- endurance cells
- react and use energy slowly so they can work for longer periods
ie. back muscles which contain slow twitch muscles to maintain your posture all day
- react instantly when triggered but quickly use up there energy and tire up
ie. a sprinter will accumulate more fast twitch muscles in their legs through continuous practice enabling themself to quickly if briefly pick up the pace
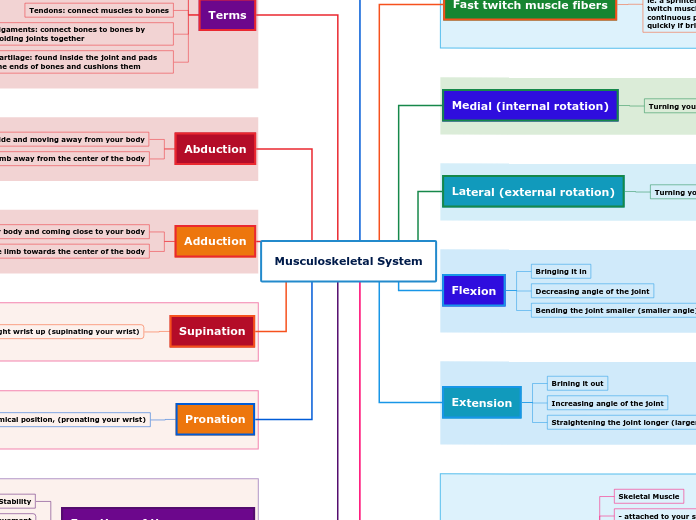
Turning your foot inward
Turning your foot outward
Bringing it in
Decreasing angle of the joint
Bending the joint smaller (smaller angle)
Brining it out
Increasing angle of the joint
Straightening the joint longer (larger angle)
Skeletal Muscle
- attached to your skeleton, voluntary
- stirated (walls of blood vessels and hollow organs) ie. spleen
Cardiac Muscle
- found in your heart, involuntary
- non-striated
ie. heart/myocardium
Smooth Muscle
- found in internal organs, involuntary
Bones- create the rigid framework that everything else uses
Muscles: pull on bones, allowing us to move
Tendons: connect muscles to bones
Ligaments: connect bones to bones by holding joints together
Cartilage: found inside the joint and pads the ends of bones and cushions them
Inside and moving away from your body
Moving the limb away from the center of the body
Moving away from your body and coming close to your body
Moving the limb towards the center of the body
Arms into anatomical position, turn your right wrist up (supinating your wrist)
Put your arms back into anatomical position, (pronating your wrist)
Stability
Movement
Shape (posture)
Support