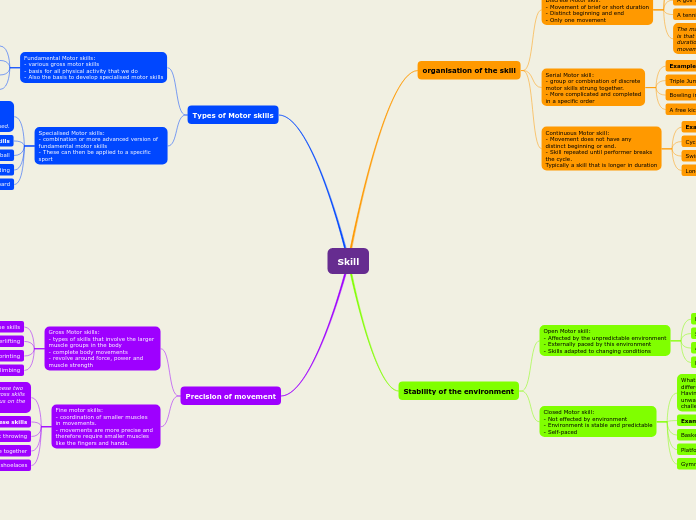
Discrete Motor skill:
- Movement of brief or short duration
- Distinct beginning and end
- Only one movement
Example of the skill
Pass in soccer
A golf swing
A tennis serve
The main difference between discrete and serial skills
is that the movements are more complicated and longer
duration. This is because serial movements and discrete
movements linked together.
Serial Motor skill:
- group or combination of discrete
motor skills strung together.
- More complicated and completed
in a specific order
Examples of the skill
Triple Jump
Bowling in cricket
A free kick in soccer
Continuous Motor skill:
- Movement does not have any
distinct beginning or end.
- Skill repeated until performer breaks
the cycle.
Typically a skill that is longer in duration
Examples of the skill
Cycling
Swimming
Long distance running
Open Motor skill:
- Affected by the unpredictable environment
- Externally paced by this environment
- Skills adapted to changing conditions
Examples of this skill
Shot for goal in AFL
A pass in hockey
Hitting a ball in baseball
Closed Motor skill:
- Not effected by environment
- Environment is stable and predictable
- Self-paced
What we can see from these two skills is the massive
difference in control and predictability for the participant.
Having to contend with the environment can also add extra unwanted pressure on the participant, making the skill more
challenging.
Examples of this skill
Basketball free throw
Platform diving
Gymnastics routine
Fundamental Motor skills:
- various gross motor skills
- basis for all physical activity that we do
- Also the basis to develop specialised motor skills
Examples of these skills
Jumping
Catching
Throwing
Specialised Motor skills:
- combination or more advanced version of fundamental motor skills
- These can then be applied to a specific sport
The examples I've used show the connection
between fundamental and specialised motor
skills and I am showing what an example of
theses three fundamental skills can be specialised.
Examples of these skills
Jumping to grab a rebound in basketball
Catching a cricket ball while fielding
Throwing a dart at a dartboard
Gross Motor skills:
- types of skills that involve the larger muscle groups in the body
- complete body movements
- revolve around force, power and muscle strength
Examples of these skills
Powerlifting
Sprinting
Rockclimbing
Fine motor skills:
- coordination of smaller muscles
in movements.
- movements are more precise and
therefore require smaller muscles like the fingers and hands.
The correlation we can see between these two
different types of movement is that gross skills
are more powerful while fine skills focus on the
precision of the task.
Examples of these skills
Dart throwing
Putting a puzzle together
Tying shoelaces