that uses light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals to produce its own foodExamples: trees, grass, seaweed, seaweed.All plants, some bacteria, some protists, the kingdom of living things, mainly small,Aquatic organisms such as algae).
dHeterotroph
An organism that feeds on other plants or animals for energy and nutrients.These organisms can't make their own food, they get their energy by eating other living things.Examples: mushrooms, fish, birds, humansIn other words, all animals, all fungi, most bacteria, most protists.
dProducer, Consumer, Dcomposer
They were being recycling.
dFood web
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Eutrophication
Trophic efficiency
A measure of the efficiency of energy flow between trophic levels in a food chain.Percentage of yield transferred from one nutrient level to the next.1. Every living thing uses energy for its own growth, reproduction and movement2. Some parts of the organism are inedible, so energy is obtained from these parts3. Some parts of the organism are indigestible, so they excrete even when eaten, with no energy transfer
dNutrient cycling
Earth’s four spheres
Lithosphere
The rocky outer part of the Earth.
dHydrosphere
The total amount of water on a planet.
dBiosphere
Made up of the parts of Earth where life exists.
dMaintain ecosystem sustainability
Water
Carbon
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Eutrophication
Overgrowth of plants and algae due to an increase in one or more growth-limiting factors required for photosynthesis.
d