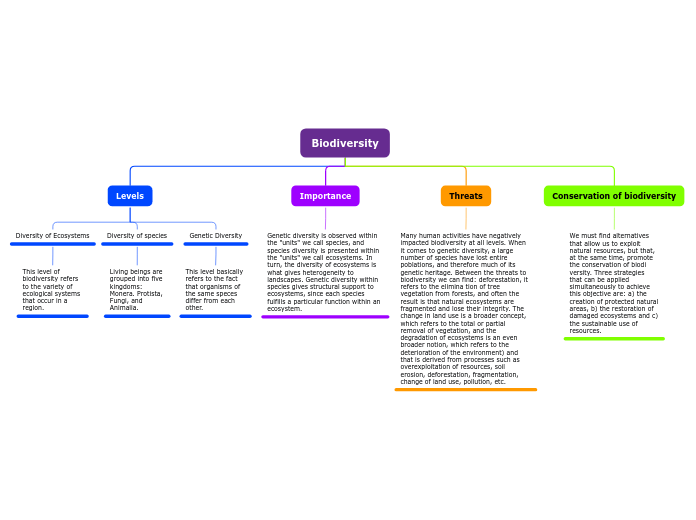
Diversity of Ecosystems
This level of biodiversity refers to the variety of ecological systems that occur in a region.
Diversity of species
Living beings are grouped into five kingdoms: Monera. Protista, Fungi, and Animalia.
Genetic Diversity
This level basically refers to the fact that organisms of the same speces differ from each other.
Genetic diversity is observed within the "units" we call species, and species diversity is presented within the "units" we call ecosystems. In turn, the diversity of ecosystems is what gives heterogeneity to landscapes. Genetic diversity within species gives structural support to ecosystems, since each species fulfills a particular function within an ecosystem.
Many human activities have negatively impacted biodiversity at all levels. When it comes to genetic diversity, a large number of species have lost entire poblations, and therefore much of its genetic heritage. Between the threats to biodiversity we can find: deforestation, it refers to the elimina tion of tree vegetation from forests, and often the result is that natural ecosystems are fragmented and lose their integrity. The change in land use is a broader concept, which refers to the total or partial removal of vegetation, and the degradation of ecosystems is an even broader notion, which refers to the deterioration of the environment) and that is derived from processes such as overexploitation of resources, soil erosion, deforestation, fragmentation, change of land use, pollution, etc.
We must find alternatives that allow us to exploit natural resources, but that, at the same time, promote the conservation of biodi versity. Three strategies that can be applied simultaneously to achieve this objective are: a) the creation of protected natural areas, b) the restoration of damaged ecosystems and c) the sustainable use of resources.